
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in sweet beet plants, revealing a fascinating process of sugar production out of thin air. Through their research, they have unlocked the secrets behind how these plants are able to convert carbon dioxide, a key component of the air we breathe, into the delicious sucrose we enjoy in our desserts.
Using cutting-edge technology, researchers have identified the specific enzymes and biochemical pathways that enable sweet beet plants to carry out this incredible feat. By harnessing the power of sunlight through photosynthesis, the plants are able to capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose. They then use a series of chemical reactions to transform glucose into sucrose, the primary sugar found in sweet beets.
This newfound understanding has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce sugar. By leveraging the natural ability of sweet beet plants to synthesize sucrose from carbon dioxide, scientists can explore ways to enhance sugar production in other food crops and reduce our reliance on traditional sugar cane and sugar beet cultivation. This could have significant implications for food security and sustainability, as well as reduce the environmental impact of sugar production.
In summary, the discovery of sweet beets making sugar out of thin air offers a fascinating glimpse into the natural world’s ability to harness the power of sunlight and convert carbon dioxide into sucrose. This breakthrough opens up exciting possibilities for the future of sugar production, with the potential for increased sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Sweet Beets Making Sugar Out of Thin Air Answer Key
The answer key for the topic “Sweet Beets Making Sugar Out of Thin Air” is a valuable resource for teachers and students alike. It provides the correct answers to the questions and exercises in the accompanying materials, allowing students to check their work and gauge their understanding of the topic. With the answer key, teachers can also easily assess their students’ progress and identify areas that may require further explanation or clarification.
In the answer key, each question or exercise is numbered, and the correct answer is provided next to it. This clear and organized format enables students to easily locate the answers they are looking for, saving them time and frustration. Additionally, the answer key may also include additional notes or explanations to help clarify any misconceptions or provide further context for the correct answer.
The answer key also serves as a useful tool for self-study or independent learning. Students who are working on their own can use the answer key to check their progress and identify any areas where they may need to review or seek additional help. It can also serve as a valuable resource for parents or tutors who are assisting with the students’ learning and want to ensure they are on the right track.
Overall, the answer key for “Sweet Beets Making Sugar Out of Thin Air” is an essential companion to the learning materials. It provides a valuable resource for teachers, students, and anyone else engaged in the study of this topic, ensuring accuracy, understanding, and effective learning.
What Are Sweet Beets?
Sweet beets, also known as sugar beets, are a type of root vegetable that is primarily grown for its high sugar content. These beets are specifically cultivated to produce a large amount of sucrose, which is used to make sugar. Unlike other varieties of beets, sweet beets have a much higher sugar content, making them a valuable crop for sugar production.
Key phrases: sweet beets, sugar beets, root vegetable, high sugar content, cultivated, sucrose, sugar production
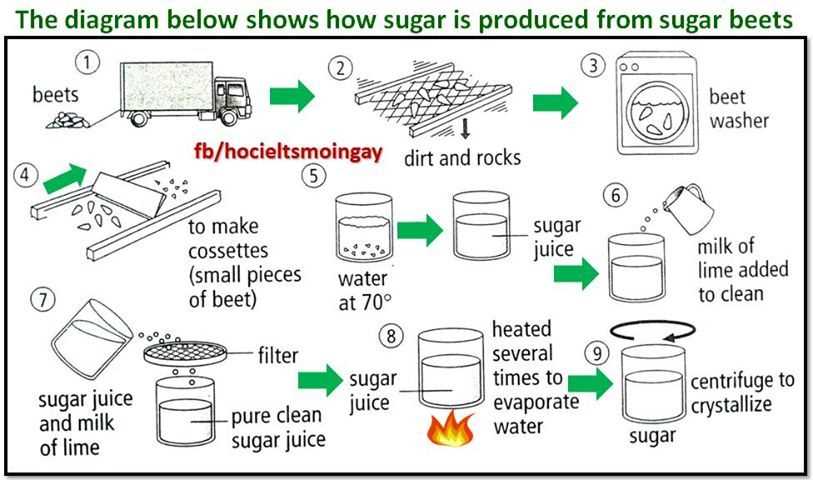
Sweet beets are typically harvested when they reach their maximum sugar content, which is usually around the time the beet has reached full maturity. The beets are then processed to extract the sugar from the plant. This process involves washing the beets, slicing them into small pieces, and then extracting the sugar juice through a process called diffusion. The sugar juice is then purified and crystallized to produce sugar crystals.
Key phrases: harvested, sugar content, processed, extract, washing, slicing, diffusion, purified, crystallized, sugar crystals
Sweet beets are an important crop for the sugar industry, as they provide a plentiful source of sucrose for sugar production. In addition to being used for sugar production, sweet beets can also be consumed as a vegetable. They can be cooked and used in various dishes, or eaten raw in salads. Sweet beets are known for their earthy and slightly sweet flavor, which pairs well with a variety of ingredients.
Key phrases: important crop, sugar industry, sucrose, sugar production, consumed, cooked, dishes, raw, salads, flavor, ingredients
In summary, sweet beets are root vegetables with a high sugar content that are primarily grown for sugar production. They are harvested when fully mature and processed to extract the sugar. Sweet beets are not only valuable for the sugar industry, but they can also be enjoyed as a flavorful vegetable in various culinary preparations.
The Process of Sugar Production in Sweet Beets

Sweet beets are an excellent source of sugar, which can be extracted through a complex process. This process involves several steps, each of which plays a crucial role in the production of high-quality sugar.
Cultivation and Harvesting: The first step in sugar production is the cultivation and harvesting of sweet beets. These beets are typically grown in well-prepared soil, and farmers carefully monitor their growth. Once the beets have reached maturity, they are carefully harvested to ensure minimal damage to the crop.
Extraction and Juice Processing: After harvesting, the sweet beets undergo a process known as extraction. This involves washing and slicing the beets, followed by the extraction of their juice. The juice is then carefully filtered and purified to remove any impurities that may affect the quality of the sugar.
- Juice Concentration: Once the juice is purified, it undergoes a concentration process to increase its sugar content. This is typically achieved through a combination of evaporation and heat treatments, which remove excess water and leave behind a concentrated syrup.
- Crystallization: The concentrated syrup is then subjected to a controlled cooling process, which causes the sugar molecules to crystallize. These sugar crystals are carefully separated from the remaining liquid, resulting in raw sugar.
- Refining: The raw sugar undergoes further processing to remove any remaining impurities, resulting in refined white sugar. This refining process involves the use of various purification techniques, such as carbonation and filtration, to ensure the sugar meets the highest quality standards.
- Packaging and Distribution: Finally, the refined sugar is packaged into various forms, such as granulated sugar or powdered sugar, and distributed to consumers and industries worldwide.
The process of sugar production in sweet beets is a complex and carefully controlled process that ensures the production of high-quality sugar. From cultivation to packaging, each step plays an integral role in delivering sugar that is not only sweet but also pure and free from impurities.
Understanding the Role of Photosynthesis in Sugar Production
Photosynthesis is an essential process for the production of sugar in plants. It is the primary way that plants convert sunlight into energy, using the energy from photons to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the green pigment called chlorophyll.
One of the key components of photosynthesis is the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll. This pigment is able to capture photons from the sun, which then excite the electrons within the chlorophyll molecules. These excited electrons are then passed through a series of electron carriers, generating energy along the way. This energy is used to power the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Carbon dioxide is obtained by plants through small openings in their leaves called stomata. These openings allow carbon dioxide to enter the plant and be used in photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide molecules are then broken down into individual carbon atoms, which are combined with hydrogen atoms from water to form glucose.
Water is another crucial component of photosynthesis. It is taken up by the roots of the plant and transported to the leaves, where it is utilized in the process of photosynthesis. Water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen atoms, with the hydrogen atoms being used to combine with carbon atoms from carbon dioxide to form glucose.
Overall, photosynthesis is a complex and intricate process that plays a vital role in sugar production. By harnessing the power of sunlight, plants are able to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which serves as a major source of energy for the plant. Without photosynthesis, the production of sugar and the survival of plants would not be possible.
The Importance of Carbon Dioxide in Sugar Production
Carbon dioxide (CO2) plays a crucial role in the production of sugar. It is a key ingredient in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert CO2, along with water and sunlight, into glucose, which is then used to create sucrose, the main type of sugar found in plants. This process is fundamental for the growth and development of plants, as sugars serve as an energy source and building blocks for various metabolic activities.
CO2 acts as the main source of carbon in sugar production. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants use specialized structures called chloroplasts to capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy is then used to convert CO2 and water into glucose. Glucose molecules are then joined together to create sucrose, which is transported throughout the plant to be used for energy, stored in roots, stems, and fruits, or transported to other parts for growth and reproduction.
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere directly affect the sugar production capacity of plants. Higher levels of CO2 can enhance photosynthesis and increase sugar production in certain plants. This has significant implications for agriculture and crop yields, as increased levels of CO2 can potentially improve the productivity of sugar crops such as sugar beet and sugarcane.
- Benefits of carbon dioxide enrichment:
- Enhanced photosynthesis and sugar production
- Increased biomass and crop yield
- Improved water and nutrient use efficiency
- Reduced photorespiration and energy loss
| Carbon Dioxide Level | Effect on Sugar Production |
|---|---|
| Normal atmospheric level (~400 ppm) | Optimal sugar production |
| High atmospheric level (>1000 ppm) | Potential for increased sugar production |
| Low atmospheric level (<200 ppm) | Reduced sugar production and growth |
In conclusion, carbon dioxide is a vital component in sugar production. Its availability and concentration in the atmosphere directly influence the growth, development, and productivity of plants. Understanding the role of CO2 in sugar production can help optimize agricultural practices and improve crop yields, ultimately contributing to the global sugar supply and food security.
How Sweet Beets Convert Carbon Dioxide into Sugar

The process of how sweet beets are able to convert carbon dioxide into sugar is a fascinating one. It begins with the beet’s leaves, which contain tiny pores called stomata. These stomata allow carbon dioxide from the air to enter the plant. Once inside, the carbon dioxide is transformed through a series of chemical reactions.
One of the key players in this process is a compound called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, and it is responsible for absorbing sunlight. Once the chlorophyll absorbs light energy, it uses this energy to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released back into the air, while the hydrogen is used to power the synthesis of sugar.
The hydrogen produced from the splitting of water combines with carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis. This reaction takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. The carbon dioxide and hydrogen molecules combine to form a sugar molecule called glucose. Glucose is the primary source of energy for plants, and it can be used for growth, reproduction, and other metabolic processes.
While sweet beets are not the only plants that undergo this process, they are particularly efficient at converting carbon dioxide into sugar. This efficiency is due in part to the high concentration of chloroplasts in their leaves. Additionally, the beets’ root system allows them to absorb nutrients and water from the soil, providing the necessary resources for photosynthesis.
Overall, the ability of sweet beets to convert carbon dioxide into sugar is a remarkable feat of nature. This process not only allows the beets to survive and thrive, but it also has important implications for our own carbon footprint. By understanding and harnessing the power of photosynthesis, we may be able to develop new ways to capture and utilize carbon dioxide, reducing our impact on the environment.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Sugar Production
Chlorophyll, as the main pigment involved in photosynthesis, plays a crucial role in the production of sugar in plants. It is responsible for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process, known as photosynthesis, is the key mechanism through which plants generate sugars, which are essential for their growth and metabolism.
Chlorophyll molecules are primarily located within the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the thylakoid membranes. These membranes contain numerous pigments, including chlorophyll, that absorb light energy. When light is absorbed by the chlorophyll pigments, it excites the electrons within them, initiating a series of chemical reactions that eventually lead to the production of glucose.
The absorption of light energy by chlorophyll is most effective in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, while it reflects or transmits green light, giving plants their characteristic green color. This is why plants appear green to our eyes; the chlorophyll pigments in their cells absorb all colors of light except for green, which is reflected back to our eyes.
Once the chlorophyll molecules have captured light energy, they transfer it to other molecules within the cell, such as chlorophyll b and carotenoids, which act as accessory pigments. These pigments help to broaden the range of light wavelengths that can be absorbed, ensuring maximum efficiency in the capture of light energy for sugar production.
Overall, chlorophyll is integral to the process of photosynthesis and the production of sugar in plants. Without it, plants would not be able to convert sunlight into the chemical energy needed to sustain their growth and development. Understanding the role of chlorophyll in sugar production is therefore essential for comprehending the fundamental processes that allow plants to thrive and ultimately support life on Earth.