
The birth of the constitution is a crucial event in the history of the United States. It marks the beginning of a new era, where the American people sought to create a system of government that would guarantee their freedom and protect their rights. The constitution worksheet answers provide valuable insights into the minds of the founding fathers and the challenges they faced in crafting this revolutionary document.
One of the key questions addressed by the constitution worksheet answers is how to strike a balance between central authority and individual rights. The founding fathers grappled with this challenge, as they sought to establish a government that would be strong enough to maintain order and protect the common good, while also respecting the rights and liberties of individual citizens. The worksheet offers a glimpse into their thought process and the compromises they made to reach a consensus.
The constitution worksheet answers also shed light on the need for checks and balances within the government. The founding fathers recognized the dangers of concentrated power and sought to prevent the emergence of a tyrannical regime. The worksheet reveals their careful crafting of a system where power is shared between different branches of government, ensuring that no single branch becomes too powerful and that each is held accountable for their actions.
In conclusion, the birth of the constitution was a momentous event that shaped the future of the United States. The constitution worksheet answers provide valuable insights into the challenges faced by the founding fathers and the principles that guided their decisions. By studying these answers, we can gain a deeper understanding of the historical context and the enduring significance of the constitution in our modern society.
The Birth of the Constitution Worksheet Answers

The Birth of the Constitution worksheet provides answers to questions about the creation of the United States Constitution. This document, which was drafted in 1787, laid the foundation for the framework of the American government that still exists today. Through a series of carefully thought out questions and answers, students can gain a deeper understanding of the historical context, the different perspectives of the founding fathers, and the compromises that were necessary to reach a consensus.
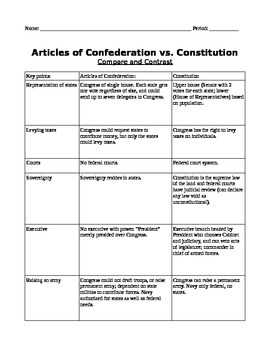
One of the key questions included in The Birth of the Constitution worksheet is about the main goals of the Constitutional Convention. The answer to this question highlights the desire of the founding fathers to create a stronger central government while still preserving individual liberties. It also emphasizes the need to address the flaws and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, which served as the initial governing document of the newly formed United States but proved to be inadequate for effectively governing the nation.
The worksheet also provides answers to questions about the key compromises made during the Constitutional Convention. These compromises include the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate over representation in Congress by creating a bicameral legislature with both a Senate and a House of Representatives. Another significant compromise was the Three-Fifths Compromise, which determined how slaves would be counted for the purposes of representation and taxation.
By examining The Birth of the Constitution worksheet answers, students can gain a deeper understanding of the historical events and decisions that shaped the United States Constitution. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the principles and values on which the American government was founded and continues to operate. It also allows students to recognize the complex and often challenging process of creating a governing document that balances the needs and perspectives of different states and individuals.
Key Points:
- The Birth of the Constitution worksheet provides answers to questions about the creation of the United States Constitution.
- The goals of the Constitutional Convention included creating a stronger central government and addressing the flaws of the Articles of Confederation.
- The main compromises during the Constitutional Convention were the Great Compromise and the Three-Fifths Compromise.
- Studying The Birth of the Constitution worksheet answers helps students understand the historical events and decisions that shaped the United States Constitution.
Background of the Constitution

The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land and serves as the framework for the government of the United States. It was adopted on September 17, 1787, by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The Constitution created a federal government with three branches: the executive branch, headed by the President; the legislative branch, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives; and the judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court.
Before the Constitution was drafted, the United States operated under the Articles of Confederation, which proved to be ineffective in governing the nation. The Articles of Confederation were the first constitution of the United States, adopted in 1781. However, it gave limited power to the central government, leading to a weak and ineffective federal government. It lacked the ability to levy taxes, regulate trade, and enforce its laws. This led to economic instability, diplomatic issues, and internal conflicts among the states.
The Constitutional Convention was called to address these issues and create a stronger central government. Delegates from twelve states attended the convention, and important figures such as George Washington, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton were among them. The delegates debated and compromised on various issues, such as representation, federal power, and the balance of power between the states and the central government. The resulting document was the United States Constitution, which established a system of checks and balances to prevent the abuse of power and protect the rights of the people.
The Constitution has been amended 27 times, with the first ten amendments known as the Bill of Rights. These amendments guarantee individual rights and liberties, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial. Over the years, the Constitution has shaped the development of the United States and provided a framework for the country’s governance. It remains a living document that is interpreted and applied by the Supreme Court to adapt to the changing needs and challenges of the nation.
Key Founders and their Roles
The birth of the Constitution of the United States was the result of the hard work and dedication of many key founders who played crucial roles in shaping the document and establishing the foundations of the American government. Some of these prominent figures include George Washington, James Madison, and Benjamin Franklin.
George Washington, the first President of the United States, played a pivotal role in the formation of the Constitution. As the presiding officer of the Constitutional Convention, Washington’s leadership and credibility greatly influenced the outcome of the deliberations. His commitment to maintaining a strong central government and his ability to unite different factions was instrumental in garnering support for the Constitution.
James Madison, often referred to as the “Father of the Constitution,” was one of the principal architects of the document. His extensive knowledge of political theories and keen insight into the flaws of the Articles of Confederation made him a driving force behind the call for a constitutional convention. Madison’s efforts in drafting the Virginia Plan, which formed the basis of the Constitution, and advocating for its ratification through the Federalist Papers, were instrumental in the creation and adoption of the Constitution.
Benjamin Franklin, a renowned inventor, scientist, and statesman, also played a significant role in the birth of the Constitution. As the oldest delegate at the Constitutional Convention, Franklin brought wisdom and experience to the proceedings. His ability to bridge gaps and find common ground among the delegates was invaluable. Additionally, his famous speech urging compromise and unity during a critical moment in the convention helped to break the stalemate and move the process forward.
These key founders, among others, played vital roles in the birth of the Constitution, and their contributions continue to shape American government and society to this day.
Creation of the Constitution
The creation of the Constitution was a pivotal moment in American history. As the nation sought to establish a more effective and stable form of government, delegates from across the country gathered in Philadelphia in 1787 to draft a new constitution. This gathering, known as the Constitutional Convention, would shape the course of the United States for centuries to come.
During the Convention, the delegates faced many challenges and debated various issues. One of the main points of contention was the balance of power between the states and the federal government. Some delegates, known as Federalists, argued for a stronger central government, while others, known as Anti-Federalists, were more concerned about protecting the rights of the states.
To address these concerns, the delegates proposed a system of checks and balances, which divided the powers of government between three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. This system ensured that no one branch would become too powerful and that each branch would have the ability to check the actions of the others.
In addition to the system of checks and balances, the delegates also included a mechanism for amending the Constitution. This allowed for future generations to adapt and modify the Constitution as needed, ensuring that it would remain relevant and effective over time.
After several months of deliberation and compromise, the delegates finally agreed on the text of the Constitution. It was then sent to the states for ratification, a process that required approval from at least nine of the thirteen states. Eventually, all thirteen states ratified the Constitution, and it went into effect in 1789.
The creation of the Constitution was a remarkable achievement, as it established a framework for a democratic government that has endured for over two centuries. It reflected the ideals and values of the American Revolution and set the stage for the growth and development of the United States into a global superpower.
Debates and Compromises

The process of creating the Constitution was not without its fair share of debates and disagreements. The delegates from the various states had differing opinions on many issues, and compromise was necessary to reach an agreement.
One of the main points of contention was the representation of states in the new government. Smaller states were concerned about being overshadowed by their larger counterparts, while larger states wanted more proportional representation. This led to the creation of the Great Compromise, which established a bicameral legislature with equal representation in the Senate and proportional representation in the House of Representatives.
Another major debate surrounded the institution of slavery. Southern states relied heavily on slavery for their economy, while northern states were strongly opposed to it. The Three-Fifths Compromise was reached, which counted each slave as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of determining representation in Congress.
The issue of the presidency also sparked lively discussions. Some delegates wanted a strong executive branch, while others feared it would become too powerful. As a compromise, the framers established a system of checks and balances, dividing powers between the three branches of government – the executive, legislative, and judicial.
Overall, the debates and compromises that took place during the creation of the Constitution were essential in creating a document that could be agreed upon by the states. These compromises laid the foundation for a balanced and effective government that has lasted for over two centuries.
Ratification Process
The ratification process played a crucial role in determining the fate of the Constitution. After the Constitutional Convention concluded in 1787, the proposed Constitution needed to be ratified by at least nine out of the thirteen states in order to become the supreme law of the land. The process of ratification involved intense debates, both in the state conventions and in public discourse, as supporters and opponents of the Constitution argued over its merits and potential flaws.
The Federalists, led by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, were fervent supporters of the Constitution. They believed in a strong centralized government that could effectively address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. The Anti-Federalists, on the other hand, argued for a more decentralized government with greater state autonomy. They were concerned that the Constitution did not adequately protect individual liberties and that it would give too much power to the central government.
During the ratification process, the Federalists took the initiative to promote the Constitution and garner support. They penned a series of essays known as the Federalist Papers, which were published in newspapers throughout the country. These essays presented a detailed analysis and defense of the Constitution, addressing the concerns raised by the Anti-Federalists. The Federalist Papers were instrumental in influencing public opinion and swaying undecided delegates in the state conventions.
In the end, the ratification of the Constitution was a hard-fought victory for the Federalists. They were able to secure the support of nine states, including influential states like New York and Virginia. However, the Anti-Federalists were not entirely defeated. As a compromise, the supporters of the Constitution agreed to add a Bill of Rights to protect individual liberties, which was subsequently ratified in 1791. This compromise helped ease the fears of the Anti-Federalists and ensure the ultimate ratification of the Constitution.
Impact and Legacy
The birth of the Constitution had a significant impact on the history of the United States. It established a framework for the government and outlined the rights and freedoms of the citizens. The Constitution created a system of checks and balances, which aimed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. This system has helped to maintain a balance of power and ensure the protection of individual rights. Additionally, the Constitution provided a structure for the federal government, outlining the roles and responsibilities of each branch and establishing a system of government that has withstood the test of time.
One of the most notable legacies of the Constitution is the Bill of Rights. These first ten amendments outlined specific rights and freedoms that are guaranteed to all citizens. The Bill of Rights has played a crucial role in protecting individual liberties, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial. It has served as a cornerstone of American democracy and has been essential in shaping the rights and freedoms that citizens enjoy today.
The Constitution has also had a lasting impact on American society and culture. It has served as a symbol of the nation’s commitment to democratic principles and the rule of law. The Constitution has been the subject of countless debates and interpretations, shaping the way Americans understand their government and their rights. It has inspired generations of citizens to engage in civic participation and work towards a more perfect union. The Constitution’s legacy can be seen in the ongoing efforts to promote equality, justice, and the protection of individual rights in the United States.