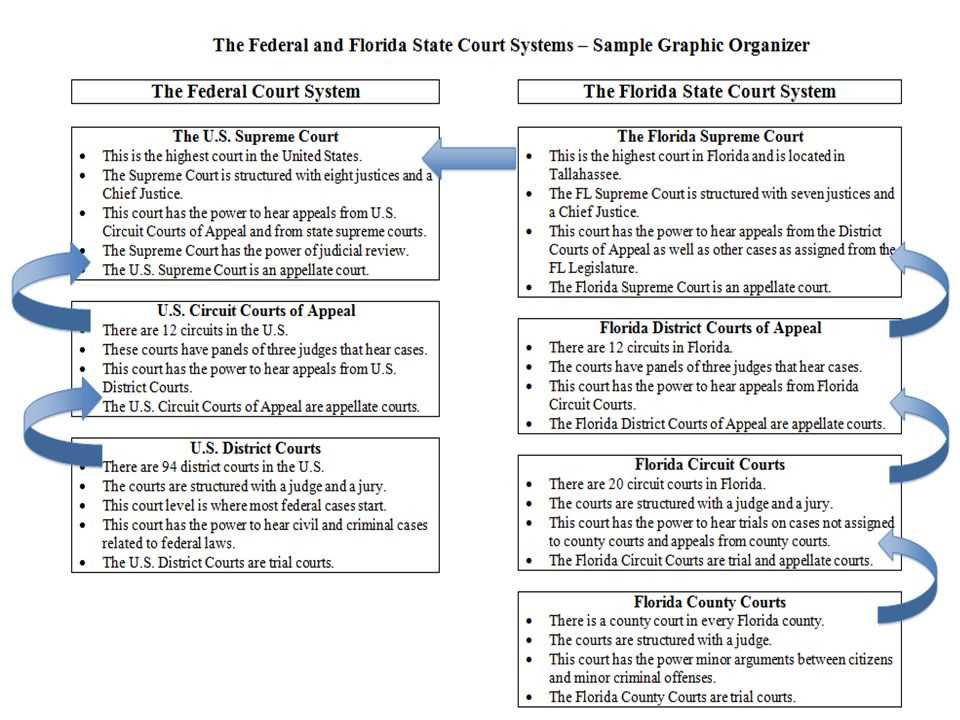
When we talk about federalism, we often hear about the “federal” aspect of it. What does it mean to be “federal” in the context of federalism? In simple terms, federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and regional or state governments. The “federal” aspect refers to the central authority, often called the federal government, that has the ultimate authority over the entire country. This central authority plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of power between different regions or states.
The federal government in federalism is responsible for making and implementing laws that apply to the entire country. It has the power to regulate matters of national concern, such as defense, foreign policy, and trade. At the same time, it shares some powers with regional or state governments, allowing them to have some degree of autonomy in governing their own jurisdictions. This distribution of power is essential to ensure a balance between a strong central authority and the autonomy of individual regions or states.
One of the key principles of federalism is the idea of dual sovereignty, where both the federal government and state or regional governments have separate spheres of authority. The federal government has exclusive powers that are outlined in the constitution, while the state or regional governments have reserved powers that are not delegated to the federal government. This concept of “the federal” in federalism ensures that no one entity has absolute power and that there are checks and balances in place to prevent the concentration of power.
In conclusion, the term “the federal in federalism” refers to the central authority, often known as the federal government, in a system of government where power is divided between the central authority and state or regional governments. This central authority plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of power and ensuring that no single entity has absolute authority. The concept of “the federal” in federalism is essential for understanding the distribution of powers and the principles of dual sovereignty within a federal system of government.
The Federal in Federalism Answers
In the context of federalism, “The Federal in Federalism Answers” refers to the powers and responsibilities of the federal government within a federal system. Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and regional or state governments. In this system, the federal government has certain powers and responsibilities that are distinct from those of the state governments.
One key aspect of the federal government’s role in federalism is its authority to make and enforce laws that apply to the entire country. This includes laws on issues such as national defense, foreign policy, interstate commerce, and civil rights. The federal government also has the power to levy and collect taxes, regulate the economy, and provide for the general welfare of the nation.
Another important function of the federal government in federalism is to act as a check on the power of the state governments. This is achieved through various means, such as the supremacy clause of the Constitution, which establishes that federal law prevails over conflicting state laws, and the power of the federal courts to interpret and enforce the Constitution and federal laws. The federal government also has the authority to intervene in the affairs of the states when necessary to protect the rights and interests of individuals or to maintain the stability of the nation as a whole.
- Key points:
- The federal government in federalism answers refers to the powers and responsibilities of the federal government within a federal system.
- The federal government has the authority to make and enforce laws that apply to the entire country.
- The federal government acts as a check on the power of the state governments.
- The federal government can intervene in the affairs of the states when necessary.
Understanding the Concept of Federalism

Federalism is a form of government where power is divided between a central authority, typically a national government, and regional or state governments. This system allows for the sharing of power, resources, and responsibilities between different levels of government. The concept of federalism is an essential aspect of many countries around the world, including the United States, Canada, Australia, and Germany.
In a federal system, the central government and regional governments each have their own jurisdiction and areas of control. This division of power is established by a constitution or a set of laws that define the rights and responsibilities of each level of government. The central government generally handles matters of national importance, such as defense, foreign affairs, and national economic policies, while the regional governments have the authority to make decisions on local issues, such as education, healthcare, and transportation.
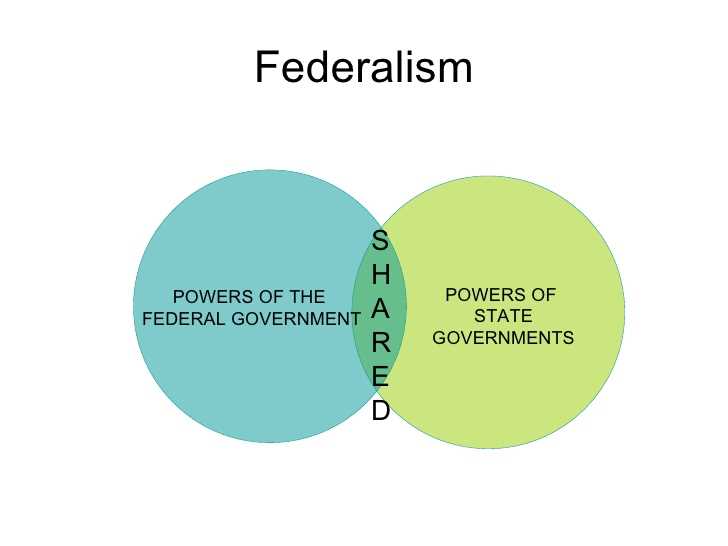
One key characteristic of federalism is the principle of dual sovereignty, which means that both the national government and the regional governments have their own separate powers and authority. This duality of power ensures that neither level of government can completely dominate the other and helps to maintain a balance of power. Another important aspect of federalism is the principle of shared sovereignty, which means that certain powers and responsibilities are shared between the different levels of government. This sharing of sovereignty allows for cooperation and coordination between the central and regional governments, ensuring that decisions are made in the best interest of the entire country.
Overall, federalism is a system of government that promotes decentralization and allows for the distribution of power among different levels of government. It helps to protect the rights and interests of both the central government and regional governments, while also ensuring that decisions are made efficiently and effectively. Through the principles of dual sovereignty and shared sovereignty, federalism provides a framework for collaboration and cooperation between different levels of government, leading to a more balanced and inclusive governance system.
The Origins of Federalism in the United States
Federalism in the United States has its roots in the early days of the country, when the founding fathers were designing a system of government that would balance power between the national government and the individual states. This concept of federalism was heavily influenced by the experiences of the American colonies under British rule and a desire to prevent a concentration of power in the hands of a single authority.
One of the key influences on the development of federalism in the United States was the Articles of Confederation, the first constitution of the country. The Articles created a weak central government with limited powers, leaving most of the authority to the individual states. This arrangement proved to be ineffective, as the central government struggled to enforce its laws and policies. This led to calls for a stronger central government, resulting in the drafting of the Constitution and the establishment of a more balanced federal system.
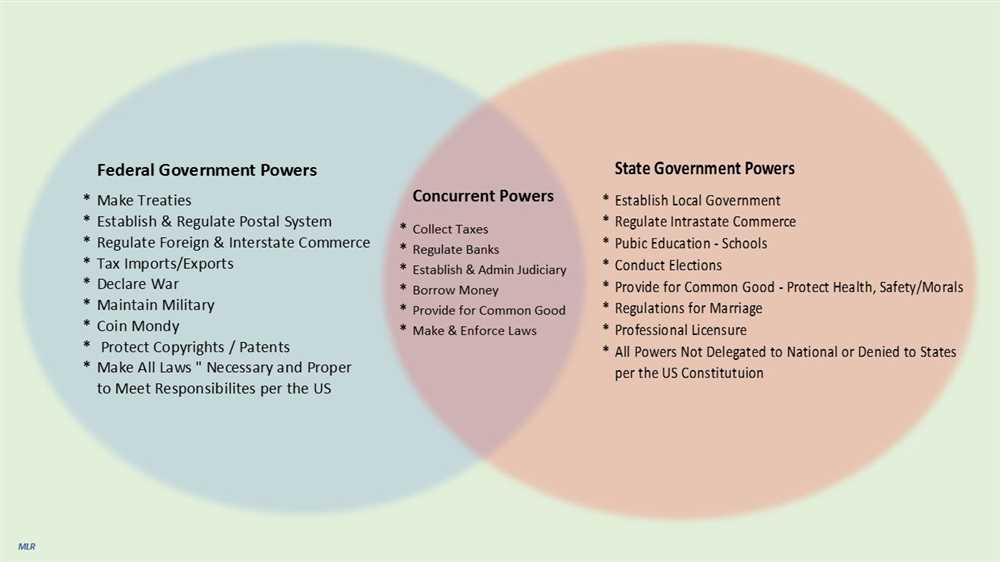
The framers of the Constitution sought to create a government that would address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation while still respecting the autonomy of the states. They divided powers between the national government and the states, with certain powers, such as the ability to regulate interstate commerce and declare war, reserved for the federal government, and others, such as the power to establish local governments and regulate intrastate commerce, left to the states. This division of powers, known as dual federalism, was intended to prevent abuse of power and ensure a checks and balances system.
To further protect the rights of the states, the Tenth Amendment was added to the Constitution, explicitly stating that any powers not delegated to the federal government were reserved for the states. This amendment served as a safeguard against the encroachment of the federal government on state authority.
In conclusion, the origins of federalism in the United States can be traced back to the desire to balance power between the national government and the states, influenced by the experiences of the colonies under British rule and the shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation. The constitutional framers created a system that divided powers between the federal government and the states, ensuring a checks and balances system and protecting the autonomy of the states.
The Division of Powers in a Federal System
In a federal system of government, power is divided between the national government and the state governments. This division of powers is an essential feature of federalism, ensuring that both levels of government have their own areas of authority and responsibilities.
One key aspect of the division of powers is the delineation of powers in the constitution. The national government is granted certain enumerated powers, such as national defense, foreign affairs, and interstate commerce. These powers are specifically mentioned in the constitution and are exclusive to the national government. On the other hand, the state governments have reserved powers, which are not specifically given to the national government and are left to the states. These reserved powers include areas such as education, criminal justice, and local government.
The division of powers is not always completely clear-cut, and there can be some overlapping areas of authority. In cases of conflict or ambiguity, the federal courts play a crucial role in interpreting the division of powers. The Supreme Court, as the highest court in the land, has the ultimate authority and responsibility to settle disputes and provide clarity on the division of powers between the national government and the state governments.
- Another aspect of the division of powers is the system of dual sovereignty. In a federal system, both the national government and the state governments are sovereign entities with their own independent powers. This means that they can exercise their authority without interference from each other. Each level of government has the ability to enact and enforce its own laws, regulations, and policies within its own jurisdiction.
- The division of powers also helps to maintain a balance between the national government and the state governments. It ensures that neither level of government becomes too powerful or dominant over the other. This system of checks and balances allows for a more democratic and decentralized form of governance, where power is dispersed among multiple levels of government.
- Furthermore, the division of powers promotes diversity and experimentation within the federal system. Since each state has its own powers and responsibilities, it can develop and implement policies that are tailored to its specific needs and preferences. This allows for different approaches to governance and policy-making, fostering innovation and the ability to respond to local needs and concerns.
In conclusion, the division of powers in a federal system is a fundamental aspect of federalism. It ensures that power is shared between the national government and the state governments, with each level of government having its own sphere of authority. This division of powers helps maintain a balance of power, promotes diversity and experimentation, and ensures that the rights and interests of both the national government and the state governments are protected.
The Role of the Federal Government in Federalism
In the system of federalism, power is divided between the federal government and the state governments. The federal government plays a crucial role in this system, as it is responsible for certain key functions that affect the entire nation. One of the primary roles of the federal government is to establish and maintain a system of laws that apply to the entire country. This includes the passing and enforcing of federal legislation, as well as the interpretation and application of the Constitution.
The federal government also has the power to collect taxes, regulate interstate commerce, and provide for the common defense. These powers are outlined in the Constitution and give the federal government the ability to address issues that transcend state boundaries. For example, the federal government has the authority to regulate industries and businesses that operate across state lines, ensuring fair competition and consumer protection. It also has the responsibility to defend the nation against external threats and maintain a strong military.
Furthermore, the federal government plays a key role in promoting uniformity and consistency in policies and programs across states. This can be seen in the areas of education, healthcare, and social services. The federal government provides funding and sets standards for these areas, ensuring that all states adhere to certain guidelines. This helps to prevent disparities and ensures that citizens across the country have access to essential services and opportunities. The federal government also serves as a mediator and arbiter in disputes between states, maintaining the peace and order within the nation.
In conclusion, the federal government in federalism has a variety of important roles and responsibilities. It establishes and enforces laws, collects taxes, regulates interstate commerce, provides for the common defense, promotes uniformity in policies and programs, and serves as a mediator between states. These functions are crucial for maintaining the unity and stability of the nation as a whole.
The Role of State Governments in Federalism

State governments play a crucial role in the functioning of federalism. They serve as the primary level of government below the national or federal government, representing the interests and needs of their respective states. This division of power allows for the distribution of authority and responsibility between the federal and state governments, ensuring a balance of power and protecting the rights and freedoms of citizens.
One important role of state governments in federalism is the implementation and enforcement of laws and policies. While the federal government creates and enacts laws at the national level, it is the responsibility of state governments to enforce those laws within their boundaries. This includes everything from traffic regulations to criminal justice systems. State governments also have the power to create and enforce their own laws and regulations, as long as they do not conflict with federal laws. This allows states to address specific issues and tailor policies to their unique needs.
State governments also have the authority to collect taxes and allocate funds for various programs and services within their states. While the federal government collects taxes for national programs and services, such as defense or social security, state governments collect taxes to fund state-specific initiatives, such as education or healthcare. This allows states to have control over their own finances and prioritize spending based on their particular needs and priorities. Additionally, state governments have the power to apply for and administer federal grants and funds, allowing them to further support their own initiatives.
Overall, the role of state governments in federalism is crucial in ensuring a balanced distribution of power and representation. By allowing states to have control over specific policies, laws, and finances, federalism recognizes the diversity and uniqueness of each state. This system of government fosters cooperation and collaboration between the federal and state governments, ultimately working towards the common goal of serving and protecting the citizens of the United States.