
The second edition of “The New Testament in Antiquity” offers a comprehensive introduction to the study of the New Testament. This widely acclaimed textbook, written by Gary M. Burge, Lynn H. Cohick, and Gene L. Green, explores the historical, cultural, and social context in which the New Testament was written.
Through a careful examination of the latest archaeological discoveries and ancient texts, the authors provide valuable insights into the world of early Christianity. This updated edition incorporates new scholarship, research, and perspectives, offering a fresh and engaging perspective on the New Testament.
The authors guide readers through the land of the New Testament, exploring the political, religious, and social influences that shaped the writings of the early Christians. From the cultural diversity of the Roman Empire to the religious traditions of Judaism and the emergence of Christianity, this book provides a rich and nuanced understanding of the context in which the New Testament was born.
With its rich visuals, engaging writing style, and comprehensive approach, “The New Testament in Antiquity” is an essential resource for students, scholars, and anyone interested in the origins and development of the early Christian movement. This second edition is available in PDF format, making it easily accessible and convenient for reading and studying.
The New Testament in Antiquity 2nd Edition PDF
The New Testament in Antiquity is a comprehensive and engaging textbook that explores the historical, social, and cultural context of the New Testament writings. This second edition is available in PDF format, providing easy access to the rich content and resources.
In this edition, authors Gary M. Burge, Lynn H. Cohick, and Gene L. Green offer a thorough examination of the New Testament texts and their significance in the ancient world. The PDF format allows readers to navigate through the book, access footnotes, and search for specific topics or keywords.
The New Testament in Antiquity 2nd Edition PDF features detailed chapters on the historical background of the New Testament, including the Greco-Roman world, Jewish history and culture, and the life of Jesus. The authors also delve into the social dynamics of the early Christian communities and the spread of Christianity throughout the Roman Empire.
- Explore the historical, social, and cultural context of the New Testament
- Access footnotes and search for specific topics or keywords
- Learn about the Greco-Roman world, Jewish history and culture, and the life of Jesus
- Understand the social dynamics of early Christian communities and the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire
Whether you are a student studying the New Testament or a curious reader interested in understanding the background of these ancient texts, The New Testament in Antiquity 2nd Edition PDF provides a valuable resource for deepening your knowledge and exploring the world of the New Testament.
The Historical Context of the New Testament
The New Testament is a collection of religious texts that form an integral part of Christian scripture. These texts, which include the four Gospels, Acts of the Apostles, various letters, and the Book of Revelation, provide insight into the life, teachings, and ministry of Jesus Christ, as well as the mission and early development of the Christian church. In order to fully understand and interpret the New Testament, it is essential to consider its historical context.
The New Testament was written during the first century AD, a time of significant historical and cultural developments. The region in which the events of the New Testament took place was under Roman rule, with the Roman Empire exercising political control over much of the Mediterranean world. This context shaped the socio-political landscape in which Jesus and his followers lived and carried out their ministry.
Key historical figures
- Emperor Augustus: The reign of Emperor Augustus marked a crucial period in Roman history. He established the Roman Empire, bringing stability and a centralized government to the region.
- Herod the Great: Herod the Great was the ruler of Judea during the time of Jesus’ birth. He was responsible for significant building projects, including the expansion of the Second Temple in Jerusalem.
- Tiberius Caesar: Tiberius Caesar succeeded Augustus as Roman Emperor and ruled during the time of Jesus’ ministry. His reign witnessed the spread of Christianity beyond Jerusalem.
Religious and cultural context
The New Testament was written in a predominantly Jewish religious and cultural context. The Jewish people were awaiting the arrival of a Messiah who would deliver them from Roman oppression. This Messianic expectation influenced the interpretation and reception of Jesus’ ministry, as his followers saw him as the long-awaited savior.
Furthermore, the New Testament reflects the diversity of the Mediterranean world at the time. It incorporates elements of Greek philosophy, Roman political and legal systems, and Jewish religious practices. These influences shape the language, imagery, and theological concepts found in the New Testament texts.
The historical context of the New Testament provides valuable insights into the writings and teachings contained within it. By considering the political, social, and religious climate in which these texts were produced, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the message and significance of the New Testament for both its original audience and contemporary readers.
The Jewish World of the New Testament

The New Testament is deeply rooted in the Jewish world of the first century. Understanding this context is essential for interpreting its texts and teachings. The Jewish people of this period lived in a complex and diverse world that influenced various aspects of their daily lives.
Religion: Judaism was the predominant religion among the Jewish people of the New Testament era. They were deeply devoted to the worship of Yahweh and followed the teachings of the Torah, which included the Mosaic laws and commandments. The Temple in Jerusalem was the central place of worship, where religious rituals and sacrifices were performed.
Social Structure: The Jewish society of this period was organized hierarchically. At the top were the religious leaders, including the high priest and the Pharisees. The common people, known as the “am ha-aretz,” made up the majority of the population. They were engaged in various occupations such as farming, fishing, and trade. Scholars and scribes were highly respected for their knowledge of religious texts and interpretation.
Politics: The Jewish people were under Roman rule during the New Testament era. This had a significant impact on their lives, as they had to navigate the complexities of living under a foreign power. The Roman authorities appointed a local ruler, known as the Herodian dynasty, to govern the region. The interactions between the Jewish religious leaders, Roman authorities, and the local population can be seen throughout the New Testament.
Eschatology: The concept of eschatology, or the study of the end times, was significant in Jewish thought during this period. Many Jews believed in the coming of the Messiah, a promised savior who would deliver them from Roman oppression and establish God’s kingdom on earth. This expectation shaped the beliefs and actions of various Jewish groups, such as the Pharisees, Sadducees, and Zealots.
The Torah and Scriptures: The Jewish people held the Torah and other Hebrew scriptures in high regard. They believed that these texts contained the word of God and provided guidance for their lives. Pharisees and scribes played essential roles in interpreting and teaching the scriptures to the people, ensuring the preservation of Jewish traditions and beliefs.
In conclusion, understanding the Jewish world of the New Testament is crucial for comprehending its texts and teachings. The religious, social, political, and eschatological context of this period shaped the beliefs, practices, and interactions of the Jewish people and influenced the development of early Christianity.
The Greco-Roman World of the New Testament
The Greco-Roman world of the New Testament provides the historical and cultural background against which the events and teachings of the early Christian movement took place. This world was characterized by the dominant influence of Greek and Roman civilizations, which shaped the political, social, religious, and intellectual climate of the time.
In terms of political power, the New Testament period saw the rise and expansion of the Roman Empire, which exerted control over vast territories in the Mediterranean region. The empire was characterized by a centralized system of government, led by the emperors, who held absolute power. This political structure had a significant impact on the social dynamics and religious landscape of the time.
One of the defining features of the Greco-Roman world was its pluralistic religious landscape. The dominant religious belief in the empire was polytheism, where multiple gods and goddesses were worshipped. The worship of these deities was an integral part of daily life, and temples dedicated to them were found in every city. However, along with polytheism, there were also various mystery cults, philosophical schools, and local religious practices that influenced the spiritual beliefs and practices of the people.
Intellectually, the Greco-Roman world was characterized by the influence of Greek philosophy and Hellenistic thought. Greek philosophy, particularly Stoicism, Epicureanism, and Platonism, provided frameworks for understanding the nature of the world and human existence. These philosophical ideas permeated the intellectual discourse of the time and had an impact on the development of early Christian thought.
Understanding the Greco-Roman world of the New Testament is crucial for interpreting the writings and teachings of the early Christians. By recognizing the historical and cultural context in which these texts were produced, we can gain insights into the beliefs, practices, and challenges faced by the early Christian communities, and better understand the significance of their message in the ancient world.
The Text and Canon of the New Testament
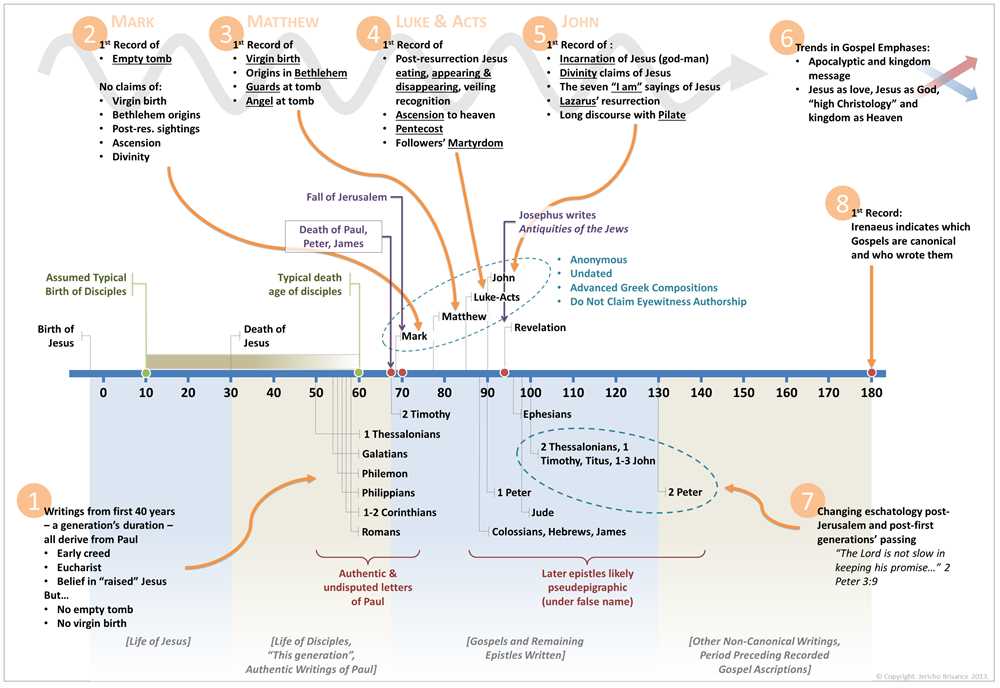
In order to understand the New Testament in antiquity, it is crucial to examine the text and canon of the scriptures. The New Testament is composed of various books written by different authors over a span of several decades. These books were originally written in Greek and eventually compiled into a collection of holy scriptures.
The process of determining which books should be included in the canon of the New Testament was a complex one. Early Christian communities considered several factors when deciding which writings should be recognized as authoritative. These factors included the apostolic origins of the texts, the teachings of Jesus, and the overall consistency and coherence of the message.
One of the key challenges in studying the New Testament is the fact that the original manuscripts no longer exist. However, scholars have access to numerous copies and translations of the texts, allowing them to reconstruct the original content to a high degree of accuracy. These manuscripts provide valuable insights into the early Christian community and the development of the text.
The New Testament text is constantly being studied and analyzed by scholars using various methodologies. Textual criticism is one such approach that seeks to reconstruct the original wording of the text by comparing different manuscripts and versions. This helps to determine the most reliable and authentic reading of the New Testament.
Overall, the text and canon of the New Testament are essential components in understanding the development and interpretation of early Christian writings. By examining the manuscripts and studying the process of canonization, scholars can gain deeper insights into the historical and theological significance of the New Testament for ancient and modern readers alike.
The Gospels and Acts: Their Origins and Message
The Gospels and Acts are foundational texts within the New Testament, providing crucial accounts of the life and teachings of Jesus Christ and the development of the early Christian movement. Understanding the origins and message of these texts is essential for grasping the historical and theological significance of the New Testament as a whole.
Origins: The Gospels and Acts were likely written between the first and second centuries CE by various authors, some of whom may have been eyewitnesses to the events they describe. Scholars believe that the authors drew from a variety of written sources, oral tradition, and personal experiences to construct their narratives. The synoptic Gospels–Matthew, Mark, and Luke–share many similarities in content and structure, suggesting a shared literary tradition. It is also believed that the Gospel of John was written independently, with a different theological focus.
Message: The Gospels and Acts convey the central teachings and actions of Jesus, emphasizing his role as the Messiah and Son of God. They portray Jesus as a teacher, healer, and miracle worker who brought about the Kingdom of God through his words and deeds. The Gospels also highlight Jesus’ death and resurrection, which are seen as pivotal events in God’s plan for salvation. Acts, on the other hand, focuses on the early Christian community and the spread of the Gospel message from Jerusalem to the surrounding regions and eventually to the Gentiles.
The Gospels and Acts provide valuable insights into the historical, social, and religious context of the time, shedding light on the beliefs, practices, and challenges faced by early Christians. They offer a lens through which we can understand the development of the Christian faith and its impact on the world. As such, the study of the Gospels and Acts is crucial for anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of Christianity and its origins.
The New Testament Letters: Their Authors and Themes
The New Testament consists of several letters that were written by various authors, each addressing specific themes and topics. These letters played a crucial role in the formation and development of early Christianity, providing guidance, instruction, and encouragement to the early Christian communities.
One of the most prominent authors of the New Testament letters is the apostle Paul. Paul wrote several letters, including Romans, Corinthians, Galatians, and Ephesians, among others. These letters were written to different churches and individuals, addressing issues such as Christian theology, the role of the church, and the Christian way of life.
Another important author of the New Testament letters is Peter, one of Jesus’ disciples. Peter wrote two letters known as 1 Peter and 2 Peter. These letters were written to the early Christian communities, offering guidance on how to live as faithful followers of Christ and addressing topics such as suffering, perseverance, and the hope of salvation.
In addition to Paul and Peter, other authors of the New Testament letters include James, John, and Jude. James, believed to be the brother of Jesus, wrote the letter of James to Jewish Christians, emphasizing the importance of faith and good works. John wrote several letters known as 1 John, 2 John, and 3 John, addressing themes such as love, truth, and obedience. Jude wrote a short letter warning against false teachers and encouraging believers to remain steadfast in their faith.
Overall, the New Testament letters provide valuable insights into the early Christian movement and its teachings. These letters continue to be studied and cherished by Christians today as they offer guidance on how to live a faithful and transformative life in Christ.


