
As 5G technology continues to revolutionize the world of telecommunications, an increasing number of questions arise regarding its integration with edge computing. Edge computing refers to the decentralization of data processing and storage, bringing computing power closer to the point of data generation. This combination of 5G and edge computing brings forth a host of benefits, but also poses unique challenges. In this article, we will address some of the most commonly asked questions about TQ 5G Edge Computing.
What is the significance of TQ 5G Edge Computing?
TQ 5G Edge Computing plays a crucial role in harnessing the full potential of 5G networks. By bringing computing power closer to the network edge, TQ 5G Edge Computing enables ultra-low latency, high-speed data processing, and improved network performance. It allows for faster decision-making, reduced data transfer times, and increased scalability, making it an essential component of various industries such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and augmented reality.
How does TQ 5G Edge Computing differ from traditional cloud computing?
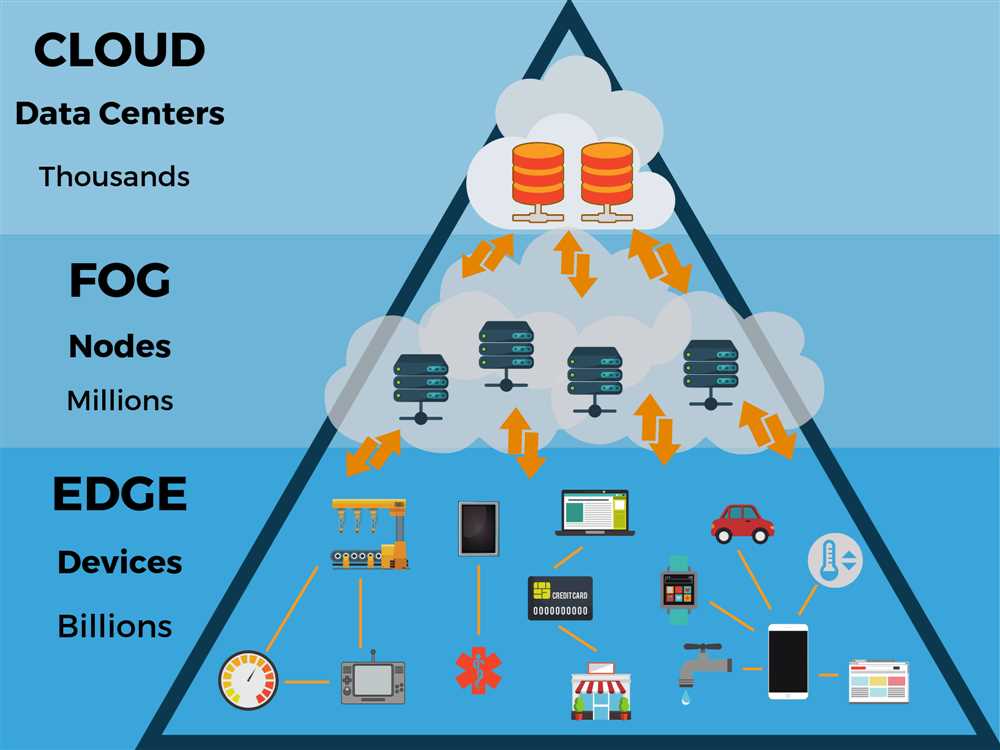
Unlike traditional cloud computing, which centralizes data processing and storage in remote data centers, TQ 5G Edge Computing distributes these tasks to edge devices located closer to the data source. This decentralized approach enables real-time processing, lower latency, and decreased bandwidth requirements. While cloud computing is more suitable for large-scale data analytics and storage, TQ 5G Edge Computing provides low-latency and high-throughput capabilities required for time-sensitive applications.
Here are some frequently asked questions and answers about Tq 5G Edge Computing that you can find in a PDF format: Tq 5G Edge Computing is a computing model that brings processing power and data storage closer to the edge of the network, reducing latency and enabling real-time data processing and analysis. It leverages the power of 5G networks to enable faster communication between devices and the edge, making it ideal for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, IoT, and virtual reality. Tq 5G Edge Computing works by placing compute, storage, and network resources closer to the devices and sensors at the edge of the network. This enables faster processing of data and reduces the need to send data back and forth to the cloud for analysis. It leverages 5G networks to enable high-speed communication between devices and the edge, ensuring real-time data processing and analysis. While Tq 5G Edge Computing offers many benefits, it also poses some challenges. One of the main challenges is the need for a robust and reliable 5G network infrastructure to ensure high-speed communication between devices and the edge. Additionally, managing and scaling edge computing resources can be complex, as it requires coordination and synchronization across multiple devices and locations. Lastly, ensuring the security and privacy of data at the edge can be challenging, as it involves securing a distributed network of edge devices. These are just a few of the questions and answers you can find in a Tq 5G Edge Computing PDF. Exploring further can help you gain a deeper understanding of this emerging technology and its potential applications. 5G Edge Computing refers to the combination of 5G connectivity and edge computing technologies to enable faster and more efficient processing of data at the network edge. With the advent of 5G networks, which provide higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to previous generations, there is an increasing need to process data closer to the source, rather than sending it back and forth to centralized cloud servers. This is where edge computing comes in. Edge computing involves processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network, in proximity to where it is generated or consumed. By distributing computing resources closer to the devices and sensors that generate data, edge computing reduces the latency and bandwidth requirements for data transmission. This enables real-time processing and analysis of data, leading to faster insights and responses. In the context of 5G, edge computing becomes even more crucial as the volume and velocity of data generated by connected devices and IoT sensors increase. With 5G edge computing, applications and services can leverage the low latency and high bandwidth capabilities of 5G networks, while also enjoying the benefits of localized processing at the network edge. The combination of 5G and edge computing opens up new possibilities for various industries and applications, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, remote healthcare, industrial automation, and augmented reality. By bringing computation closer to the devices and enabling real-time data processing, 5G edge computing offers improved performance, enhanced reliability, and reduced reliance on centralized data centers. 5G Edge Computing is an essential component of the 5G network architecture that brings processing power closer to the end-users, enabling faster and more efficient data processing. This proximity to the edge of the network reduces latency, improves reliability, and enhances the overall user experience. With the increasing demand for real-time data processing, 5G Edge Computing plays a critical role in supporting emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and augmented reality. By leveraging the capabilities of edge computing combined with the high-speed and low-latency connectivity of 5G, these technologies can operate seamlessly and efficiently. The importance of 5G Edge Computing can be seen in various industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and entertainment. In the healthcare sector, for example, edge computing allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of patient data, enabling faster medical interventions and improved healthcare outcomes. In manufacturing, edge computing enables predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of machines, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced downtime. In the entertainment industry, edge computing enables immersive experiences such as virtual reality and augmented reality gaming by reducing latency and processing data closer to the user. Furthermore, 5G Edge Computing also plays a crucial role in addressing the growing demand for data processing and storage. By offloading processing tasks from centralized data centers to the edge of the network, it helps alleviate network congestion and reduce the dependence on cloud computing resources. This distributed approach to data processing not only improves network efficiency but also enhances data security and privacy. In conclusion, 5G Edge Computing is important because it enables faster, more reliable, and efficient data processing, supports emerging technologies, enhances user experiences, and addresses the increasing demand for data processing and storage. Its implementation across various industries brings significant benefits and opens up new possibilities for innovation and growth. 5G Edge Computing is a technology that brings computing power and storage closer to the edge of the network, enabling faster processing and reduced latency for applications and services. It involves the deployment of edge servers, which are distributed closer to the network edge, such as cell towers or data centers, rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. With 5G Edge Computing, data can be processed and analyzed in real time at the edge of the network, allowing for quick response times and improved performance. This is particularly important for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries, and augmented reality experiences. The architecture of 5G Edge Computing consists of three main components: the core network, the edge computing infrastructure, and the end devices. The core network handles the overall management and coordination of the network, while the edge computing infrastructure includes the edge servers, which are responsible for processing and storing data. The end devices, such as smartphones or IoT devices, connect to the edge servers to access the computing resources. One of the key advantages of 5G Edge Computing is its ability to offload processing and storage from the centralized cloud servers to the edge servers. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to and from the cloud, resulting in faster response times and reduced network congestion. It also improves the security and privacy of data, as sensitive information can be processed locally at the edge. In summary, 5G Edge Computing brings computing power and storage closer to the edge of the network, enabling faster processing, reduced latency, and improved performance for applications and services. It utilizes edge servers, distributed at the network edge, to process and store data in real time, resulting in quicker response times and enhanced user experiences. In the era of 5G, edge computing has emerged as a revolutionary concept that brings numerous benefits to various industries. With its low latency and high bandwidth capabilities, 5G edge computing offers businesses and individuals faster and more efficient data processing and delivery. This technology enables real-time data analysis and response, enabling businesses to make quicker decisions and improve their overall operations. 1. Reduced Latency: One of the key advantages of 5G edge computing is its ability to reduce latency significantly. By bringing data processing closer to the edge of the network, it minimizes the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination. This low latency enables real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries, and immersive gaming experiences, enhancing user experience and safety. 2. Enhanced Reliability: Another benefit of 5G edge computing is its improved reliability. By distributing computing power to the edge of the network, it reduces the dependency on centralized cloud infrastructure. This decentralization makes the network more resilient to failures and disruptions, ensuring continuous connectivity and service availability even in challenging environments. 3. Cost Optimization: 5G edge computing also enables cost optimization for businesses. By processing data locally at the edge, it reduces the need for large-scale data transfers to centralized servers, minimizing bandwidth requirements and associated costs. Additionally, edge computing enables intelligent data filtering and processing, allowing businesses to prioritize critical information and reduce unnecessary data transmission, further reducing operational expenses. In conclusion, 5G edge computing brings significant benefits to various industries, including reduced latency, enhanced reliability, cost optimization, enhanced privacy and security, and scalability and flexibility. By leveraging these advantages, businesses can unlock new opportunities, improve efficiency, and deliver superior user experiences. Implementing 5G edge computing comes with several challenges that need to be addressed in order to harness the full potential of this technology. These challenges include: Network infrastructure: The successful implementation of 5G edge computing requires a robust and reliable network infrastructure. This includes the installation of sufficient base stations and the deployment of high-speed fiber optic cables to handle the increased data traffic that will be generated. Security concerns: With the proliferation of connected devices and the massive amounts of data being processed at the edge, security becomes a critical concern. The distributed nature of edge computing makes it more vulnerable to cyberattacks, requiring advanced security measures to protect the data and devices. Latency: One of the primary advantages of 5G edge computing is its ability to process data closer to the end user, reducing latency and enabling real-time applications. However, achieving ultra-low latency requires effective management of network congestion and the deployment of edge computing resources in close proximity to the users. Interoperability: As edge computing involves multiple devices, applications, and service providers, ensuring interoperability between different systems and platforms can be a significant challenge. Standardization efforts are necessary to establish interoperable frameworks and protocols to facilitate seamless integration and communication between edge devices and the cloud. Resource allocation: Effective resource allocation is crucial for optimizing the performance and efficiency of edge computing networks. Determining the optimal allocation of computing, storage, and network resources across the edge infrastructure requires sophisticated algorithms and dynamic resource management techniques. Overcoming these challenges will be key to unlocking the full potential of 5G edge computing and realizing its promise of faster, more reliable, and low-latency connectivity for a wide range of applications and industries.Tq 5g Edge Computing Questions and Answers PDF
1. What is Tq 5G Edge Computing?

2. What are the benefits of Tq 5G Edge Computing?
3. How does Tq 5G Edge Computing work?
4. What are some use cases for Tq 5G Edge Computing?
5. What are the challenges of Tq 5G Edge Computing?
What is 5G Edge Computing?
Why is 5G Edge Computing important?
How does 5G Edge Computing work?
Benefits of 5G Edge Computing
Challenges of implementing 5G Edge Computing