The two peg test is a common method used in the field of engineering for measuring the accuracy and alignment of machinery and equipment. This test involves the use of two pegs or reference points on a machine, which are used as a basis for measuring the relative positions of other components.
During the two peg test, a measuring instrument, such as a laser or dial gauge, is used to measure the distance between the two pegs. This initial measurement serves as a reference point, and any subsequent measurements can be compared to this baseline to determine if the machine is aligned correctly.
One of the key advantages of the two peg test is its simplicity and versatility. It can be used to measure alignment in a wide range of applications, from simple machinery to complex industrial systems. The test can be performed quickly and easily, making it a popular choice for engineers and technicians.
In addition, the two peg test is a non-destructive testing method, meaning it does not damage or alter the machine being tested. This makes it a valuable tool for routine maintenance and troubleshooting, as it allows engineers to identify and correct alignment issues without causing further damage or downtime.
What is the Two Peg Test and Its Importance in Engineering
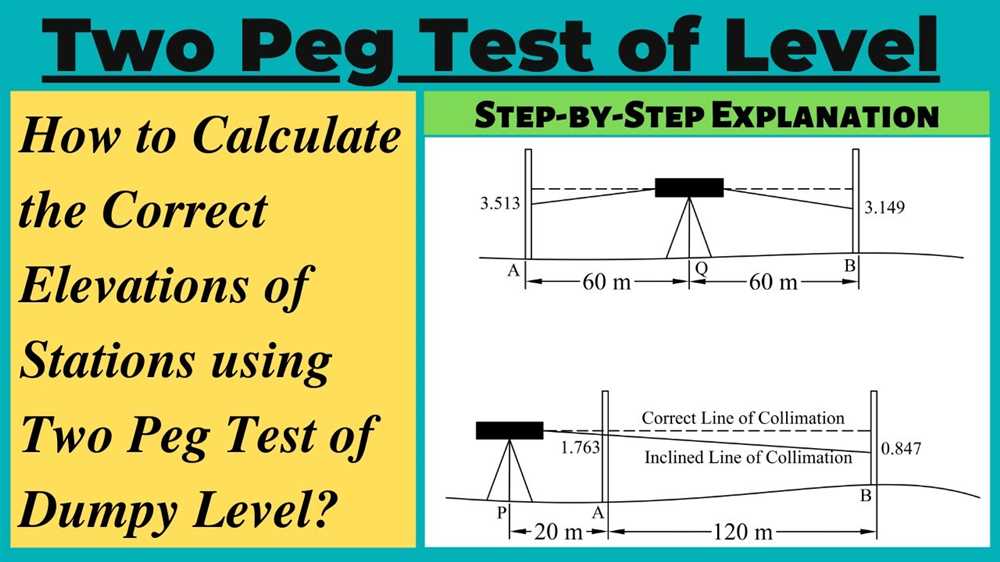
The Two Peg Test is a commonly used technique in engineering to determine the accuracy and precision of surveying instruments, such as theodolites or total stations. It involves setting up two reference points, or pegs, at known coordinates, and then measuring the angles and distances between these pegs using the instrument being tested. This test allows engineers to assess the performance of their surveying equipment and make necessary adjustments to ensure reliable and accurate measurements.
During the Two Peg Test, the instrument is set up and leveled between the two reference points. Angles are measured by sighting through the instrument and aligning it with the pegs, while distances are measured using the instrument’s capabilities, such as an EDM (electronic distance measurement) system. By comparing the measured angles and distances with the known coordinates of the pegs, engineers can identify any errors or discrepancies in the instrument’s readings.
The importance of the Two Peg Test in engineering cannot be overstated. Accurate surveying is essential in numerous fields, including construction, civil engineering, and land development. By ensuring that surveying instruments are properly calibrated and accurate, engineers can avoid costly mistakes, such as incorrect building placements or inaccurate land measurements. The Two Peg Test provides a standardized method to check the performance of surveying instruments, allowing engineers to have confidence in their measurements and make informed decisions based on reliable data.
In addition to verifying the accuracy of surveying instruments, the Two Peg Test also helps in identifying any systematic errors or biases in the instrument’s measurements. If consistent deviations from the known coordinates are observed, engineers can adjust for these errors during their future surveys. This adjustment process, known as calibration, helps maintain the accuracy of the instrument over time. Regularly performing the Two Peg Test allows engineers to detect and correct any inaccuracies before they impact the quality and integrity of their surveying work.
In conclusion, the Two Peg Test is a fundamental tool in engineering that ensures the accuracy and reliability of surveying instruments. By comparing the measured angles and distances with known coordinates, engineers can verify the performance of their equipment and make necessary adjustments. This test plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of surveying work, preventing costly mistakes, and providing engineers with reliable data for informed decision-making.
Defining the Two Peg Test

The two peg test is a method used to determine the accuracy of a surveying instrument, such as a theodolite or level. It involves setting up two pegs at a known distance apart and using the instrument to measure the horizontal and vertical angles between the pegs. By comparing these measured angles with the expected values, the accuracy of the instrument can be assessed.
To perform the two peg test, the instrument is set up at one of the pegs and leveled. A target is then set up at the other peg, and the instrument is aligned with it. The operator measures both the horizontal and vertical angles to the target. These angles are then compared to the expected values, which can be calculated based on the known distance between the pegs. Any discrepancies between the measured and expected values can indicate errors in the instrument’s calibration or alignment.
Procedure for the Two Peg Test:
1. Set up two pegs at a known distance apart.
2. Set up the surveying instrument at one of the pegs and ensure it is leveled.
3. Set up a target at the other peg.
4. Align the instrument with the target.
5. Measure the horizontal and vertical angles to the target.
6. Calculate the expected values for the angles based on the known distance between the pegs.
7. Compare the measured angles with the expected values.
8. Assess the accuracy of the instrument based on any discrepancies between the measured and expected values.
The two peg test is an important quality control measure in surveying, as it helps ensure the accuracy of measurements and the reliability of surveying instruments. By regularly performing this test, surveyors can identify and correct any errors or inaccuracies in their instruments, leading to more accurate and reliable surveying data.
Understanding the Significance of the Two Peg Test
The two peg test is an essential tool used to assess the accuracy of a measuring instrument such as a level or a theodolite. It involves setting up two pegs or stakes at a certain distance apart and then using the instrument to measure the vertical difference between the two pegs. This test helps to determine the precision and reliability of the instrument, ensuring that accurate measurements can be obtained in various applications.
The significance of the two peg test lies in its ability to detect any errors or discrepancies in the measuring instrument. By comparing the measured vertical difference between the two pegs with the known distance between them, any systematic errors or biases in the instrument can be identified and corrected. This allows for more accurate and reliable measurements to be made in construction, engineering, surveying, and other fields where precise measurements are crucial.
Procedure:
1. Set up two pegs or stakes at a known distance apart. This distance should be sufficient to cover the range of measurements needed for the specific application.
2. Place the measuring instrument, such as a level or theodolite, on one of the pegs and ensure it is properly calibrated and leveled.
3. Observe the position of the instrument’s crosshairs or bubble level while looking through the eyepiece or viewfinder.
4. Move the instrument to the second peg and take note of any changes in the position of the crosshairs or bubble level.
5. Measure the vertical difference between the two pegs using the instrument’s scale or other measuring features.
6. Compare the measured vertical difference with the known distance between the pegs.
7. Calculate the error or bias in the instrument and make any necessary adjustments or corrections.
The two peg test is a simple yet powerful technique for ensuring the accuracy of measuring instruments. By regularly performing this test, technicians and professionals can maintain the precision and reliability of their instruments, leading to more accurate and trustworthy measurements in their work.
The Procedure of Conducting the Two Peg Test
The two peg test is a common method used to evaluate a person’s hand-eye coordination and motor skills. It involves using two pegs, placed a certain distance apart, and the individual must transfer an object from one peg to the other. This test is often used in occupational therapy to assess a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks.
To conduct the two peg test, the following steps are typically followed:
- Set up the pegs: The two pegs are placed on a flat surface, such as a table or counter, a specific distance apart. The distance between the pegs can vary depending on the purpose of the test, but it is usually around 6-12 inches.
- Choose an object: An object is selected for the individual to transfer from one peg to the other. This object can be anything small and easily graspable, like a small ball or a wooden block.
- Explain the task: The individual is instructed on what they need to do. They are told to pick up the object from one peg and place it onto the other peg without dropping it or touching the pegs with their hands.
- Perform the test: The individual then attempts to complete the task. Their movements, coordination, and speed are observed and recorded. It is important to note any difficulties or errors during the test.
- Repeat and analyze: The test may be repeated multiple times to ensure reliability. The results are then analyzed to assess the individual’s hand-eye coordination and motor skills. Any patterns or trends in the performance are observed and evaluated.
The two peg test provides valuable information about a person’s manual dexterity, coordination, and ability to perform tasks that require precise movements. It can be used as a baseline measurement or to track progress in occupational therapy interventions. By identifying any areas of weakness, therapists can develop targeted interventions to improve a person’s hand-eye coordination and motor skills.
Gathering the Required Tools and Equipment
Before you begin the two peg test, it is important to gather all the necessary tools and equipment. Having everything prepared and organized will ensure a smooth and efficient execution of the test.
To perform the two peg test, you will need the following:
- Pegs: Two identical pegs made of durable material, such as metal or plastic. The pegs should be long and sturdy enough to withstand the test without bending or breaking.
- Measuring Tape: A measuring tape or ruler with clear and accurate measurements. This will be used to measure the distance between the pegs.
- Level: A spirit level or bubble level to ensure that the pegs are perfectly vertical and aligned with each other.
- Hammer or Mallet: A hammer or mallet to securely drive the pegs into the ground.
- Marker: A marker or chalk to mark the location of the pegs on the ground for easy reference.
- Notebook and Pen: A notebook or paper and a pen to record the measurements and observations during the test.
Make sure that all the tools and equipment are in good working condition and easily accessible. It is also recommended to wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, while performing the two peg test to prevent any injuries.
Setting up the Pegs and Taking Measurements

Before starting the two peg test, it is important to properly set up the pegs and take accurate measurements. This will ensure reliable results and make the test easier to perform.
Step 1: Choose the right location:
Find a suitable location for the test. It should be a flat and level surface, preferably outdoors. Avoid areas with slopes or irregularities that might affect the accuracy of the measurements.
Step 2: Place the first peg:
Take one of the pegs and firmly insert it into the ground at a point where you want to start the measurement. Make sure it is anchored securely and stands vertically.
Step 3: Align the second peg:
Take the second peg and position it at another point where you want to measure the distance from the first peg. Ensure that the second peg is aligned with the first one, forming a straight line.
Step 4: Measure the distance:
Using a measuring tape, measure the distance between the two pegs. Make sure the tape is pulled tight and straight for an accurate measurement. Record the distance for later calculations.
Step 5: Repeat the process:
If you need to perform multiple measurements, repeat steps 2 to 4 for each set of pegs. This will allow you to collect data for different distances and analyze the results more effectively.
By following these steps and setting up the pegs correctly, you can ensure accurate measurements and gather reliable data for the two peg test. Remember to take multiple measurements and record the results for further analysis.
Executing the Two Peg Test
The two peg test is a common method used to check the accuracy of the alignment of machine tools. This test involves placing two pegs or probes in specified positions, and then measuring the distance between them using an instrument such as a dial gauge or laser interferometer. The goal of the test is to ensure that the machine tool is properly aligned and capable of producing accurate and precise results.
Before performing the two peg test, it is important to carefully prepare the machine tool and the test setup. This includes cleaning and leveling the machine tool, as well as ensuring that the pegs are securely mounted in their specified positions. The test should be conducted in a controlled environment to minimize external factors that could affect the accuracy of the measurements.
To execute the two peg test:
- Start by zeroing the measuring instrument at a reference point.
- Move the instrument to the first peg and record the measurement.
- Move the instrument to the second peg and record the measurement.
- Calculate the distance between the two pegs by subtracting the measurement at the first peg from the measurement at the second peg.
- Compare the calculated distance with the specified distance to determine if the machine tool is aligned within acceptable tolerances.
- If the measured distance deviates from the specified distance, adjustments may need to be made to the machine tool to improve its alignment.
Regularly performing the two peg test can help ensure that machine tools maintain their accuracy over time. It is recommended to conduct this test after any major adjustments or repairs to the machine tool, as well as periodically as part of routine maintenance. By properly executing the two peg test, operators can have confidence in the accuracy and precision of their machine tools, leading to improved quality and efficiency in their work.