In Unit 1 of Macroeconomics, we delve into the concept of supply curves and explore their significance in understanding market dynamics. An understanding of supply curves is crucial for analyzing how changes in price and other factors affect the quantity supplied by producers in a given market.
This article aims to provide comprehensive answers to the Activity 1.6 of Unit 1 of Macroeconomics, which focuses on supply curves. By understanding and mastering the concepts covered in this activity, you will gain a deeper understanding of market equilibrium, price determination, and the behavior of producers in response to changing market conditions.
Through a series of questions and scenarios, Activity 1.6 challenges you to apply your knowledge of supply curves and analyze how changes in various factors such as input costs, technology, and expectations can shift or affect the shape of the supply curve.
By providing detailed answers and explanations to the questions in Activity 1.6, this article aims to enhance your understanding of supply curves and help you develop the analytical skills necessary for comprehending and predicting market dynamics.
Unit 1 Macroeconomics Activity 1.6 Supply Curves Answers
In Unit 1 of macroeconomics, Activity 1.6 focuses on understanding supply curves and their relationship to the price of a good or service. Supply curves show the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer at different prices. In this activity, students are tasked with analyzing and interpreting different scenarios to determine how changes in price affect the supply curve.
One possible answer to the activity involves a scenario where the price of a good decreases. In this case, the supply curve would shift to the left, indicating that producers are willing to offer less of the good at the lower price. This could be due to factors such as increased production costs or a decrease in the profitability of producing the good. As a result, the quantity supplied would decrease and the equilibrium price would adjust to a new level.
Another scenario that could be considered in the activity is one where the price of a good increases. In this case, the supply curve would shift to the right, indicating that producers are willing to offer more of the good at the higher price. This could be due to factors such as lower production costs or an increase in the profitability of producing the good. As a result, the quantity supplied would increase and the equilibrium price would adjust to a new level.
Overall, this activity helps students understand the relationship between price and supply and how changes in price can impact the supply curve. The analysis and interpretation of different scenarios allow students to see the real-world implications of these changes and how they affect the market equilibrium.
Supply Curves in Macroeconomics
In macroeconomics, supply curves are graphical representations of the relationship between the quantity of a product that producers are willing and able to supply at various price levels. They are a fundamental tool used to understand the behavior of suppliers and how they respond to changes in market conditions.
Supply curves are important in macroeconomics because they help explain the supply side of the market and the factors that influence the production and availability of goods and services. By analyzing supply curves, economists can make predictions about how changes in price, input costs, technology, and other factors will impact the quantity of goods and services supplied.
Supply curves are typically upward sloping, indicating that as the price of a product increases, producers are willing to supply more of that product. This positive relationship is due to the law of supply, which states that as the price of a product increases, producers have a greater incentive to supply more in order to maximize their profits.
However, it is important to note that supply curves can also shift. Factors such as changes in technology, input costs, government regulations, and expectations of future prices can cause the entire curve to shift left or right. These shifts in the supply curve indicate changes in the overall quantity of goods and services that suppliers are willing and able to produce at every price level.
By understanding the concept of supply curves, economists and policymakers can make informed decisions about issues such as price controls, taxation, subsidies, and regulations that affect the availability of goods and services in the economy. Supply curves provide a framework for analyzing the behavior of suppliers and their responses to various economic forces, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of macroeconomic dynamics.
How are supply curves obtained and what factors affect them?
The supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing and able to supply. It is obtained by plotting the various combinations of price and quantity supplied at different points in time.
The factors that affect supply curves include the cost of production, technological advancements, and market conditions. Firstly, the cost of production plays a major role in determining the supply curve. If the cost of inputs such as labor, raw materials, and capital increases, the supply curve will shift upwards, indicating that producers are willing to supply less at each price level. Conversely, if the cost of production decreases, the supply curve will shift downwards, indicating that producers are willing to supply more at each price level.
Secondly, technological advancements can also affect the supply curve. If a new technology is adopted that improves production efficiency, it can lead to a shift in the supply curve to the right, indicating that producers are now able to supply more at each price level. On the other hand, if there is a technological setback or inefficiency, the supply curve may shift to the left, indicating that producers are able to supply less at each price level.
Lastly, market conditions such as changes in consumer preferences, government policies, and external factors like natural disasters or pandemics can impact the supply curve. For example, if there is an increase in demand for a certain product, the supply curve may shift to the right as producers adjust their output to meet the higher demand.
In conclusion, supply curves are obtained by plotting the relationship between price and quantity supplied, and they are influenced by factors such as the cost of production, technological advancements, and market conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing and predicting changes in supply and determining the equilibrium price and quantity in a market.
Understanding the concept of equilibrium in the context of supply curves
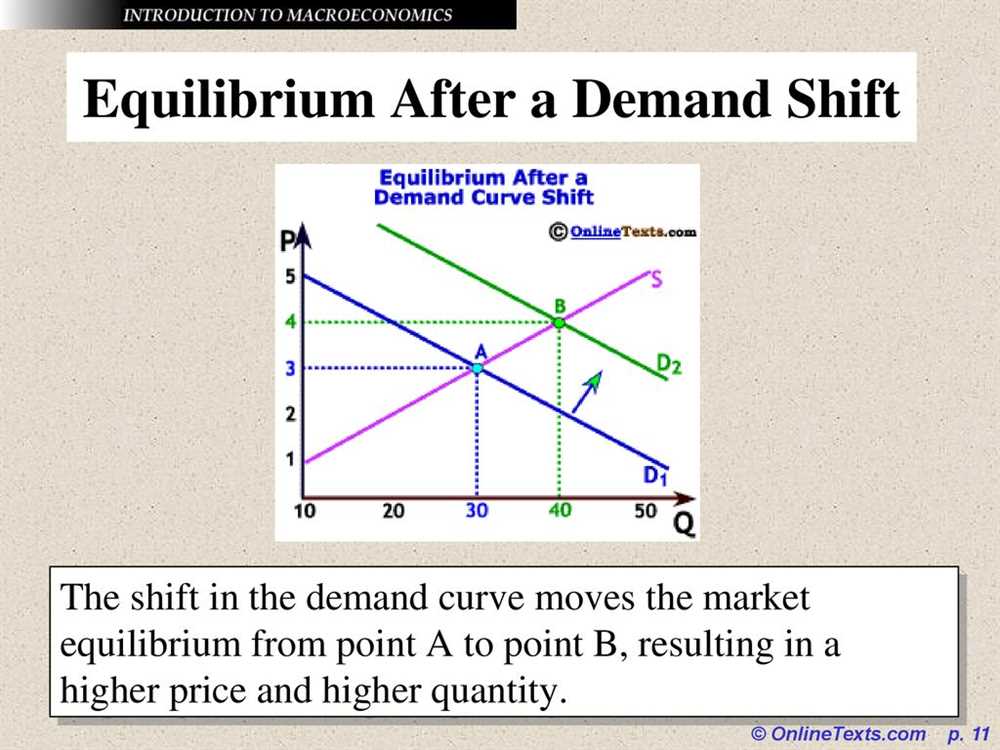
In the field of macroeconomics, supply curves play a crucial role in understanding how markets function. The concept of equilibrium is a fundamental principle that helps economists analyze the interaction between supply and demand. Equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied matches the quantity demanded at a given price.
The supply curve represents the relationship between the quantity supplied and the price of a product. As the price increases, producers are motivated to supply more of the product, resulting in an upward-sloping supply curve. Conversely, as the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases as well, resulting in a downward-sloping supply curve. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and the equilibrium quantity is the quantity that is produced and consumed at that price.
The concept of equilibrium is essential because it helps us understand how prices are determined in the market. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no shortage or surplus of the product. Producers are producing exactly what consumers are willing to buy at that particular price. If the price is above the equilibrium price, there will be a surplus, and producers will be motivated to lower the price to sell their excess supply. On the other hand, if the price is below the equilibrium price, there will be a shortage, and producers will increase the price to take advantage of the high demand.
To summarize, understanding the concept of equilibrium in the context of supply curves allows economists to analyze the dynamics of supply and demand in a market. By identifying the equilibrium price and quantity, economists can assess the efficiency and stability of the market and make predictions about potential changes in the future. It provides a framework for understanding how prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand forces in the market.
How do changes in supply affect the equilibrium price and quantity?
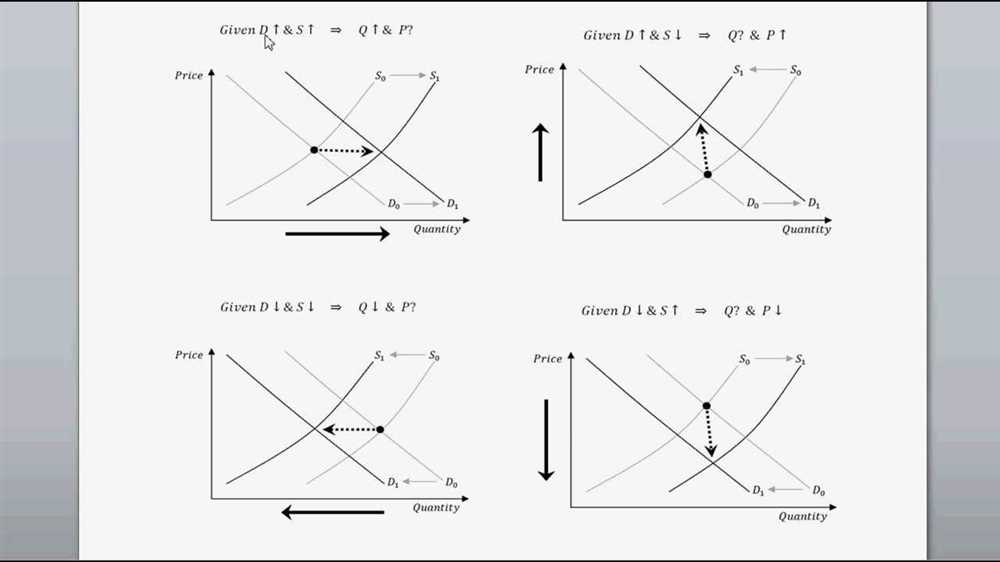
Changes in supply have a direct impact on the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. The supply curve represents the relationship between the quantity of a product that producers are willing to sell and the price of that product. When there is a change in supply, the entire supply curve shifts either to the right or to the left.
If the supply curve shifts to the right, it means that producers are willing to supply more of the product at each given price. This leads to an increase in the equilibrium quantity and a decrease in the equilibrium price. This occurs because there is now an excess supply of the product, and producers need to lower the price in order to sell their increased quantity.
On the other hand, if the supply curve shifts to the left, it means that producers are willing to supply less of the product at each given price. This results in a decrease in the equilibrium quantity and an increase in the equilibrium price. This happens because there is now an excess demand for the product, and producers can afford to raise the price to maximize their profits.
Overall, changes in supply have a significant impact on the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. Understanding these changes is crucial for both producers and consumers, as they determine the availability and affordability of goods and services in the economy.
Elasticity of supply and its impact on supply curves
When studying macroeconomics, one of the key concepts to understand is the elasticity of supply. Elasticity of supply refers to the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to changes in price. In other words, it measures how easily and quickly producers can adjust the amount of goods or services they are willing and able to sell in response to price changes. This concept is important because it directly affects the shape and slope of the supply curve.
Supply curves illustrate the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing to sell. A perfectly elastic supply curve is horizontal, indicating that quantity supplied is highly responsive to changes in price. This means that even a small change in price can lead to a significant change in the quantity supplied. On the other hand, a perfectly inelastic supply curve is vertical, indicating that quantity supplied does not change at all in response to price changes. In reality, most supply curves fall somewhere between these two extremes.
The elasticity of supply plays a crucial role in determining the shape of the supply curve. For goods with highly elastic supply, such as agricultural products, the supply curve is typically flatter. This means that producers can easily increase or decrease the quantity supplied in response to changes in price. On the other hand, goods with inelastic supply, such as rare antiques, have steeper supply curves as it is more difficult for producers to adjust the quantity supplied. Understanding the elasticity of supply is important for both producers and policymakers as it helps forecast market responses to changes in price and identify potential supply shortages or surpluses.
The relationship between supply curves and producer surplus
Supply curves play a crucial role in understanding the concept of producer surplus in the field of economics. The supply curve represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing and able to supply. It shows how a change in price affects the quantity supplied, assuming all other factors remain constant.
Producer surplus, on the other hand, refers to the difference between the price at which producers are willing to sell a good or service and the price they actually receive. It represents the additional profit earned by producers when the market price is higher than their minimum acceptable price.
When the market price is equal to or higher than the equilibrium price determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves, producers experience positive producer surplus. This is because they are able to sell their goods at a price higher than their production costs, resulting in additional profit. As the price increases, the producer surplus also increases as producers are able to receive a higher price for their goods.
However, when the market price falls below the equilibrium price, producers may experience negative producer surplus. This occurs when producers are forced to sell their goods at a price lower than their production costs, resulting in a loss. In such cases, producers may be hesitant to supply the goods, and the supply curve may shift to the left, reducing the quantity supplied.
In summary, the supply curve and producer surplus are closely related. Changes in the market price affect the quantity supplied and the amount of producer surplus. When the market price is higher than the equilibrium price, producers earn positive producer surplus, while a price lower than the equilibrium results in negative producer surplus. Understanding this relationship is important in analyzing the behavior of producers and their decision-making in response to fluctuations in market conditions.
Using supply curves to analyze market equilibrium and efficiency
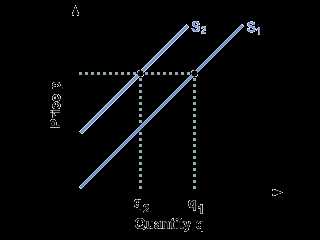
Supply curves provide a visual representation of the relationship between the quantity of a good or service that suppliers are willing and able to offer at different price levels. By examining supply curves, economists can analyze market equilibrium and efficiency.
In a free market, equilibrium is reached when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. This is illustrated on a supply and demand graph by the point where the supply curve intersects with the demand curve. At this equilibrium point, the market efficiently allocates resources, and there is no shortage or surplus of the good. If the price is below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied, resulting in a shortage. If the price is above the equilibrium price, quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, resulting in a surplus.
Furthermore, studying supply curves can help identify the factors that affect the supply of a good or service. For example, an increase in production costs, such as higher wages or raw material prices, can shift the supply curve to the left, indicating a decrease in the quantity supplied at each price level. On the other hand, technological advancements or government subsidies can shift the supply curve to the right, indicating an increase in the quantity supplied at each price level.
In summary, supply curves are an essential tool for analyzing market equilibrium and efficiency. By examining the intersection of supply and demand curves, economists can determine the equilibrium price and quantity, and assess the efficiency of resource allocation in a market. Additionally, studying supply curves allows for a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the supply of goods or services, aiding in the analysis of market dynamics and policy interventions.