
In algebra, polynomial functions play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of mathematical equations. These functions are formed by combining variables, coefficients, and exponents in various ways. In Unit 5 of our course, we explored polynomial functions in detail, studying their properties, graphs, and solving related problems.
After putting in the hard work and completing the Unit 5 test, students eagerly await the answer key to verify their solutions and evaluate their understanding. The Unit 5 test polynomial functions answer key provides a comprehensive list of correct answers to the exam questions. This key serves as a valuable tool for students to double-check their work, identify any mistakes, and learn from them.
The answer key not only gives the correct solutions but also provides explanations for each step. This helps students understand the reasoning behind each answer and improve their problem-solving skills. By carefully reviewing the answer key, students can identify any knowledge gaps or weak areas that require further study.
Ultimately, the Unit 5 test polynomial functions answer key serves as a learning resource that enables students to assess their understanding of the material and make necessary improvements. It empowers them to take control of their learning journey and strive for academic success in algebra and beyond.
Unit 5 Test Polynomial Functions Answer Key
Here is the answer key for the Unit 5 Test on polynomial functions:
Question 1:
The degree of a polynomial is determined by the highest exponent in the expression. In this question, the highest exponent is 4, so the degree is 4.
Question 2:
To find the zeros of a polynomial function, we set the expression equal to zero and solve for the variable. In this question, the zeros are x = -2, x = 3, and x = 5.
Question 3:
To find the end behavior of a polynomial function, we look at the leading term. In this question, the leading term is 2x^3, so the end behavior is as x approaches negative infinity, the function approaches negative infinity, and as x approaches positive infinity, the function approaches positive infinity.
Question 4:
The sum and product of the zeros of a polynomial function can be found using Vieta’s formulas. In this question, the sum of the zeros is -2 + 3 + 5 = 6, and the product of the zeros is -2 * 3 * 5 = -30.
Question 5:
The function f(x) = (x – 2)(x + 1)(x – 4) is a factored form of a polynomial. To find the standard form of the polynomial, we expand the expression to get f(x) = x^3 – 5x^2 + 6x – 8.
Make sure to check your work for any arithmetic errors and provide proper justification for your answers. Good luck!
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Polynomial functions are mathematical expressions that involve variables raised to different powers and combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication. They play a crucial role in various fields of mathematics and have numerous applications in real-world problems. Understanding polynomial functions is essential for mastering algebra and calculus.
Definition: A polynomial function is a function of the form:
f(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + … + a1x + a0
Here, the coefficients (a0, a1, …, an) are real numbers, and the exponents (0, 1, …, n) are non-negative integers. The highest power of x in the function is called the degree of the polynomial.
Characteristics: Polynomial functions can have multiple terms, each consisting of a constant multiplied by a power of the variable. The leading term, with the highest exponent, determines the shape and behavior of the function. The degree of the polynomial indicates the number and complexity of its roots.
Polynomials have specific properties that help in their analysis and graphing. For instance, the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that every polynomial of degree n has exactly n complex roots (counting multiplicity). Additionally, the End Behavior Theorem describes the behavior of polynomial functions as x approaches positive infinity or negative infinity based on the sign of the leading term.
In conclusion, understanding polynomial functions is crucial in algebra and calculus, as they provide a powerful mathematical tool for solving problems and modeling real-world phenomena. By analyzing their properties, such as degree, roots, and end behavior, we can gain insights into their graphing and behavior. Polynomial functions offer a rich field of study that continues to be explored in various branches of mathematics.
Key Concepts in Polynomial Functions
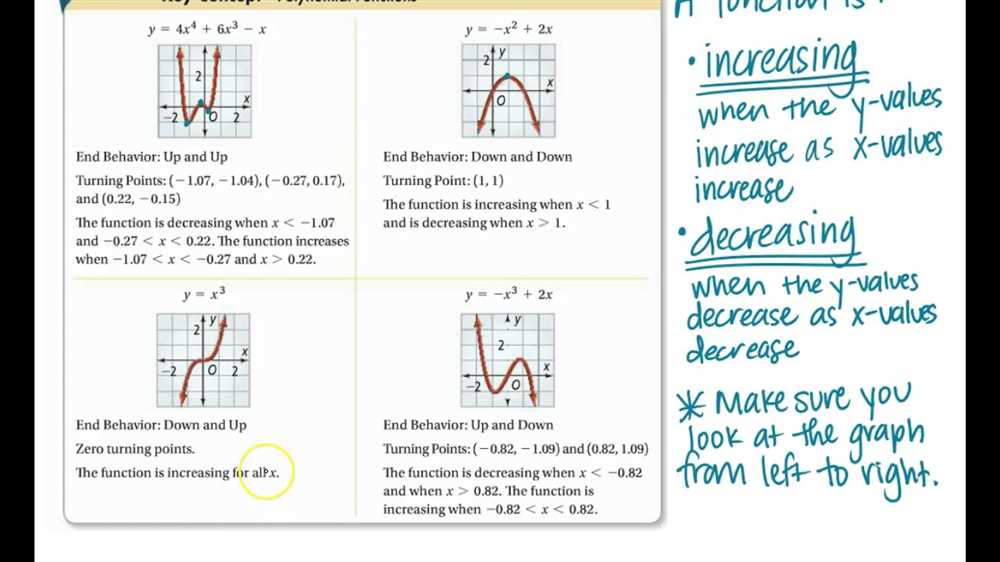
Polynomial functions are important mathematical tools that are used to model and analyze a wide variety of real-world phenomena. They are characterized by their ability to represent complex relationships between independent and dependent variables, such as time and distance, sales and price, or population and resources.
One key concept in polynomial functions is the degree of the polynomial. The degree is determined by the highest power of the variable in the expression. For example, a polynomial with the expression 2x^3 + 5x^2 – 3x + 1 has a degree of 3, since the highest power of x is 3. The degree of a polynomial function can give us insights into its behavior, such as identifying the number of roots it has or the maximum and minimum values it can attain.
Another important concept in polynomial functions is the leading coefficient. The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the term with the highest power of the variable. In the previous example, the leading coefficient is 2. The leading coefficient can affect the shape of the graph of the polynomial function, specifically determining whether the graph opens upwards or downwards and how steep the slope of the graph is.
Polynomial functions also have roots, which are the values of the variable that make the polynomial equal to zero. These roots can be real or complex numbers and can be found by factoring the polynomial or using numerical methods such as the Newton-Raphson method. The roots of a polynomial function can provide valuable information about its behavior, such as the x-intercepts of the graph or the values at which the polynomial changes sign.
In conclusion, understanding key concepts in polynomial functions, such as degree, leading coefficient, and roots, is essential for analyzing and interpreting the behavior of these functions. By mastering these concepts, mathematicians and scientists can use polynomial functions to model and solve real-world problems and gain deeper insights into the world around us.
Solving Polynomial Equations

Polynomial equations are algebraic equations that involve variables raised to integer powers and can include constants and coefficients. Solving polynomial equations is an essential skill in algebra and is used to find the values of the variables that make the equation true.
There are several methods for solving polynomial equations, including factoring, graphing, and using the quadratic formula. Factoring involves breaking down the polynomial equation into factors and setting each factor equal to zero. By solving each factor, we can find the values of the variables that satisfy the equation.
Graphing can also be used to solve polynomial equations. By plotting the equation on a graph, we can visually determine where the function intersects the x-axis. The x-values of these intersections are the solutions to the equation.
Another method for solving polynomial equations is by using the quadratic formula, which is specifically designed to solve quadratic equations. The quadratic formula states that the solutions to the equation ax^2 + bx + c = 0 are given by x = (-b ± √(b^2 – 4ac)) / 2a. This formula allows us to find the exact solutions to quadratic equations.
In conclusion, solving polynomial equations requires understanding various methods such as factoring, graphing, and using the quadratic formula. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the equation and the desired level of precision in finding the solutions. By mastering these techniques, one can effectively solve polynomial equations and apply them to various real-world situations.
Graphing Polynomial Functions
A polynomial function is a mathematical expression that consists of a sum of terms, each of which is a constant multiplied by one or more variables raised to a non-negative integer power. These functions are widely used in many areas of mathematics and science to model real-world phenomena.
To graph a polynomial function, it is important to understand its key features, such as the degree, leading coefficient, and end behavior. The degree of a polynomial function is determined by the highest power of the variable in the function. The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the term with the highest power of the variable.
One way to graph a polynomial function is by identifying its x-intercepts, which are the values of x for which the function equals zero. These can be found by setting the function equal to zero and solving for x. The x-intercepts are also the roots or solutions of the polynomial equation.
The end behavior of a polynomial function is determined by the degrees of the polynomial and the sign of the leading coefficient. If the degree is even and the leading coefficient is positive, the graph of the polynomial will have the same end behavior as a quadratic function, opening upward on both ends. If the degree is odd and the leading coefficient is positive, the graph will have opposite end behavior, opening downward on both ends.
By understanding these key features and using techniques such as factoring, long division, and synthetic division, it is possible to accurately graph a polynomial function and analyze its behavior. Graphing polynomial functions allows us to visualize and better understand the patterns and relationships represented by these mathematical expressions.
Factoring Polynomial Expressions

Factoring is an important skill in algebra that allows us to simplify polynomial expressions by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable parts. By factoring polynomials, we can find their roots, identify their linear factors, and solve equations involving these expressions.
The process of factoring involves finding the common factors of a polynomial expression and then rewriting it as a product of these factors. The most basic type of factoring is factoring out the greatest common factor (GCF) of the expression. This often involves looking for common factors such as numbers or variables that can be divided evenly from each term of the polynomial. By factoring out the GCF, we can simplify the expression and make further factoring easier.
Another type of factoring is factoring quadratic expressions. Quadratic expressions are polynomials of degree 2, and they can often be factored into two linear factors. To factor a quadratic expression, we can use methods such as factoring by grouping, factoring trinomials, or using the quadratic formula. By factoring quadratic expressions, we can find their roots and solve quadratic equations efficiently.
Factoring polynomial expressions is a valuable skill in algebra that helps us simplify expressions, find roots, and solve equations. By understanding the different types of factoring and practicing various factoring techniques, we can build our algebraic proficiency and solve more complex problems involving polynomial functions.
Long Division and Synthetic Division of Polynomials

Polynomials are mathematical expressions that consist of variables, coefficients, and exponents. They play an important role in various branches of mathematics, including algebra and calculus. One common operation performed on polynomials is division, which helps to simplify complex expressions and find the solutions to polynomial equations.
Long division is a method used to divide one polynomial by another. It involves dividing each term of the dividend by the divisor and then subtracting the resulting quotient from the dividend. This process is repeated until the remainder has a lower degree than the divisor. The final result is the quotient, with the remainder expressed as a fraction or decimal.
Synthetic division is a simpler and more efficient method of dividing polynomials in certain cases. It is particularly useful when dividing a polynomial by a linear divisor of the form (x – a), where “a” is a constant. Synthetic division involves a series of simple operations, such as multiplication, addition, and subtraction, to find the quotient and remainder. It eliminates the need for writing out long division steps and can be done quickly. However, it can only be used when the divisor is of a specific form.
Both long division and synthetic division of polynomials are important techniques for solving polynomial equations and simplifying complex expressions. They are commonly used in algebraic manipulation, calculus, and various other fields of mathematics. Understanding these methods and practicing them allows for a better understanding of polynomial functions and their behavior.
The Remainder and Factor Theorems
The Remainder Theorem and the Factor Theorem are two crucial concepts in the study of polynomial functions. These theorems provide important insights into the behavior and properties of polynomial equations.
The Remainder Theorem states that if a polynomial function P(x) is divided by a binomial (x – a), then the remainder of the division is equal to P(a). In other words, if we substitute the value of a into the polynomial equation, the resulting value will be the remainder. This theorem is useful for finding the values of polynomials at specific points, as well as determining whether a given binomial is a factor of the polynomial.
The Factor Theorem is closely related to the Remainder Theorem. It states that if a polynomial function P(x) is zero when x = a, then (x – a) is a factor of P(x). In other words, if we find that a particular value of x makes the polynomial equal to zero, we can conclude that (x – a) is a factor of the polynomial equation. This theorem allows us to factorize polynomial equations and determine their roots.
By applying the Remainder Theorem and the Factor Theorem, we can gain a deeper understanding of polynomial functions, their factors, and their properties. These theorems provide powerful tools for solving polynomial equations and analyzing their behavior.