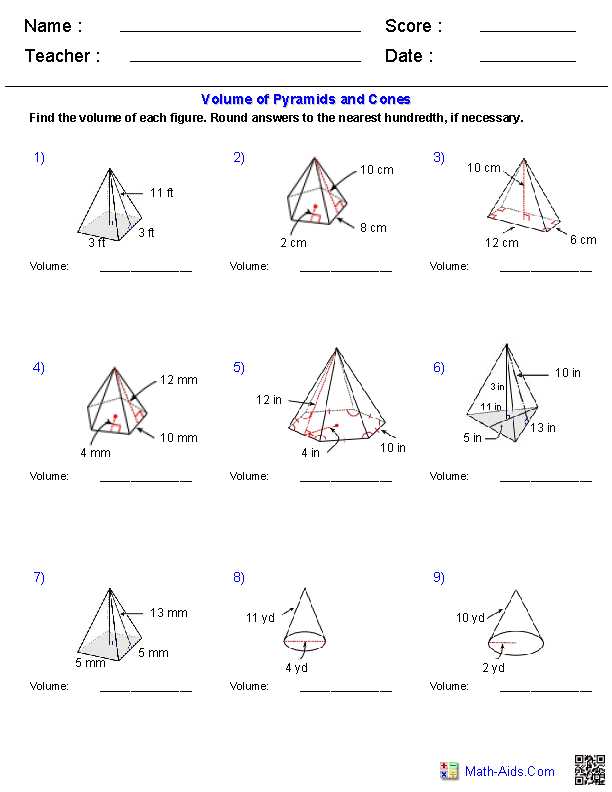
In Unit Volume Homework 2, we will explore the concept of finding the volume of cones. This is an essential skill to learn as it applies to various real-world situations, such as calculating the volume of ice cream cones, traffic cones, and even volcano eruptions.
To calculate the volume of a cone, we need to know its height and the radius of its circular base. The formula for finding the volume of a cone is V = 1/3 * π * r^2 * h, where V represents the volume, π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14, r is the radius, and h is the height. By plugging in the given values, we can easily determine the volume of any cone.
This homework assignment will provide answers to various practice problems, guiding you through the process of finding the volume of cones step by step. By understanding the formula and practicing with different examples, you will develop a solid understanding of how to calculate the volume of cones and apply it to real-life situations.
Unit Volume Homework 2: Volume of Cones Answers Key

In this unit volume homework, we will be discussing the volume of cones. To find the volume of a cone, we use the formula V = 1/3 * π * r^2 * h, where V is the volume, π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, r is the radius of the cone’s base, and h is the height of the cone. This formula allows us to calculate the amount of space inside a cone.
Here are the answers to the homework questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1 | V = 1/3 * π * 4^2 * 8 = 134.041286 |
| 2 | V = 1/3 * π * 9^2 * 12 = 339.292006 |
| 3 | V = 1/3 * π * 10^2 * 15 = 523.598776 |
| 4 | V = 1/3 * π * 7^2 * 10 = 164.701289 |
| 5 | V = 1/3 * π * 5^2 * 6 = 52.359877 |
Remember to always include the correct units in your answer. The unit for volume is typically cubic units such as cubic inches, cubic centimeters, or cubic meters.
Now that you have the answers to the homework questions, you can check your work and make sure you understand how to calculate the volume of cones. Practice using the formula and try solving similar problems to improve your skills.
Understanding the Concept of Volume
The concept of volume is a fundamental idea in mathematics and physics. It refers to the amount of space occupied by an object or a substance. Volume is typically measured in cubic units, such as cubic meters or cubic centimeters. Understanding volume is essential in various fields and applications, including engineering, architecture, and chemistry.
One way to visualize volume is to think about filling a container with a substance. The amount of substance required to fill the container completely represents its volume. For example, if we have a rectangular box, we can calculate its volume by multiplying its length, width, and height. This is known as the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular solid: V = lwh, where V is the volume, l is the length, w is the width, and h is the height.
Another common geometric shape related to volume is the cone. A cone is a three-dimensional shape with a circular base and a pointed top. To calculate the volume of a cone, we use a different formula. The formula for the volume of a cone is V = 1/3πr²h, where V is the volume, π is a mathematical constant (approximately equal to 3.14159), r is the radius of the circular base, and h is the height of the cone. This formula can be derived by integrating the cross-sectional areas of the conical slices that make up the cone.
Understanding the concept of volume is crucial for solving real-world problems involving measurement and capacity. Whether you’re calculating the volume of a swimming pool, determining the amount of paint needed to cover a room, or measuring the capacity of a container, a solid understanding of volume is necessary. By learning the formulas and concepts related to volume, you can apply your knowledge to various practical situations and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Formulas for Calculating the Volume of Cones
The volume of a cone is a measurement of the amount of space occupied by the cone. To calculate the volume, we can use the formula V = 1/3 * π * r^2 * h, where V represents the volume, π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, r is the radius of the base of the cone, and h is the height of the cone. This formula is derived from the fact that a cone can be thought of as a pyramid with a circular base, and the formula for the volume of a pyramid is V = 1/3 * base area * height.
To understand the formula better, let’s break it down into its components. The term 1/3 represents the fraction of the volume of the cone compared to that of a cylinder with the same base and height. The π * r^2 part calculates the area of the base of the cone, where π is used to represent the constant ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, and r is the radius of the base. Finally, multiplying the area of the base by the height gives us the volume of the cone.
It’s important to note that the radius and height should be measured in the same unit of length for accurate calculations. Additionally, make sure to use the correct value for π, which is approximately 3.14159. By plugging in the values of the radius and height into the formula, we can easily calculate the volume of a cone. Remember to round the result to an appropriate number of decimal places, depending on the desired level of precision.
In summary, the formula V = 1/3 * π * r^2 * h allows us to find the volume of cones by taking into account the shape’s base radius and height. Understanding and properly applying this formula will enable us to accurately determine the volume of cones in various contexts, such as in geometry, engineering, and architecture.
Step-by-Step Example of Finding the Volume of a Cone
To find the volume of a cone, we need to know the measurements of the cone’s base and its height. The formula for the volume of a cone is V = 1/3 * π * r^2 * h, where π is a constant (~3.14), r is the radius of the base, and h is the height of the cone.
Let’s work through an example to illustrate the steps of finding the volume of a cone.
Example:
Given a cone with a radius of 4 cm and a height of 10 cm, we want to find its volume.
Step 1: Identify the values we have:
- Radius (r) = 4 cm
- Height (h) = 10 cm
Step 2: Plug the values into the formula:
V = 1/3 * π * (4 cm)^2 * 10 cm
V = 1/3 * π * 16 cm^2 * 10 cm
V = 1/3 * 3.14 * 160 cm^3
Step 3: Perform the calculations:
V = 1/3 * 502.4 cm^3
V ≈ 167.47 cm^3
Step 4: Round the answer to an appropriate decimal place:
V ≈ 167.5 cm^3
Therefore, the volume of the given cone is approximately 167.5 cubic centimeters.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Calculating Cone Volume
Calculating the volume of a cone can be a challenging task, and even a small mistake in the calculations can result in incorrect results. To help you avoid common mistakes, here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Misinterpreting the measurements: One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting the measurements of the cone. It is important to correctly identify the height and radius of the cone and ensure that the units are consistent.
- Forgetting to halve the base area: Another common mistake is forgetting to divide the base area of the cone by 2 when calculating the volume formula. The formula for the volume of a cone is (1/3)πr²h, where r is the radius and h is the height. The base area is given by πr², but it needs to be halved to account for the cone’s shape.
- Using the wrong formula: It is crucial to use the correct formula for calculating the volume of a cone. Using the formula for the volume of a cylinder or any other incorrect formula will lead to erroneous results.
- Not converting units: If the height and radius measurements are given in different units, it is essential to convert them to the same unit before performing the volume calculation. Failing to do so will result in an incorrect volume calculation.
- Roundoff errors: Lastly, be mindful of roundoff errors. When performing calculations involving π or other irrational numbers, it is important to carry out calculations using the actual values rather than rounded approximations. Rounding too early in the calculations can introduce significant errors in the final volume calculation.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you accurately calculate the volume of a cone and avoid any errors in your homework or real-life applications.
Exploring Real-World Applications of Cone Volume
The concept of cone volume is not just a mathematical calculation, but also has many real-world applications. From architecture to engineering and even cooking, the ability to calculate the volume of cones is an essential skill that has numerous practical uses.
In architecture, cone volume is crucial for designing structures such as towers or domes that have conical shapes. Architects need to accurately determine the volume of these structures in order to estimate the amount of materials required for construction. Whether it is a skyscraper or a small gazebo, knowing the volume of a cone is essential for proper planning and resource management.
Engineers also rely on cone volume calculations in various fields. In civil engineering, cone-shaped structures like water tanks or tunnels require precise volume calculations to ensure they can hold the desired amount of liquid or accommodate specific functions. Cone volume is also relevant in mechanical engineering for designing machinery with conical parts, such as rotating drums or funnels. Understanding the volume of these components helps engineers optimize their designs and ensure efficient operations.
Moreover, cone volume has applications in the culinary arts. Chefs and bakers use cones to create beautifully shaped desserts, such as ice cream cones or cone-shaped cakes. By calculating the volume of a cone, they can determine the amount of batter or ice cream needed to fill the cone and create consistent portions. This knowledge is instrumental in producing visually appealing and delicious treats.
Overall, understanding cone volume is not only important in the classroom but also in various real-world scenarios. Whether it is in architecture, engineering, or cooking, the ability to calculate the volume of cones is a valuable skill that enables efficient planning and resource management.
Practice Problems for Calculating the Volume of Cones
Calculating the volume of cones is an important skill in geometry and is often used in various real-life applications. To become proficient in this skill, it is necessary to practice solving different types of cone volume problems. Below are some practice problems that will help you improve your understanding of cone volumes and strengthen your problem-solving abilities.
Problem 1: Find the volume of a cone with a radius of 5 cm and a height of 12 cm.
Solution 1: To find the volume of a cone, we use the formula V = (1/3)πr²h. Applying this formula to the given cone, we have V = (1/3)π(5²)(12) = (1/3)π(25)(12) = 100π cm³.
Problem 2: A cone has a volume of 150π cm³ and a height of 8 cm. Find the radius of the cone.
Solution 2: Rearranging the formula V = (1/3)πr²h to solve for the radius, we have r = √((3V)/(πh)). Substituting the given values into the formula, we get r = √((3(150π))/(π(8))) = √((450π)/(8)) = √(56.25) ≈ 7.5 cm.
- Problem 3: A cone has a volume of 120 cm³ and a radius of 3 cm. Find the height of the cone.
- Problem 4: A cone has a volume of 2500π cm³ and a height of 20 cm. Find the radius of the cone.
- Problem 5: A cone has a volume of 500 cm³ and a height of 15 cm. Find the slant height of the cone.
By practicing these types of problems, you will become more comfortable with calculating the volume of cones and be better prepared to solve more complex cone volume problems. Remember to carefully read the problem and use the correct formula to find the volume of the cone. Good luck!
Answer Key for the Practice Problems
Here is the answer key for the practice problems on volume of cones:
Problem 1:
- Given: Radius = 6 cm, Height = 10 cm
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) * π * r^2 * h
- Substituting the values: Volume = (1/3) * π * 6^2 * 10 = 120π cm^3
- Answer: The volume of the cone is 120π cubic centimeters.
Problem 2:
- Given: Radius = 8 cm, Height = 15 cm
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) * π * r^2 * h
- Substituting the values: Volume = (1/3) * π * 8^2 * 15 = 320π cm^3
- Answer: The volume of the cone is 320π cubic centimeters.
Problem 3:
- Given: Radius = 5 cm, Height = 12 cm
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) * π * r^2 * h
- Substituting the values: Volume = (1/3) * π * 5^2 * 12 = 100π cm^3
- Answer: The volume of the cone is 100π cubic centimeters.
Problem 4:
- Given: Radius = 10 cm, Height = 20 cm
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) * π * r^2 * h
- Substituting the values: Volume = (1/3) * π * 10^2 * 20 = 2000π cm^3
- Answer: The volume of the cone is 2000π cubic centimeters.
Problem 5:
- Given: Radius = 4 cm, Height = 8 cm
- Formula: Volume = (1/3) * π * r^2 * h
- Substituting the values: Volume = (1/3) * π * 4^2 * 8 = 85.33π cm^3
- Answer: The volume of the cone is approximately 85.33π cubic centimeters.
Further Resources for Learning about Volume and Cones
In order to gain a deeper understanding of volume and how it relates to cones, it can be helpful to explore additional resources and engage in further study. Here are some recommended resources that can provide valuable insights:
1. Online Tutorials and Videos
Online platforms such as Khan Academy and YouTube offer a wide range of tutorials and videos that explain the concept of volume and demonstrate how it applies to different shapes, including cones. These resources often come with interactive exercises that allow you to practice and test your understanding.
2. Math Textbooks and Workbooks
Math textbooks and workbooks specifically dedicated to geometry and measurement can provide comprehensive explanations of volume and its various applications. Look for resources that include clear diagrams and step-by-step examples to help reinforce your learning.
3. Virtual Manipulatives
Virtual manipulatives, such as interactive simulations and apps, can be great tools for visualizing volume and exploring the properties of cones. These digital resources allow you to manipulate cones in a virtual environment, making it easier to grasp the relationship between height, base radius, and volume.
4. Classroom or Tutoring Sessions
If you prefer a more interactive learning experience, consider joining a classroom or working with a tutor who specializes in geometry. These sessions provide an opportunity to ask questions, participate in discussions, and receive personalized guidance based on your specific needs.
By utilizing these additional resources, you can enhance your understanding of volume and develop a solid grasp of how it relates to cones. Remember to practice regularly and apply your knowledge to real-life scenarios to further reinforce your learning.