
If you’re studying the urinary system, you may have come across a worksheet with questions that require answers. Having a comprehensive understanding of this system is crucial for medical professionals, students, and individuals looking to maintain their overall health. In this article, we will provide you with the answers to a urinary system worksheet, helping you solidify your knowledge and grasp the important concepts within this topic.
First and foremost, let’s explore the functions of the urinary system. It is responsible for several vital processes in our bodies, including the removal of waste products, regulation of blood pressure, production of hormones, and maintenance of water balance. The key components of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Now, let’s delve into some specific questions that you may have encountered on your urinary system worksheet. One common question is: “What are the main functions of the kidneys?” The kidneys perform essential tasks, such as filtering waste products from the blood, regulating electrolyte levels, and producing urine. They also play a significant role in maintaining blood pressure and the production of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
Another question you may have encountered is: “What is the path of urine flow from the kidneys?” The urine formed in the kidneys travels down the ureters, slender tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. From the bladder, the urine is excreted through the urethra, a tube that leads to the external opening of the body.
In conclusion, understanding the urinary system is paramount for various reasons. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a student preparing for an exam, or simply interested in maintaining your own health, familiarizing yourself with the concept is essential. By providing you with the answers to urinary system worksheet questions, we hope to contribute to your understanding and mastery of this crucial topic.
Urinary System Worksheet Answers PDF
The urinary system is an important part of the human body, responsible for filtering waste products from the bloodstream and regulating fluid balance. To better understand how the urinary system works, it is important to have access to educational resources such as worksheets that provide comprehensive answers to key questions. With the urinary system worksheet answers PDF, learners can study and review important concepts related to the urinary system at their own pace.
The urinary system worksheet answers PDF contains a variety of questions and corresponding answers that cover topics such as the anatomy of the urinary system, the functions of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, as well as the process of urine formation and elimination. The worksheet answers provide detailed explanations and diagrams to help learners visualize and understand the various components and processes involved in the urinary system.
Access to the urinary system worksheet answers PDF can be beneficial for students, teachers, and healthcare professionals alike. Students can use the worksheet answers as a study guide or reference tool to reinforce their understanding of urinary system concepts. Teachers can incorporate the worksheet answers into their lesson plans to supplement classroom instruction and assess student knowledge. Healthcare professionals can use the worksheet answers to refresh their knowledge and stay up-to-date on important urinary system concepts.
In conclusion, the urinary system worksheet answers PDF is a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their understanding of the urinary system. By providing detailed answers and explanations, the worksheet helps learners grasp key concepts related to the structure and function of the urinary system. Whether used for studying, teaching, or professional development, the urinary system worksheet answers PDF is an essential tool for anyone seeking to master this important aspect of human physiology.
Understanding the Urinary System
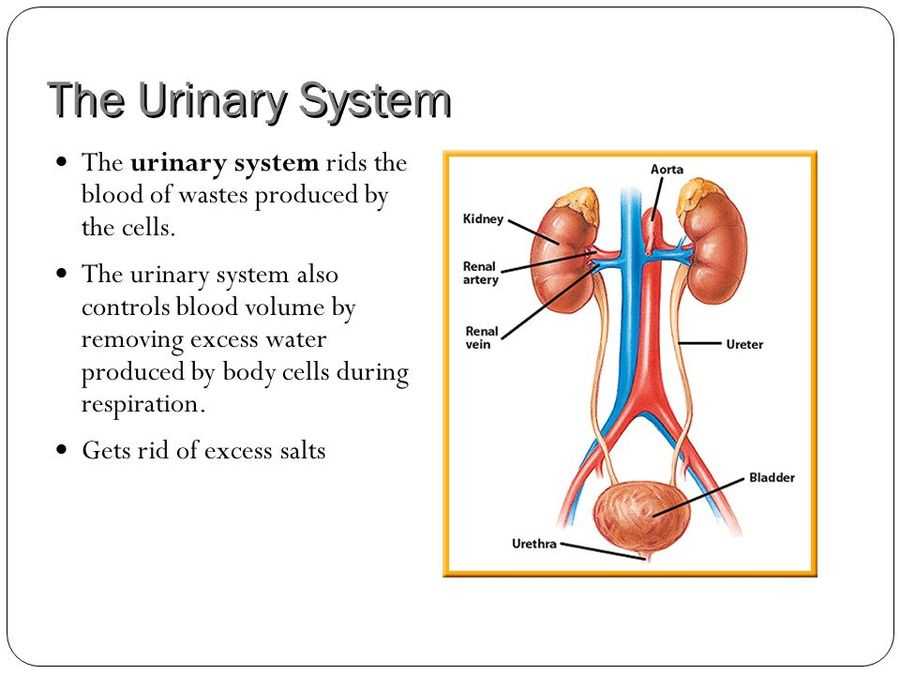
The urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functioning of the body. It is responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine, which helps to remove waste products from the body and maintain proper fluid balance. Understanding how the urinary system works is essential to recognizing potential problems and maintaining good urinary health.
The urinary system consists of several organs that work together to perform its functions. These organs include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are the primary filtration organs, responsible for removing waste products, excess water, and toxins from the blood to form urine. The urine is then transported through the ureters, which are tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder acts as a reservoir for storing urine until it can be eliminated through the urethra, which is the tube connecting the bladder to the external environment.
The kidneys are the key organs of the urinary system. Their main function is to filter blood and produce urine. Each kidney contains millions of tiny filtering units called nephrons, which remove waste products and excess water from the blood. The urine produced by the kidneys travels down the ureters and is stored in the bladder until it is eliminated.
Understanding the urinary system is important for recognizing and managing urinary disorders. Common problems include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, urinary incontinence, and kidney failure. By understanding how the urinary system works, individuals can take steps to maintain good urinary health, such as drinking enough water, maintaining a healthy diet, and practicing good hygiene.
- The urinary system plays a crucial role in removing waste products and maintaining fluid balance in the body.
- Key organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- The kidneys are responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
- Common urinary disorders include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, urinary incontinence, and kidney failure.
- Understanding the urinary system helps individuals maintain good urinary health through proper hydration, diet, and hygiene practices.
Importance of the Urinary System
The urinary system plays a crucial role in regulating the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. It is responsible for filtering waste products and toxins from the bloodstream, and excreting them in the form of urine. These waste products include urea, uric acid, and creatinine, which are byproducts of metabolism that can be harmful if they build up in the body. The kidneys, which are a key component of the urinary system, help maintain the proper levels of these substances by adjusting the amount of water and electrolytes reabsorbed or excreted.
The urinary system also helps maintain proper blood pressure and volume. The kidneys release a hormone called renin, which stimulates the production of another hormone, known as aldosterone. Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to increase the reabsorption of sodium and water, leading to an increase in blood volume and, consequently, blood pressure. This regulation of blood pressure is vital for maintaining overall cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, the urinary system is involved in the production of red blood cells. The kidneys release a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cells are crucial for delivering oxygen to tissues and organs throughout the body, and maintaining healthy levels is essential for optimal functioning.
In addition to these functions, the urinary system also helps regulate the pH balance of the body by controlling the excretion of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. This acid-base balance is crucial for proper cellular function and maintaining overall homeostasis.
In conclusion, the urinary system is of utmost importance for maintaining the overall health and balance of the body. It not only filters waste products and maintains fluid and electrolyte balance, but also plays a role in regulating blood pressure, producing red blood cells, and controlling the body’s pH balance. Without the proper functioning of the urinary system, various health issues can arise, making it essential to take care of this vital system.
Functions of the Urinary System
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, is responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, as well as excreting waste products and toxins. The urinary system consists of several organs, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Filtration and Waste Removal: The kidneys are the main organs responsible for the filtration of blood and the removal of waste products from the body. Each kidney contains millions of tiny filters called nephrons, which help in filtering out waste substances, excess water, and electrolytes from the bloodstream. These waste products are then transformed into urine, which is transported to the bladder for storage and subsequent elimination.
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: The urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. It regulates the volume and composition of body fluids by selectively reabsorbing essential substances, such as water, glucose, and electrolytes, back into the bloodstream. This process ensures that the body maintains the optimum concentration of ions, nutrients, and water necessary for normal cell function.
Blood Pressure Regulation: The kidneys also contribute to the regulation of blood pressure. They produce a hormone called renin, which helps in controlling blood pressure by regulating the amount of sodium and water reabsorbed by the kidneys. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a complex pathway that involves the kidneys and other organs to regulate blood pressure and maintain fluid balance in the body.
Acid-Base Balance: The urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining the acid-base balance of the body. It helps in regulating the pH levels of body fluids by excreting excess hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions. This process helps in keeping the blood pH within a narrow range, which is essential for normal physiological processes.
Detoxification: The urinary system aids in the detoxification process by eliminating waste products and toxins from the body. It helps in removing substances such as urea, uric acid, and drugs from the bloodstream, preventing them from accumulating and causing harm. This detoxification process is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing the buildup of harmful substances in the body.
- Overall, the urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. Its functions include filtration and waste removal, fluid and electrolyte balance, blood pressure regulation, acid-base balance, and detoxification. Without a properly functioning urinary system, the body would not be able to eliminate waste products, regulate fluid balance, or maintain normal physiological processes.
Common Urinary System Disorders
The urinary system plays a vital role in the excretion of waste products and maintenance of fluid balance in the body. However, certain disorders can affect its normal functioning, leading to various symptoms and complications.
One common disorder of the urinary system is urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, usually through the urethra, and multiply in the bladder. Symptoms of a UTI may include frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and pelvic pain in women. UTIs are more common in women due to the shorter length of their urethra.
Kidney stones are another common disorder of the urinary system. These are hard, crystal-like deposits that form in the kidneys due to the accumulation of minerals and salts. Kidney stones can cause intense pain in the back or side, blood in the urine, and difficulty urinating. Treatment options for kidney stones may include medications to help pass the stones, lithotripsy to break them into smaller pieces, or surgical removal.
Chronic kidney disease is a progressive condition that affects the kidneys’ ability to filter waste products from the blood. It can result from various causes, such as diabetes, hypertension, or infections. Symptoms of chronic kidney disease may include fatigue, fluid retention, decreased urine output, and electrolyte imbalances. Treatment options for chronic kidney disease depend on the underlying cause and may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or dialysis.
Another common urinary system disorder is urinary incontinence, which refers to the involuntary leakage of urine. This condition can occur due to weakened pelvic floor muscles, nerve damage, or hormonal changes. Types of urinary incontinence include stress incontinence (leakage during physical exertion), urge incontinence (strong, sudden need to urinate), and overflow incontinence (inability to completely empty the bladder). Treatment options for urinary incontinence include pelvic floor exercises, medications, or surgical procedures.
Overall, these common urinary system disorders can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It is important to seek medical attention if experiencing any symptoms related to the urinary system to receive appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Key Components of the Urinary System
The urinary system is a complex network of organs and structures responsible for filtering and eliminating waste products from the body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s balance of fluids, electrolytes, and pH levels. This system consists of several key components, each performing specific functions to ensure proper urine production and excretion.
Kidneys
The kidneys are the main organs of the urinary system. They are bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the ribcage. The kidneys filter waste products, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood and produce urine. They also play a role in regulating blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and acid-base equilibrium.
Ureters
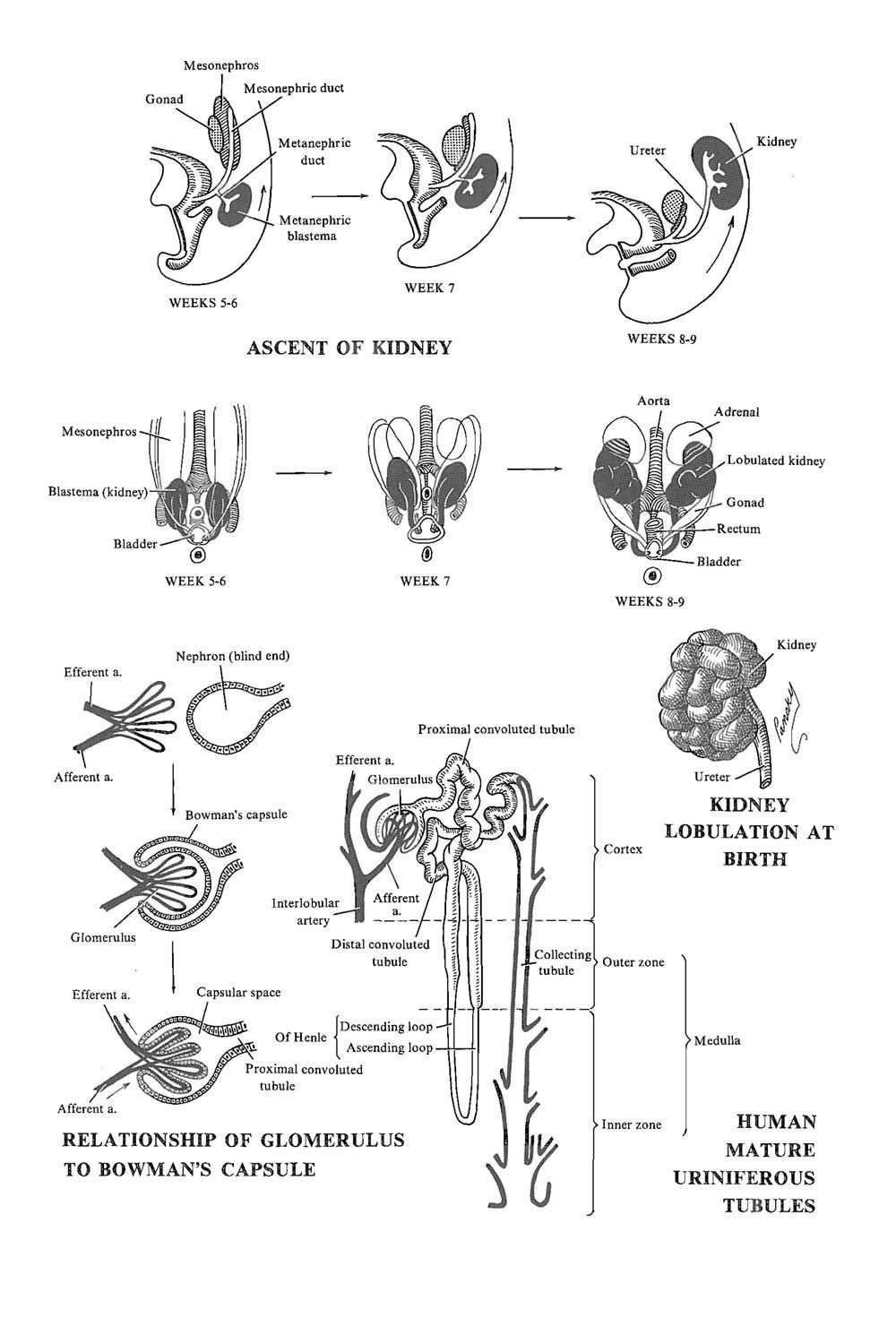
The ureters are long, narrow tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. They transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder through peristalsis, a rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles. The ureters ensure the one-way flow of urine and prevent its backflow into the kidneys.
Bladder
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ located in the pelvic area. It serves as a reservoir for urine storage until it is eliminated from the body. The bladder can expand and contract to accommodate varying amounts of urine. When it is full, the bladder sends signals to the brain, triggering the urge to urinate.
Urethra

The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males, it also serves as a passage for semen during ejaculation. The length of the urethra is shorter in females compared to males, making them more prone to urinary tract infections.
Sphincters
The urinary system also includes two sphincter muscles that control the flow of urine. The internal sphincter, located at the junction of the bladder and urethra, remains contracted to prevent urine leakage. The external sphincter, located just below the internal sphincter, is under voluntary control and can be relaxed to allow urine to pass.
Nerves and Blood Vessels
The urinary system is supplied with a network of blood vessels that deliver oxygen and nutrients to the organs. It is also innervated by a complex network of nerves that regulate urinary function. These nerves control the contraction of the bladder muscles and the relaxation of the sphincters, coordinating the process of micturition, or urination.
In conclusion, the urinary system comprises several key components, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, sphincters, nerves, and blood vessels. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining proper urine production, storage, and elimination, ensuring the body’s overall homeostasis.