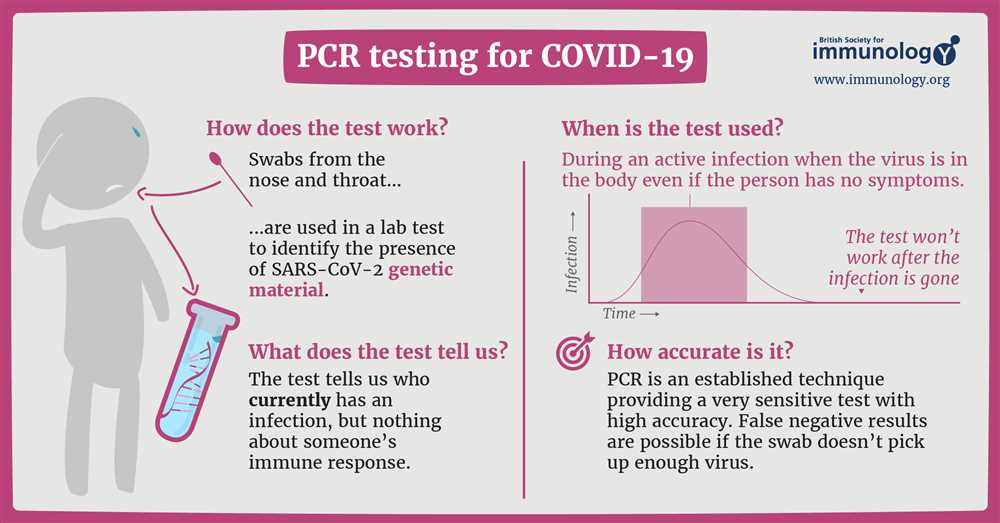
In this illustration, a medical test is being performed to diagnose a certain condition or disease. The test being shown in the image is important in determining the presence or absence of the condition, and can provide valuable information for healthcare professionals to develop a treatment plan.
During the test, a sample is taken from the patient, which could be blood, urine, tissue, or any other relevant material. This sample is then processed in a laboratory, where specialized equipment and techniques are used to analyze it. The results of the test can reveal important information about the patient’s health status and help guide medical interventions.
One of the primary purposes of this test is to detect any abnormalities or irregularities in the sample that may indicate the presence of a specific condition or disease. This could include identifying certain biomarkers or indicators that are associated with the condition being tested for. By interpreting these findings, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses and ensure appropriate treatment is delivered.
Test Purpose
The purpose of a test is to assess the performance, functionality, or quality of a system or product. It is an essential step in the development process as it helps identify any flaws, errors, or limitations that may exist. The results of a test can provide valuable insights and feedback, which can be used to improve the system or product.
Tests can be conducted for various reasons, depending on the specific context and requirements. One common purpose of testing is to ensure that a system or product meets the specified criteria and performs as expected. This could involve testing its functionality, reliability, compatibility, or security.
Another purpose of testing is to verify that changes or updates to a system or product have not introduced any new issues or vulnerabilities. This is often done through regression testing, where previously tested aspects are retested to ensure that they still function correctly after the changes.
In addition, testing can be used to measure the performance of a system or product under different conditions or loads. Performance testing helps identify any bottlenecks, performance issues, or scalability problems that may arise and provides insights into the system’s ability to handle expected workloads.
Overall, the purpose of testing is to validate and verify the system or product’s functionality, performance, and quality, ensuring that it meets the intended requirements and performs as expected in different scenarios.
Test setup
In order to perform the test illustrated in the image, a specific test setup is required. The setup consists of several components that are carefully arranged to ensure accurate measurements and reliable results.
Firstly, a test bench is prepared, which typically includes a sturdy table or platform where the test apparatus is placed. This provides a stable foundation for the test and reduces any vibrations or disturbances that could affect the measurements.
- Test apparatus: The specific apparatus being tested is carefully positioned on the test bench. This could be a mechanical device, electronic equipment, or any other type of object that requires testing.
- Sensors: Various sensors are attached to the test apparatus to measure different parameters or variables during the test. These sensors can include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, accelerometers, or any other type of sensor relevant to the test being performed.
- Data acquisition system: A data acquisition system is set up to collect and record the measurements from the sensors. This system typically includes hardware such as analog-to-digital converters and amplifiers, as well as software for data visualization and analysis.
- Power supply: Depending on the requirements of the test, a proper power supply is connected to the test apparatus to provide the necessary electrical energy. This could be a battery, a power generator, or a standard AC power outlet.
The test setup is carefully designed and arranged to ensure that the test is conducted under controlled conditions and that accurate measurements are obtained. This allows researchers or engineers to evaluate the performance, functionality, or characteristics of the test apparatus and make informed decisions based on the results.
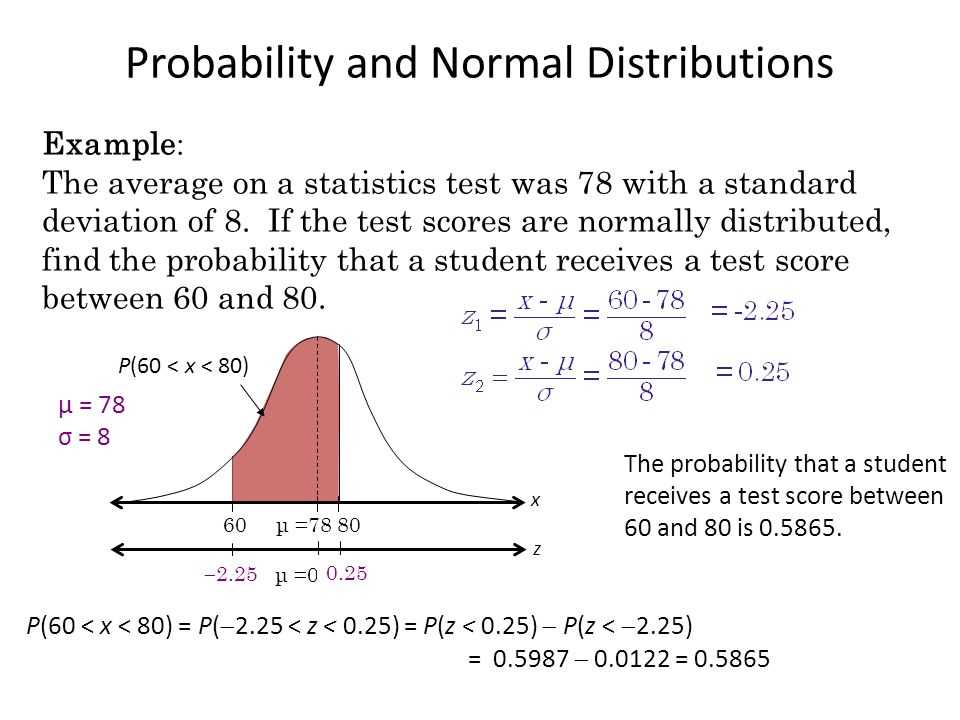
Test conditions
The test conditions in this illustration refer to the specific conditions under which the test is being performed. These conditions can include various factors such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and other environmental parameters that may affect the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
In order to ensure accurate and consistent test results, it is important to establish and maintain controlled test conditions. This may involve creating a controlled environment in a laboratory setting, where the test equipment and specimens can be kept at the desired conditions throughout the duration of the test.
- Temperature: Temperature control is often critical in many tests, as it can greatly influence the behavior and properties of the materials or systems being tested. Tests may be conducted at ambient temperature or at specific elevated or lowered temperatures, depending on the requirements of the test.
- Pressure: Some tests may involve subjecting the specimens to varying levels of pressure. Pressure chambers or other equipment may be used to simulate specific pressure conditions during the test.
- Humidity: For certain tests, controlling the humidity level is important. This is particularly relevant for tests involving materials or systems that may be affected by moisture or humidity.
Additionally, other factors such as lighting conditions, vibrations, electromagnetic interference, and time duration may also be critical test conditions depending on the specific test being performed. It is essential to carefully define and monitor these conditions to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
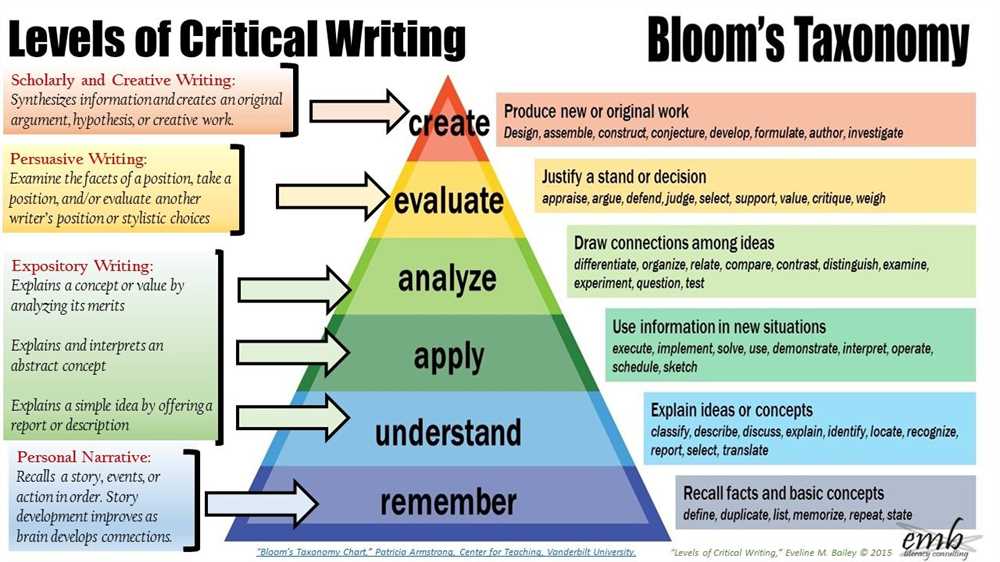
Testing procedure
When conducting tests, it is important to follow a systematic and structured procedure to ensure accurate results. The testing procedure typically involves several key steps, beginning with the identification of the test objective and the selection of appropriate testing methods. This is followed by the preparation of the testing environment and the collection of necessary equipment and materials.
Once the testing setup is complete, the next step is to perform the actual test. This may involve conducting various measurements, observations, or experiments, depending on the nature of the test. It is important to carefully follow the specified test procedure, recording all relevant data and observations accurately.
The collected data is then analyzed and interpreted to draw meaningful conclusions. This may involve statistical analysis, comparison of results with established standards or norms, or other relevant methods. The results are then documented in a clear and concise manner, often in the form of a test report or a presentation.
After the test is completed, it is important to conduct a thorough review and verification of the testing procedure and the results. This may involve checking for any deviations or errors, confirming the accuracy of the recorded data, and ensuring that the test objectives have been met. This review process helps to validate the reliability and validity of the test results.
In summary, a well-defined testing procedure is essential for conducting tests accurately and reliably. It helps to ensure consistency in the testing process, reduces the risk of errors or biases, and allows for meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. Following a standardized testing procedure is crucial in various fields, including scientific research, quality control, and product development.
Test results
After conducting the test, the results are obtained and analyzed. These test results provide valuable information regarding the specific test being performed. They help in assessing the performance, accuracy, and reliability of the test.
The test results are usually presented in a structured format, with key parameters and measurements highlighted. They may include numerical data, graphical representations, and descriptive summaries. These results are essential for drawing conclusions and making decisions based on the test outcomes.
When interpreting the test results, it is important to consider the reference ranges or normal values specific to the test being performed. These reference values help in determining whether the obtained results are within the expected range or if they indicate any abnormalities or deviations.
Test results play a crucial role in various fields, including scientific research, medical diagnostics, and product quality control. They provide objective evidence and support decisions related to treatment protocols, product specifications, or research outcomes.
In some cases, the test results may need to be cross-referenced with previous or subsequent tests to establish a trend or monitor changes over time. Comparing the results to baseline measurements can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions or the progression of a certain condition.
Overall, test results are significant in determining the outcome of the test and shaping further actions or recommendations. Whether it is a lab test, medical imaging, or any diagnostic procedure, the results serve as a valuable tool in assessing and understanding the subject being tested.