
Direct object pronouns are an essential part of understanding and using the English language. They replace the direct object in a sentence to make it shorter and more concise. In this worksheet answer key, we will go through various exercises and their corresponding answers to help you practice using direct object pronouns correctly.
These exercises will cover different scenarios, such as replacing the direct object with a pronoun in a sentence, choosing the correct pronoun based on the gender and number of the noun, and combining direct object pronouns with other parts of speech. By going through this worksheet answer key, you will enhance your understanding of direct object pronouns and improve your overall English language skills.
Using direct object pronouns correctly is crucial in order to communicate effectively in English. This worksheet answer key will provide you with the necessary tools and examples to master the usage of direct object pronouns. Whether you are a beginner or an intermediate English learner, these exercises will reinforce your knowledge and help you become more confident in using direct object pronouns correctly in your everyday conversations and writing.
Worksheet 2 Direct Object Pronouns Answer Key
In this answer key, you will find the correct answers for worksheet 2 on direct object pronouns. Direct object pronouns are used to replace the noun that receives the action of the verb in a sentence. They help to make sentences more concise and avoid repetition.
Below is the answer key for worksheet 2:
- Exercise 1
- 1. them
- 2. us
- 3. me
- 4. him
- 5. her
- Exercise 2
- 1. them
- 2. it
- 3. you
- 4. us
- 5. her
It is important to practice using direct object pronouns in order to become proficient in their usage. By replacing nouns with pronouns, sentences become more efficient and clear. Remember to always match the pronoun to the correct gender and number of the noun it replaces.
Direct object pronouns are typically placed before the conjugated verb in Spanish sentences. However, in negative sentences or commands, the pronoun is attached to the end of the verb. It is also possible to use double object pronouns in Spanish, where both the indirect and direct object pronouns are used in the same sentence.
Using direct object pronouns correctly will help you to communicate more effectively in Spanish and improve your overall fluency. Practice exercises like worksheet 2 will ensure that you gain confidence in using these pronouns correctly in different contexts.
What Are Direct Object Pronouns?
In the study of grammar, direct object pronouns play a crucial role. They are pronouns that replace and refer to the direct object of a verb in a sentence. The direct object is the noun or noun phrase that receives the action of the verb. Direct object pronouns serve to make sentences more concise and avoid repetition.
Direct object pronouns in English include words such as “me,” “you,” “him,” “her,” “it,” “us,” and “them.” These pronouns can be used to replace both people and things. For example, instead of saying “John is eating the pizza,” we can use the direct object pronoun “it” to say “John is eating it.” The pronoun “it” refers back to the pizza, which is the direct object of the verb “eating.”
Direct object pronouns can be placed before or after the verb in a sentence, depending on the sentence structure. When placed before the verb, they are attached to it with a hyphen. For example, “I saw him” can be written as “I him saw.” In Spanish and other Romance languages, direct object pronouns have different forms and placements, adding another layer of complexity to the topic.
It is important to learn and understand direct object pronouns in order to communicate effectively in both speaking and writing. By using them correctly, we can convey our ideas more efficiently and avoid repetitive language. Practicing with worksheets and exercises can help reinforce the understanding and usage of direct object pronouns.
How to Identify Direct Object Pronouns
Identifying direct object pronouns in a sentence can be a useful skill for understanding and analyzing language. Direct object pronouns are words that replace a noun or noun phrase that is the direct object of a verb. They provide a more concise and efficient way of expressing the object of an action.
To identify direct object pronouns in a sentence, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the verb: Start by identifying the verb in the sentence. The verb is the action word that expresses what the subject is doing.
- Ask “who” or “what”… Ask the question “who” or “what” after the verb to determine the direct object. The answer to this question will be the direct object.
- Look for pronouns: Look for pronouns that replace the direct object. Direct object pronouns include words like “him,” “her,” “it,” “them,” and “me.” These pronouns will be the direct object pronouns in the sentence.
- Check for agreement: Ensure that the direct object pronoun agrees in gender and number with the noun it replaces. For example, if the direct object is a masculine singular noun, the pronoun should be “him” or “it.” If the direct object is a feminine plural noun, the pronoun should be “them.”
By following these steps, you can easily identify direct object pronouns and understand how they function in a sentence. Practicing and recognizing direct object pronouns will enhance your language skills and enable you to communicate more effectively in English.
Using Direct Object Pronouns in Sentences
Direct object pronouns are used to replace a noun that is the direct object of a verb. They help simplify sentences and make them more concise. In Spanish, direct object pronouns come before the verb and agree in gender and number with the noun they are replacing.
For example, instead of saying “I see the book,” you can say “I see it” by using the direct object pronoun “it” to replace the noun “book”. Similarly, instead of saying “She buys the clothes,” you can say “She buys them” by using the direct object pronoun “them” to replace the noun “clothes”.
Here are some examples of how to use direct object pronouns in sentences:
- I eat the apple. I eat it.
- We read the newspaper. We read it.
- He likes the cake. He likes it.
- She cleans the house. She cleans it.
When the verb is in the past tense, the direct object pronoun is placed before the conjugated verb. For example, instead of saying “I saw Maria,” you can say “I saw her” by using the direct object pronoun “her” to replace the noun “Maria”.
Here are some examples of how to use direct object pronouns in sentences with the past tense:
- I saw Juan. I saw him.
- We bought the car. We bought it.
- He visited his grandparents. He visited them.
- She called her friend. She called her.
Using direct object pronouns can make your sentences more concise and efficient. By practicing with them, you can become more fluent in Spanish and improve your communication skills.
Worksheet 2: Practice Exercise
In this practice exercise, we will be working with direct object pronouns. Direct object pronouns are used to replace the noun that receives the action of the verb in a sentence. They help to make sentences more concise and avoid repetition. Let’s dive in!
Instructions:
- Read the sentences carefully.
- Identify the direct object in each sentence.
- Replace the direct object with the corresponding direct object pronoun.
- Write the new sentence using the direct object pronoun.
- Check your answers with the provided answer key.
Example:
Sentence: I saw Maria at the park yesterday.
Direct object: Maria
Direct object pronoun: her
New sentence: I saw her at the park yesterday.
Now it’s your turn to practice. Remember to carefully analyze each sentence and select the appropriate direct object pronoun. Have fun!
Answers to Worksheet 2: Practice Exercise
In this exercise, we will review the direct object pronouns in Spanish and their usage in sentences. Take a look at the worksheet:
Direct Object Pronouns:
| Person | Direct Object Pronoun | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | me | Me gusta el libro. (I like the book.) |
| 2nd person singular | te | Te veo mañana. (I’ll see you tomorrow.) |
| 3rd person singular | lo/la | Lo compré ayer. (I bought it yesterday.) |
| 1st person plural | nos | Nos gusta bailar. (We like to dance.) |
| 2nd person plural | os | Os ayudaré mañana. (I’ll help you all tomorrow.) |
| 3rd person plural | los/las | Los vi en el cine. (I saw them at the movies.) |
Now let’s go through the answers:
- 1. Me
- 2. Te
- 3. Lo
- 4. Nos
- 5. Os
- 6. Las
- 7. La
- 8. Lo
- 9. Te
- 10. Los
These are the correct answers for each sentence. Make sure to check your responses and understand the usage of direct object pronouns in each context. Keep practicing to improve your understanding!
Common Mistakes with Direct Object Pronouns
Direct object pronouns are a crucial part of the Spanish language, but they can also be a source of confusion and mistakes. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for when using direct object pronouns.
Forgetting to use the pronoun: One common mistake is forgetting to use the direct object pronoun altogether. Instead of saying “Lo tengo” (I have it), someone might say “Tengo” (I have) without specifying what they have. It’s important to remember to use the correct pronoun to clarify the object being referred to.
Using the wrong pronoun: Another mistake is using the wrong direct object pronoun. Spanish has different pronouns for masculine, feminine, singular, and plural objects. For example, saying “La quiero” (I want her) when referring to a masculine object would be incorrect. It’s important to use the appropriate pronoun that matches the gender and number of the object being referred to.
Placing the pronoun incorrectly: The placement of the direct object pronoun is also a common area of confusion. In Spanish, the pronoun usually comes before the verb. For example, instead of saying “Comí la manzana” (I ate the apple), someone might incorrectly say “Comí el la manzana”. It’s important to place the direct object pronoun correctly before the verb for proper syntax.
Confusing pronouns with names: Sometimes, people mistakenly use pronouns when referring to someone by their name. Instead of saying “Juan lo conozco” (I know him), someone might say “Juan Juan conozco”. It’s important to remember that when using a person’s name, the pronoun is not necessary.
Not agreeing with the noun: Lastly, it’s important to remember that direct object pronouns must agree in gender and number with the noun they are replacing. For example, saying “Las quiero” (I want them, referring to masculine objects) would be incorrect. It’s important to use the correct pronoun that agrees with the gender and number of the noun being replaced.
By being aware of these common mistakes with direct object pronouns, language learners can improve their understanding and usage of these important grammatical elements.
Tips for Mastering Direct Object Pronouns
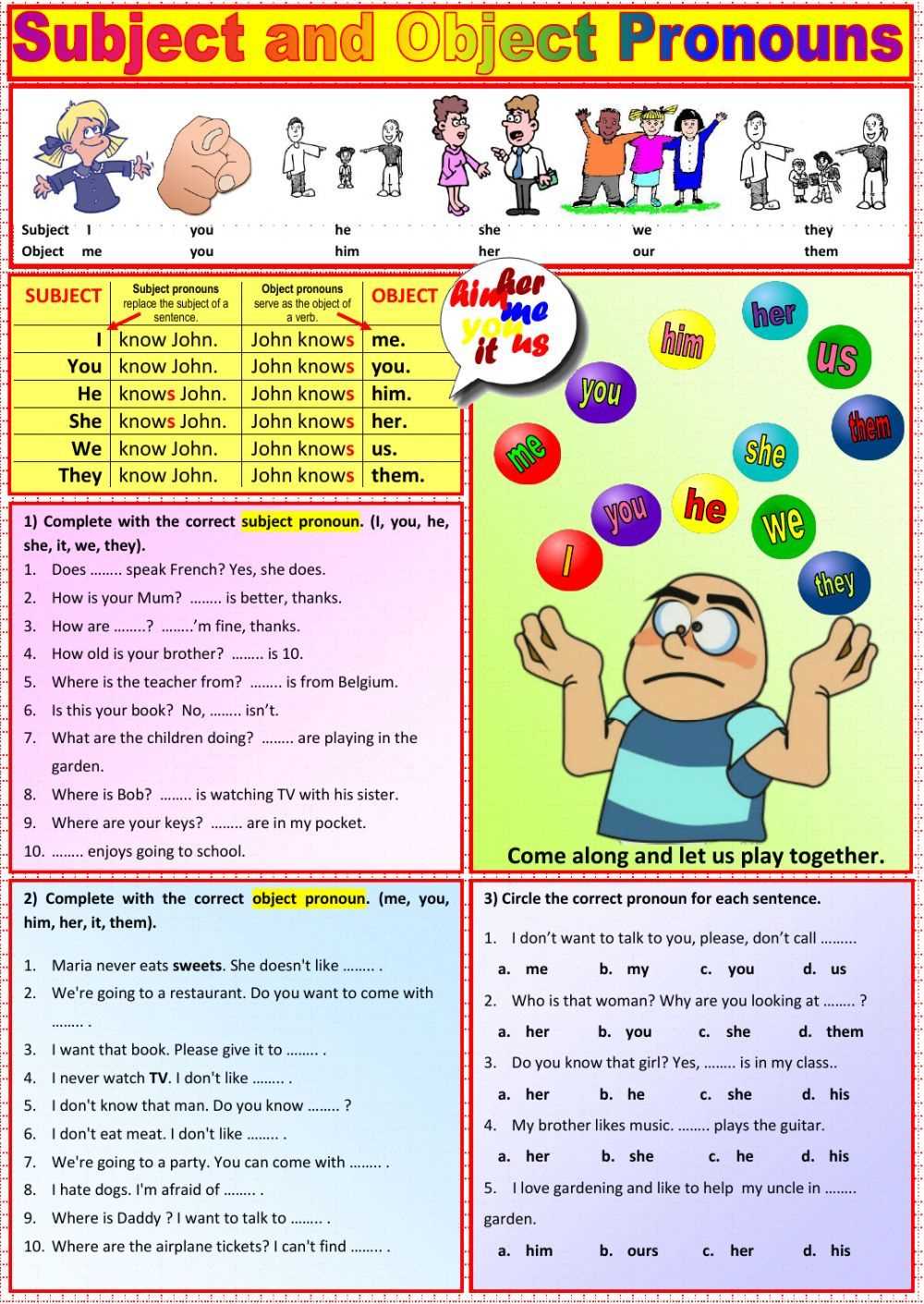
Learning how to use direct object pronouns correctly is a crucial step in becoming fluent in a foreign language. These pronouns replace direct objects in a sentence, making the sentence more concise and streamlined. To help you master direct object pronouns, here are some useful tips:
1. Understand the Role of Direct Object Pronouns
Direct object pronouns stand in for the noun that receives the action of the verb. They answer the question “What or whom?” in relation to the verb. For example, in the sentence “I bought a book,” the direct object is “a book.” By using the direct object pronoun “it,” the sentence becomes “I bought it.”
2. Memorize the Pronoun Chart
Direct object pronouns differ in form depending on the person and gender of the noun they replace. It is essential to memorize the chart of direct object pronouns to use them accurately. The chart includes pronouns like “me,” “you,” “him,” “her,” “it,” “us,” “you all,” and “them.”
3. Practice with Real-Life Examples
To become comfortable using direct object pronouns, practice with real-life examples. For instance, when describing your daily routine, substitute direct objects with their respective pronouns. Instead of saying “I drink coffee every morning,” say “I drink it every morning.”
4. Pay Attention to Word Order

In sentences with direct object pronouns, the pronoun typically comes before the verb. However, in negative sentences and commands, the pronoun usually comes before the negative word or the verb. For example, “I don’t want it” or “Give it to me.”
5. Seek Feedback and Correct Mistakes
As with any aspect of language learning, seeking feedback from native speakers or language instructors can be incredibly helpful. They can point out any mistakes you make when using direct object pronouns and provide suggestions for improvement.
By following these tips and practicing regularly, you will gradually become more confident and accurate in using direct object pronouns. Soon, you will find yourself seamlessly incorporating them into your conversations and written work.