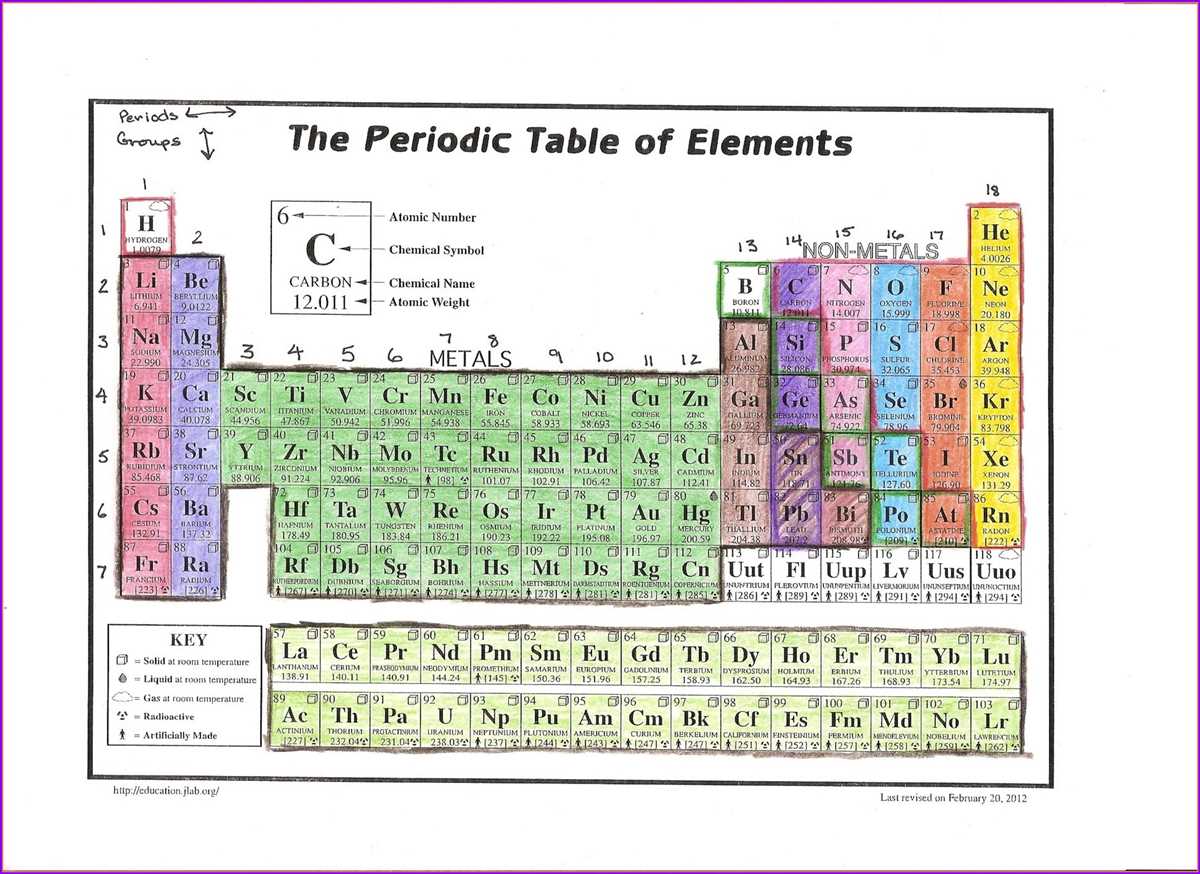
As we delve deeper into the study of chemistry, one of the fundamental concepts we encounter is the periodic table. The periodic table is a powerful tool used to organize and categorize the vast array of chemical elements. It provides us with essential information about each element, such as its atomic number, symbol, and atomic mass. Moreover, the periodic table also reveals patterns and trends in the properties and behaviors of elements.
In this article, we explore the “alien periodic table” and the periodic trends associated with it. The “alien periodic table” is a hypothetical concept that introduces a different set of elements with unique properties and behaviors entirely unfamiliar to us. This imaginative approach allows scientists to further understand and analyze the periodic trends that govern the behavior of elements in our own periodic table.
By studying the “alien periodic table,” scientists can discern patterns in various atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and electron affinity. These periodic trends help us understand the underlying principles that govern chemical reactions, bonding, and the behavior of different elements. Through comparing and contrasting these trends with our own periodic table, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental nature of atoms and how they interact with each other.
Alien Periodic Table Periodic Trends Answer Key
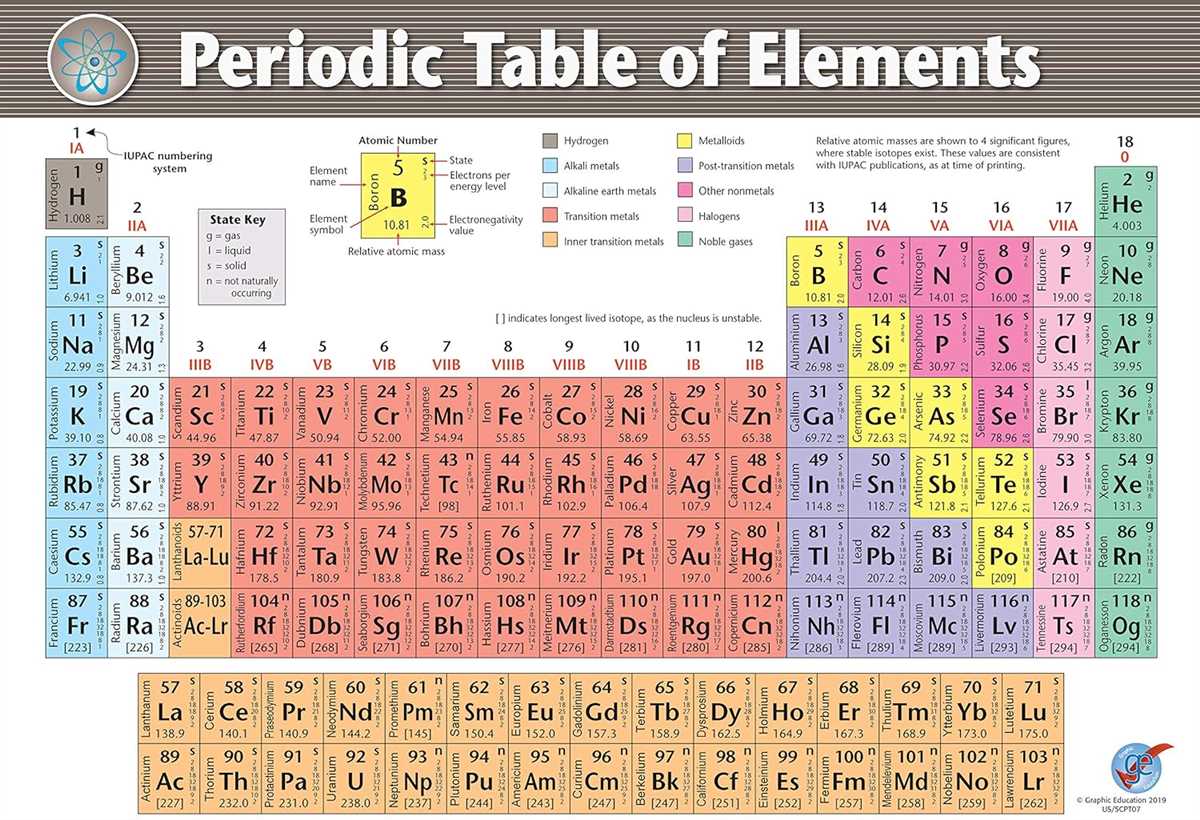
The Alien Periodic Table is a hypothetical chart of the elements as they would appear on an alien planet. This table allows us to explore the periodic trends of these alien elements, which can provide insights into the behavior and properties of unknown materials. By comparing the alien periodic table to our own periodic table, we can identify patterns and make predictions about how these alien elements might behave.
The answer key for the Alien Periodic Table periodic trends can be used to understand the relationships between various properties of the elements. It provides information on trends such as atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity. With this answer key, scientists can analyze and interpret the data from the Alien Periodic Table to make predictions about the properties of the alien elements.
One of the key trends that can be observed in the Alien Periodic Table is the trend in atomic radius. Atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron of an atom. In general, as you move across a period from left to right, the atomic radius decreases. This trend is due to the increasing positive charge in the nucleus, which attracts the electrons more strongly and pulls them closer to the nucleus. However, as you move down a group, the atomic radius increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases, leading to a larger atomic size.
Another important trend that can be observed is the trend in ionization energy. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. Generally, ionization energy increases as you move across a period from left to right. This is because the electrons are held more tightly by the increasing positive charge in the nucleus. However, ionization energy decreases as you move down a group. This is because the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus and are shielded by inner electron shells, making them easier to remove.
In conclusion, the Alien Periodic Table periodic trends answer key provides valuable information on the behavior and properties of the elements in the hypothetical alien world. By studying these trends, scientists can gain insights into the nature of unknown materials and make predictions about their properties.
Understanding Periodic Trends
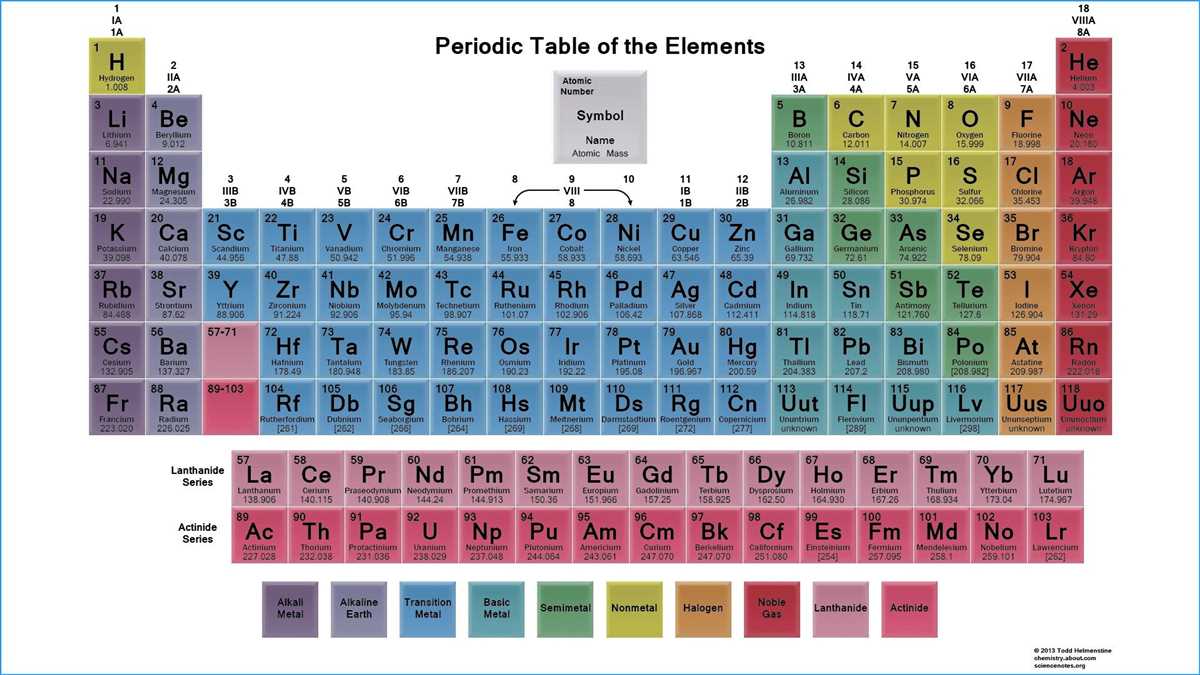
The periodic table is a powerful tool that allows us to organize and understand the properties of elements. By examining the periodic table, we can identify patterns and trends that enable us to make predictions about the behavior of different elements. These trends, known as periodic trends, provide valuable insight into the chemical reactivity, physical properties, and atomic structure of elements.
One of the most fundamental periodic trends is the periodicity of atomic size or atomic radius. As we move across a period from left to right, the atomic size tends to decrease. This is due to the increasing positive charge in the nucleus, which attracts the negatively charged electrons more strongly, causing the electron cloud to shrink. On the other hand, as we move down a group, the atomic size tends to increase. This is because the electrons occupy higher energy levels, resulting in a larger electron cloud.
Another important periodic trend is the periodicity of ionization energy. Ionization energy refers to the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. As we move across a period from left to right, the ionization energy generally increases. This is because the electrons are held more tightly by the increased nuclear charge, making it more difficult to remove an electron. Conversely, as we move down a group, the ionization energy tends to decrease. This is because the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus and experience less attraction, making them easier to remove.
In addition to atomic size and ionization energy, the periodic table also reveals trends in other properties such as electronegativity, electron affinity, and metallic character. These trends provide valuable information about an element’s ability to attract electrons, form compounds, and conduct electricity. By understanding and analyzing these periodic trends, scientists can gain deeper insights into the behavior of elements and use this knowledge to make informed decisions in various fields such as chemistry, materials science, and technology.
Explanation of the Key Elements in the Alien Periodic Table
The Alien Periodic Table is a unique representation of chemical elements that exist in an extraterrestrial world. These elements have different properties and characteristics compared to the elements found on Earth. In order to understand this alien periodic table, it is important to familiarize ourselves with the key elements and their roles in this alternate periodic table.
1. Xarconium (XZ): Xarconium is a highly reactive element that exhibits extraordinary conductivity. It is often used in advanced alien technology for its ability to store and transfer large amounts of energy. Xarconium plays a crucial role in powering the alien spacecraft and other high-tech devices.
2. Zalithium (Za): Zalithium is an extremely dense element that is used in the construction of alien buildings and structures. Its exceptional strength and durability make it a key material for the creation of long-lasting extraterrestrial infrastructure.
3. Cryen (Cr): Cryen is a unique element with exceptional cooling properties. It is used in alien refrigeration systems to maintain extremely low temperatures, making it essential for preserving alien food and other perishable items.
4. Plasmonite (Pn): Plasmonite is a versatile element that exhibits both solid and liquid properties. It is commonly used in the production of alien electronics and integrated circuits due to its ability to conduct electricity while maintaining shape flexibility.
Key Elements in the Alien Periodic Table:
- Gravite (Gv): Gravite is an element that possesses anti-gravitational properties. It is utilized in the construction of anti-gravity devices and vehicles.
- Nebulon (Nb): Nebulon is a gaseous element that can be found in the atmospheres of alien planets. It plays a vital role in the composition of alien atmospheres and affects temperature and climate conditions.
- Quantumium (Qt): Quantumium is an element with extraordinary quantum properties. It is used in the creation of alien quantum computers and teleportation devices.
- Biolumin (Bl): Biolumin is a luminescent element that emits light naturally. It is commonly found in alien organisms and is responsible for their unique glowing effects.
These are just a few examples of the key elements in the Alien Periodic Table. Each element has its own distinct properties and applications within the extraterrestrial world. Exploring this alien periodic table allows us to expand our understanding of chemistry beyond the familiar elements found on Earth.
Periodic Trends in Atomic Radius
The atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, which can be determined by measuring the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell. The periodic table provides a visual representation of the atomic radius trends across elements. By examining these trends, scientists can gain insight into the behavior and properties of different elements.
One key trend in atomic radius is the variation across periods. As you move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases. This is due to the increasing number of protons in the nucleus, which results in a stronger attractive force on the electrons. As a result, the electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus, leading to a smaller atomic radius.
Another trend can be observed when moving down a group. In general, as you move down a group, the atomic radius increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases, resulting in a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell. The addition of more electron shells weakens the attractive force of the nucleus, allowing the electrons to occupy larger orbits and leading to a larger atomic radius.
It is important to note that there are some exceptions to these trends due to the influence of other factors, such as the presence of transition metals and the effects of electron configuration. However, the overall trends in atomic radius provide valuable information for understanding the properties and behavior of elements in the periodic table.
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy
The ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or a positive ion. It is an important property that can help us understand the reactivity and chemical behavior of elements. In the periodic table, the ionization energy generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
One of the main factors that affect the ionization energy is the distance between the outermost electron and the nucleus. As you move across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, resulting in a stronger positive charge that attracts the electrons more strongly. This increased attraction makes it more difficult to remove an electron, leading to higher ionization energy.
Another factor that influences ionization energy is the shielding effect. As you move down a group, the number of energy levels or shells increases, which creates more shielding or screening between the outermost electrons and the nucleus. This shielding effect reduces the attraction between the outermost electron and the nucleus, making it easier to remove an electron and resulting in lower ionization energy.
The periodic trends in ionization energy can also be explained by the concept of electron configurations. The noble gases, which have completely filled electron shells, have the highest ionization energies because their electrons are strongly held and less likely to be removed. On the other hand, the alkali metals, which have a single electron in their outermost shell, have the lowest ionization energies because their electrons are loosely held and more likely to be removed.
In summary, the ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group in the periodic table. This trend can be attributed to the increasing nuclear charge and the shielding effect. Understanding these trends can provide valuable insights into the chemical behavior and reactivity of elements.
Periodic Trends in Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It is an important concept in understanding the properties and behavior of elements. In this article, we have explored the periodic trends in electronegativity using the Alien Periodic Table. Let’s summarize the key findings:
- Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table. This means that elements on the right side of the table are more electronegative than elements on the left side.
- Electronegativity tends to decrease from top to bottom within a group. This means that elements at the top of a group are more electronegative than elements at the bottom of the group.
- Electronegativity is influenced by factors such as atomic size, nuclear charge, and electron shielding. As atomic size increases, electronegativity generally decreases. As nuclear charge increases, electronegativity generally increases. Electron shielding also affects electronegativity, with more shielding leading to lower electronegativity.
- In the Alien Periodic Table, electronegativity values are represented by color. The color gradient provides a visual representation of the trends in electronegativity across the table.
Overall, the periodic trends in electronegativity can be seen as a reflection of the atomic structure and characteristics of the elements. The knowledge of these trends can help in predicting the behavior of elements in chemical reactions and understanding the properties of compounds.