
Money laundering is a serious crime that has far-reaching consequences for economies and individuals alike. To combat this illegal activity, financial institutions employ various measures, one of which is the implementation of anti-money laundering (AML) policies and procedures. AML programs are designed to detect and prevent money laundering by identifying suspicious transactions and reporting them to the relevant authorities.
One organization that provides comprehensive training on AML is the European Financial Intelligence Unit (EU FIU). They have created a computer-based learning (CBL) program that aims to educate individuals working in the financial sector on the best practices to combat money laundering. This program covers topics such as the legal and regulatory framework surrounding AML, the role of financial institutions in detecting and reporting suspicious transactions, and the consequences of non-compliance.
Through the EU FIU’s CBL program, participants can gain a deeper understanding of the techniques used by money launderers, such as layering and integration, and learn how to recognize and report red flags. The program also emphasizes the importance of customer due diligence and know-your-customer procedures, as these play a crucial role in preventing money laundering activities.
What is Anti Money Laundering (AML)?
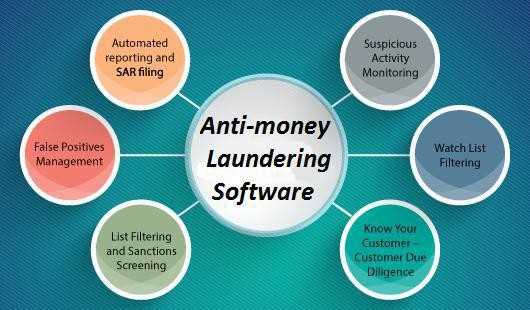
Anti Money Laundering (AML) refers to a set of laws, regulations, and procedures that are designed to prevent the illegal process of making illicitly obtained funds appear legitimate. Money laundering is the process of converting the proceeds of criminal activity into seemingly legitimate funds, so that they can be used freely without raising suspicion.
AML regulations are implemented by governments and financial institutions to combat money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities. These regulations require entities such as banks, financial institutions, and other businesses to identify and verify the identity of their customers, monitor their transactions for suspicious activity, and report any suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities.
AML measures involve several steps, such as customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, reporting of suspicious transactions, and ongoing training and awareness programs for employees. Financial institutions are required to establish robust systems and controls to detect and prevent money laundering and comply with AML regulations.
Failure to comply with AML regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and reputational damage for businesses. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to have comprehensive AML programs in place to ensure compliance and protect themselves from the risks associated with money laundering and other illicit activities.
History and Definition of AML

Money laundering has been a problem for centuries, as individuals and criminal organizations seek to disguise the origins of illicit funds. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts have been developed and refined in response to this ongoing challenge.
Definition: Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to a set of laws, regulations, and processes implemented by governments and financial institutions to detect and prevent the laundering of illicitly obtained funds. The primary goal of AML measures is to disrupt the flow of criminal proceeds and protect the integrity of the financial system.
AML’s roots can be traced back to the early 20th century, when governments began enacting legislation specifically aimed at combating money laundering. In the United States, for example, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) was passed in 1970 and mandated financial institutions to report certain transactions and maintain records to assist in the detection of money laundering activities.
As criminal methods evolved and became more sophisticated, so did the AML framework. International efforts to combat money laundering gained momentum in the late 1980s, with the establishment of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) by the G7 countries. The FATF developed a set of recommendations that served as the basis for AML measures globally.
The FATF recommendations cover a broad range of issues related to AML, including customer due diligence, record keeping, reporting suspicious transactions, and the implementation of comprehensive AML programs by financial institutions. These recommendations have been widely adopted and provide a common framework for AML efforts across different jurisdictions.
Over time, the scope of AML efforts has expanded beyond traditional financial institutions to include sectors such as real estate, casinos, and virtual currencies. AML regulations now place greater emphasis on risk-based approaches, the use of technology and data analysis, and international cooperation.
Key Takeaways:
- AML refers to laws, regulations, and processes aimed at detecting and preventing money laundering.
- The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) in the US was an early example of legislation targeting money laundering.
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) developed recommendations that form the basis for AML efforts globally.
- AML efforts have expanded to cover various sectors and now emphasize risk-based approaches and international cooperation.
The Importance of AML Regulations
In today’s global economy, money laundering has become an increasingly prevalent issue. Criminal organizations and individuals use various techniques to conceal the origins of illicit funds, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to trace and prosecute these activities. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations play a crucial role in combating money laundering and protecting the integrity of the financial system.
Preventing Criminal Activities:
AML regulations are designed to prevent criminals from using the financial system to launder money obtained from illegal activities such as drug trafficking, human trafficking, corruption, and terrorism. By implementing stringent AML measures, financial institutions are required to establish due diligence procedures to verify the identity of their customers, monitor transactions for suspicious activities, and report any suspicious transactions to the appropriate authorities. These regulations act as a deterrent to money launderers and assist in the identification and investigation of potential criminal activities.
Preserving Financial Stability:
Money laundering poses a significant threat to the stability and integrity of the financial system. When illicit funds are introduced into the financial system, it can lead to distortions in market prices, increase the risk of financial crime, and undermine the public’s trust in the system. AML regulations help maintain the stability of financial institutions by minimizing the risk of money laundering and ensuring that only legitimate funds are transacted within the system. By promoting transparency, accountability, and trust, AML regulations contribute to a well-functioning financial system.
International Cooperation:
Money laundering is a global issue that transcends borders. AML regulations facilitate international cooperation between countries to combat money laundering effectively. Through the sharing of financial intelligence, collaboration in investigations, and the establishment of common standards, countries can work together to detect and prevent money laundering activities. AML regulations provide a framework for cooperation and coordination among various jurisdictions, creating a united front against money laundering.
Protecting Society:
Money laundering enables criminals to profit from their illegal activities and perpetuates further criminal behavior. AML regulations aim to protect society by preventing criminals from enjoying the proceeds of their illicit activities. These regulations also help reduce the funding of terrorist organizations and other criminal networks, contributing to global security. By implementing effective AML measures, governments and financial institutions can work together to safeguard society from the harmful effects of money laundering.
In conclusion, AML regulations are of utmost importance in the fight against money laundering. They serve as a crucial tool in preventing criminal activities, preserving financial stability, promoting international cooperation, and protecting society. By adhering to these regulations, financial institutions can contribute to a safer and more secure global financial system.
Common Types of Money Laundering Techniques
Money laundering is a criminal activity that involves disguising the origins of illegally obtained funds to make them appear legitimate. There are various techniques that money launderers use to achieve this goal and obscure the illegal nature of their funds. Understanding these common types of money laundering techniques is crucial for detecting and preventing such activities.
1. Structuring
Structuring, also known as smurfing, involves breaking down large amounts of money into smaller deposits that are below the reporting threshold. By making multiple small deposits, money launderers try to avoid arousing suspicion from authorities. These deposits are often made in different bank accounts and in various locations to further complicate the tracing of funds.
2. Shell Companies
Shell companies are businesses that exist only on paper and have no real operations. Money launderers create shell companies to create the appearance of legitimate business transactions. They use these companies to move funds between different accounts, making it difficult for authorities to trace the source of the funds. Shell companies can also be used to purchase assets, such as real estate or luxury items, further legitimizing the money.
3. Trade-Based Laundering
Trade-based money laundering involves manipulating international trade transactions to move funds across borders. Money launderers may overstate or understate the value of goods being traded, misrepresent the quantity of goods, or use false invoices and documentation. This technique allows them to move funds without raising suspicion, as international trade transactions are often complex and involve multiple parties.
4. Online Payment Systems
The advent of modern technology has also given rise to new money laundering techniques. Online payment systems, such as digital currencies and prepaid cards, can be used to launder money. These platforms provide anonymity and allow quick and easy transfers of funds. Money launderers can exploit these systems to move funds across borders and convert them into different currencies, making it difficult to trace the source and destination of the funds.
5. Offshore Accounts
Offshore accounts are often used by money launderers to hide and protect their illicit funds. By depositing funds in offshore jurisdictions with strict bank secrecy laws, money launderers can avoid detection and scrutiny from authorities. Offshore accounts also provide opportunities for further layering and integration of the illicit funds into the global financial system.
These are just a few examples of the common types of money laundering techniques employed by criminals. It is essential for financial institutions, law enforcement agencies, and regulators to remain vigilant and stay updated on the ever-evolving methods used by money launderers to prevent and combat this illegal activity.
Anti Money Laundering Compliance and Best Practices
Anti Money Laundering (AML) compliance is a critical aspect of the financial industry, helping to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. Implementing best practices in AML compliance is essential for financial institutions to protect themselves and their customers from potential risks and comply with regulatory requirements.
In order to effectively address AML compliance, financial institutions should have robust AML policies and procedures in place. These should include customer due diligence measures, transaction monitoring systems, and procedures for reporting suspicious activities. Regular audits and risk assessments should also be conducted to ensure the effectiveness of the AML program.
Customer due diligence (CDD) is a key component of AML compliance. This involves conducting thorough background checks on customers to verify their identity and assess the potential risks associated with their transactions. Financial institutions should have clear guidelines in place for conducting CDD, such as verifying customer information through reliable sources and conducting ongoing monitoring of customer accounts.
Transaction monitoring is another crucial aspect of AML compliance. Financial institutions should have robust systems in place to monitor transactions and detect any suspicious activities that may indicate money laundering or terrorist financing. Real-time monitoring, pattern recognition, and data analytics can all be utilized to effectively identify suspicious transactions and flag them for further investigation.
Reporting suspicious activities is an important obligation for financial institutions. They should have systems in place that enable employees to report any suspicious activities they observe. This creates an environment where employees are encouraged to be vigilant and proactive in detecting and reporting potential money laundering or terrorist financing activities.
Overall, implementing best practices in AML compliance is essential for financial institutions to mitigate risks and protect themselves and their customers. By having robust policies and procedures, conducting thorough customer due diligence, implementing effective transaction monitoring systems, and facilitating employee reporting, financial institutions can establish a strong AML compliance program.
Certified Blockchain Lawyer (CBL) Answers to AML Questions:
The field of anti-money laundering (AML) regulations is constantly evolving, particularly in the context of digital assets and blockchain technology. As the use of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance platforms continues to grow, it is crucial for lawyers to stay updated on the latest AML requirements.
Summary of Certified Blockchain Lawyer (CBL) Answers:
1. The role of a Certified Blockchain Lawyer (CBL) is to provide legal guidance and expertise in the field of blockchain technology, particularly in relation to AML regulations. CBLs have a deep understanding of the AML landscape and can help clients navigate the complexities of compliance.
2. CBLs advise clients on the necessary AML procedures and protocols to implement when dealing with cryptocurrencies and other blockchain-based assets. They assist in developing and enforcing AML policies to mitigate the risk of money laundering or illicit activities.
3. CBLs are knowledgeable about the various AML regulations and guidelines issued by regulatory bodies and organizations, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). They stay updated on any changes or updates to AML regulations to ensure compliance.
4. CBLs assist clients in conducting due diligence on their customers and counterparties. This includes verifying customer identities, ensuring the source of funds is legitimate, and assessing the risk level associated with each transaction.
5. CBLs provide guidance on implementing Know Your Customer (KYC) and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) processes to prevent money laundering. They help clients establish robust procedures for verifying customer identities and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
6. CBLs collaborate with other professionals, such as compliance officers and technology experts, to develop comprehensive AML strategies. They work closely with their clients’ teams to ensure that AML measures are integrated into their blockchain-based operations.
7. CBLs educate their clients on the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with blockchain technology and digital assets. They help clients understand the importance of AML compliance and the potential legal consequences of non-compliance.
8. CBLs assist clients with reporting suspicious transactions or activities to the relevant authorities. They ensure that their clients follow the appropriate reporting procedures and maintain necessary records to demonstrate compliance.
Overall, Certified Blockchain Lawyers (CBLs) play a crucial role in helping businesses and individuals navigate the complex landscape of AML regulations in the context of blockchain technology. Their expertise is essential in ensuring compliance and mitigating the risk of money laundering and illicit activities.