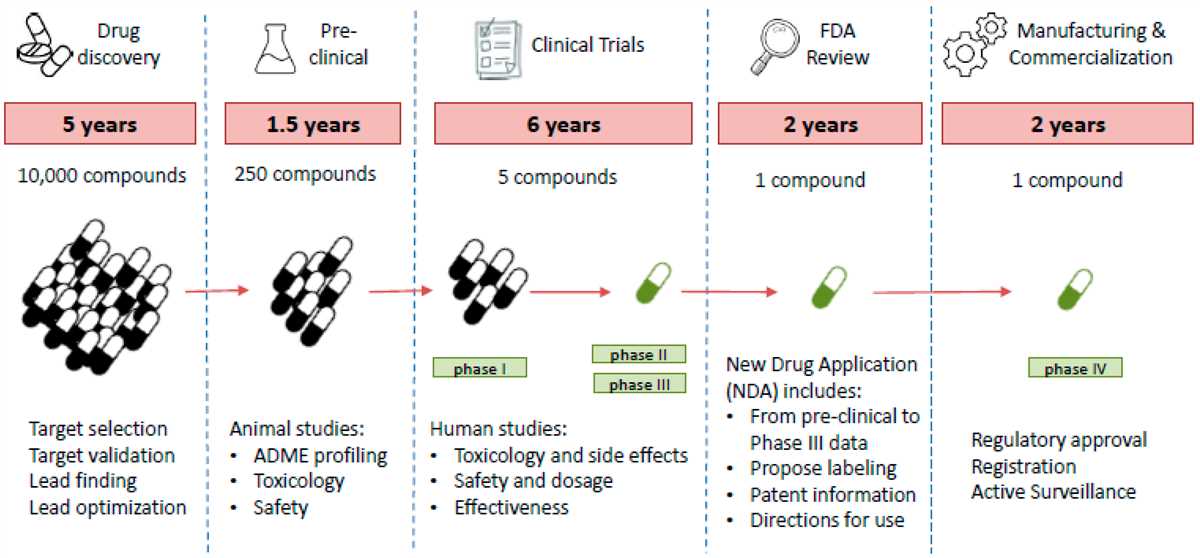
Antibiotics have been hailed as a miracle of modern medicine, saving countless lives and providing relief from bacterial infections. However, their effectiveness is becoming increasingly threatened by the rise of antibiotic resistance. This phenomenon occurs when bacteria evolve and develop ways to survive the drugs designed to kill them.
In recent years, antibiotic resistance has become a pressing global health concern. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics, both in human and animal populations, have contributed to the proliferation of resistant strains of bacteria. The misuse of antibiotics in agriculture, particularly in livestock production, is a significant driver of resistance, as it allows for the transfer of resistant bacteria from animals to humans through the food chain.
The consequences of antibiotic resistance are far-reaching. It leads to longer and more severe illnesses, increased healthcare costs, and a higher mortality rate. Common infections that were once easily treatable, such as urinary tract infections and pneumonia, are now becoming difficult to eradicate. If left unchecked, antibiotic resistance could render our current arsenal of antibiotics ineffective, leaving us vulnerable to infections that were previously easily manageable.
Antibiotic Resistance Can We Ever Win Worksheet Answers
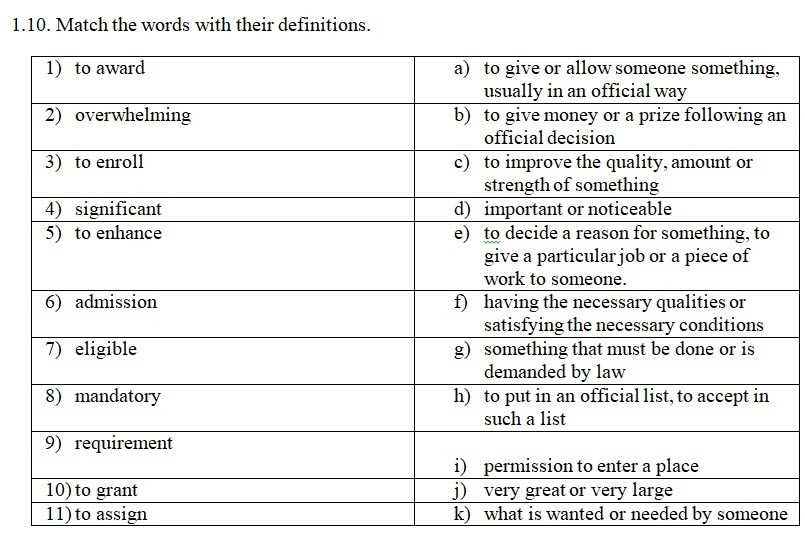
The issue of antibiotic resistance has become a growing concern in recent years. With the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, many bacteria have developed resistance to these drugs, making it harder to treat infections. This worksheet provides answers to questions regarding the challenges and possible solutions to antibiotic resistance.
1. Why is antibiotic resistance a problem?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt and develop mechanisms to survive and multiply in the presence of antibiotics. This makes infections caused by these resistant bacteria more difficult to treat, leading to longer hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and, in some cases, death. It poses a major threat to public health and modern medicine.
2. How does antibiotic resistance develop?
Antibiotic resistance can develop in multiple ways. One of the main factors is the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in both human and animal settings. When antibiotics are used unnecessarily or incorrectly, bacteria have more opportunities to be exposed to these drugs and develop resistance. Additionally, the natural ability of bacteria to mutate and exchange genetic material contributes to the development and spread of resistance.
3. Can we ever win the battle against antibiotic resistance?
While antibiotic resistance is a complex and challenging problem, it is not insurmountable. Efforts are being made to improve antibiotic stewardship, educate healthcare professionals and the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics, and develop alternative treatment strategies. Additionally, research into new antibiotics and novel approaches, such as phage therapy and CRISPR-Cas technology, offer potential solutions. However, addressing antibiotic resistance requires global collaboration, strict regulations, and changes in behavior and practices at all levels.
4. What can individuals do to help address antibiotic resistance?
Individuals can play a role in combating antibiotic resistance by following proper antibiotic use guidelines. This includes only taking antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional, completing the full course of treatment as instructed, and not sharing or saving antibiotics for future use. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent the spread of infections and reduce the need for antibiotics.
In conclusion, antibiotic resistance is a significant challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. By addressing the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, promoting research and development of new treatments, and improving global cooperation, we can strive towards winning the battle against antibiotic resistance and safeguard the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations.
The Importance of Understanding Antibiotic Resistance
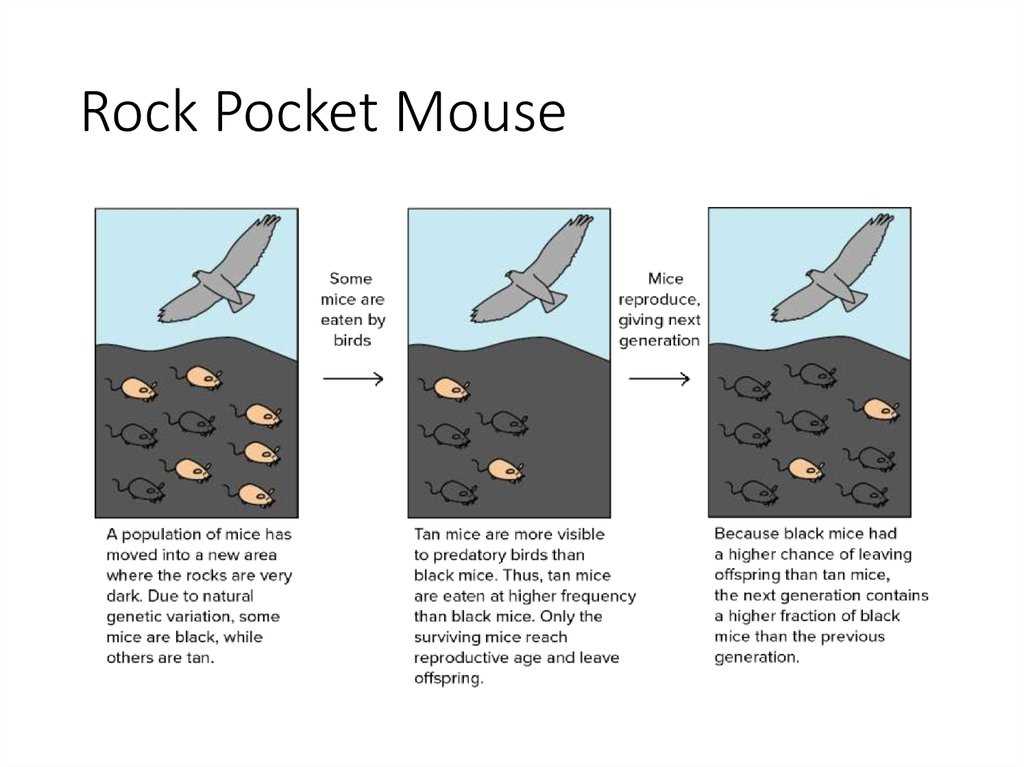
In recent years, the issue of antibiotic resistance has become a growing concern in the medical community and society as a whole. Antibiotics have long been considered a miracle drug, able to cure bacterial infections and save countless lives. However, the misuse and overuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a serious threat to public health.
The key to tackling antibiotic resistance lies in understanding its mechanisms and implications. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve and develop ways to withstand the effects of antibiotics, rendering the drugs ineffective in killing them. This resistance can occur naturally through genetic mutations or be acquired through horizontal gene transfer. Without a deep understanding of these processes, it is challenging to develop effective strategies to combat antibiotic resistance.
To address the problem, researchers and healthcare professionals need to stay updated on the latest scientific findings and treatment guidelines. Education and awareness programs should be implemented to educate the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics and the consequences of misuse. Additionally, healthcare professionals need to be trained in antibiotic stewardship, which involves prescribing antibiotics responsibly and using them only when necessary.
Understanding antibiotic resistance is also crucial for the development of new antibiotics. The discovery and development of new antibiotics have slowed down in recent decades, and the emergence of antibiotic resistance has further complicated the process. However, a deep understanding of resistance mechanisms can inform the design of new antibiotics that target specific bacterial vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, understanding antibiotic resistance is essential for addressing this global health threat. It allows for the development of effective prevention and treatment strategies, as well as the discovery of new antibiotics. By investing in research and education, we can hope to overcome this challenge and preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations.
Factors Contributing to Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve and develop mechanisms to resist the effects of antibiotics, rendering them ineffective in treating bacterial infections. There are several factors that contribute to the development and spread of antibiotic resistance.
Overuse and misuse of antibiotics: One of the primary factors contributing to antibiotic resistance is the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. This includes inappropriate prescribing of antibiotics, failure to complete the full course of antibiotics, and using antibiotics in livestock feed. The widespread use of antibiotics has led to the selective pressure on bacteria, promoting the development of resistant strains.
Poor infection control: Inadequate infection control practices in healthcare settings contribute to the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Failure to effectively clean and disinfect medical equipment, improper hand hygiene, and improper waste management can all contribute to the transmission of resistant bacteria between patients.
Lack of new antibiotics: The development of new antibiotics has slowed down significantly in recent years, leading to a limited arsenal of effective antibiotics. This lack of new drugs makes it challenging to treat infections caused by resistant bacteria and increases the likelihood of antibiotic resistance.
Global travel and trade: The ease of global travel and trade has facilitated the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria worldwide. Resistant strains can spread rapidly across countries, making it difficult to control their dissemination and manage outbreaks.
Poor hygiene and sanitation: In communities with poor hygiene and sanitation practices, the risk of bacterial infections is higher. These conditions create an environment favorable for the transmission and proliferation of resistant strains.
Overall, addressing antibiotic resistance requires a multifaceted approach. It involves implementing strict antibiotic stewardship programs, promoting infection control practices, investing in research and development of new antibiotics, and improving global surveillance systems to track the emergence and spread of resistant bacteria.
How Antibiotics Work and How Bacteria Become Resistant

Antibiotics work by either killing bacteria or stopping their growth. They do this by targeting specific components in bacteria that are essential for their survival and reproduction. For example, some antibiotics disrupt the cell wall of bacteria, causing them to burst and die. Others interfere with the bacteria’s ability to make proteins or replicate their DNA.
However, bacteria have the ability to develop resistance to antibiotics over time. This happens through various mechanisms, including mutation and the transfer of resistance genes between bacteria. When exposed to antibiotics, some bacteria may naturally possess genetic variations that make them less susceptible to the drug’s effects. These bacteria have a survival advantage and can multiply, leading to the emergence of resistant strains.
The development of antibiotic resistance is a serious concern for public health. It reduces the effectiveness of antibiotics, making it harder to treat bacterial infections. This can result in prolonged illness, increased healthcare costs, and even death. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics in both humans and animals contribute to the problem. When antibiotics are used unnecessarily or not taken as prescribed, it provides opportunities for bacteria to develop resistance.
In order to combat antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to promote responsible antibiotic use. This includes educating healthcare professionals and the public about the appropriate use of antibiotics, as well as implementing strategies to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria. Additionally, continued research and development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments are needed to stay ahead of bacterial resistance.
How Antibiotics Work and How Bacteria Become Resistant (Summary):
- Antibiotics target specific components in bacteria to kill them or stop their growth.
- Bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics through mutation and the transfer of resistance genes.
- The development of antibiotic resistance is a serious public health concern.
- Responsible antibiotic use and strategies to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria are crucial in combating antibiotic resistance.
Methods to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern in the field of medicine, as bacteria continue to evolve and develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics. In order to combat this issue, various methods and strategies have been proposed and implemented.
1. Antibiotic Stewardship Programs: One effective approach is the implementation of antibiotic stewardship programs, which aim to optimize the use of antibiotics. These programs involve strict guidelines and protocols for prescribing antibiotics, ensuring that they are used only when necessary and in the appropriate dosage and duration. By reducing unnecessary antibiotic use, antibiotic stewardship programs help slow the development of antibiotic resistance.
2. Development of New Antibiotics: Another crucial aspect in combating antibiotic resistance is the continuous development of new antibiotics. Researchers are constantly working on discovering and creating new antibiotics that can effectively target and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This involves extensive laboratory testing and clinical trials to ensure the safety and efficacy of these new drugs. The discovery of novel antibiotics can provide alternative treatment options for infections caused by resistant bacteria.
3. Alternative Therapies: In addition to developing new antibiotics, researchers have also explored alternative therapies to combat antibiotic resistance. These include the use of bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect and kill bacteria. Bacteriophage therapy has shown promise in treating infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Other alternative therapies such as antimicrobial peptides and immune-boosting approaches are also being investigated.
4. Public Education and Awareness: Increasing public education and awareness about antibiotic resistance is crucial in combating this issue. Many people still misuse antibiotics or fail to complete the full course of treatment, which can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. Educating the public about the proper use of antibiotics, the consequences of antibiotic resistance, and the importance of completing the full course of treatment can help prevent the spread of resistant bacteria.
5. Enhanced Infection Prevention and Control: An important strategy to combat antibiotic resistance is to prevent infections in the first place. This involves implementing and enforcing strict infection prevention and control measures in healthcare facilities and community settings. By effectively controlling the spread of infections, the need for antibiotics can be reduced, thereby minimizing the development of antibiotic resistance.
In conclusion, combating antibiotic resistance requires a multi-faceted approach involving antibiotic stewardship programs, the development of new antibiotics, exploring alternative therapies, increasing public education and awareness, as well as enhancing infection prevention and control measures. It is crucial for healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and the public to work together in order to address this global health threat.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance in the Future
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem that has the potential to impact the lives of millions of people worldwide. However, by implementing certain measures and strategies, we can work towards preventing antibiotic resistance in the future.
1. Promote responsible antibiotic use:
One of the key steps in preventing antibiotic resistance is promoting responsible antibiotic use. This includes educating healthcare professionals and the general public about the appropriate use of antibiotics, emphasizing the importance of completing the full course of antibiotics, and discouraging the unnecessary use of antibiotics for viral infections.
2. Develop new antibiotics:
Another important strategy is investing in the development of new antibiotics. With the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, there is a pressing need for the discovery and development of new antibiotics that can effectively treat these infections. Increased funding and research in this area are crucial to tackle antibiotic resistance.
3. Enhance surveillance and monitoring:
Surveillance and monitoring play a vital role in preventing antibiotic resistance. By closely monitoring antibiotic use, resistance patterns, and the prevalence of resistant bacteria, healthcare professionals can identify trends and take necessary actions to curb the spread of resistance.
4. Implement infection prevention and control measures:
Infection prevention and control measures are essential in reducing the transmission of resistant bacteria. Improved hygiene practices, such as handwashing, proper sterilization of medical equipment, and strict adherence to infection control protocols, can help prevent the spread of infections and the development of antibiotic resistance.
5. Promote research and development of alternative therapies:
In addition to developing new antibiotics, it is also important to promote research and development of alternative therapies. This includes exploring and investing in alternative treatment options such as phage therapy, probiotics, and immunotherapies. Diversifying treatment options can help reduce reliance on antibiotics and minimize the development of resistance.
In conclusion, preventing antibiotic resistance in the future requires a multi-faceted approach. By promoting responsible antibiotic use, developing new antibiotics, enhancing surveillance and monitoring, implementing infection prevention and control measures, and promoting research into alternative therapies, we can work towards overcoming this global health challenge and ensuring the continued efficacy of antibiotics.