The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a widely used standardized assessment tool designed to evaluate the speech sound production skills of children and adults. Developed by Wayne Secord and his colleagues at the University of Arizona, the AAT has become a crucial instrument for speech-language pathologists (SLPs) in diagnosing and treating speech sound disorders.
The AAT consists of a comprehensive set of tasks that target specific speech sounds and phonological processes. It assesses an individual’s ability to produce sounds in various word positions and contexts, and provides valuable information about their overall speech intelligibility. By administering the test, SLPs can determine whether an individual exhibits any articulation errors, phonological processes, or speech sound substitutions that may impact their communication skills.
One of the unique features of the AAT is its normative data, which allows SLPs to compare an individual’s performance to that of their peers. This data helps in establishing the severity of the speech sound disorder and provides a basis for developing appropriate intervention plans. Additionally, the AAT includes a scoring system that allows SLPs to quantify and analyze the errors made by the individual, making it easier to track their progress over time.
What is the Arizona Articulation Test?
The Arizona Articulation Test is a standardized assessment tool used by speech-language pathologists to evaluate the articulation skills of individuals. It is commonly administered to children, adolescents, and adults who may have difficulty producing sounds correctly. This test is designed to identify any speech sound errors or disorders, as well as provide information on the severity and type of articulation difficulties.
During the Arizona Articulation Test, the individual is asked to say a specific list of words or sentences out loud, while the examiner listens and records their production of sounds. The test evaluates various aspects of articulation, including consonant sounds, clusters, and vowel sounds. It also assesses the individual’s ability to correctly produce sounds in different word positions, such as the beginning, middle, and end of words.
The results of the Arizona Articulation Test provide valuable information for speech-language pathologists in determining appropriate treatment plans and interventions. The test allows clinicians to identify specific speech sound errors, track progress over time, and set goals for therapy. It also helps in determining the overall intelligibility and speech clarity of the individual. By using this assessment tool, speech-language pathologists can tailor therapy sessions to target the specific areas of articulation that need improvement.
Overall, the Arizona Articulation Test plays a crucial role in the assessment and treatment of articulation disorders. It provides a standardized and objective measure of an individual’s articulation skills, helping speech-language pathologists make informed decisions about intervention strategies and monitor progress effectively. This test is widely recognized and utilized in the field of speech-language pathology to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for individuals with speech sound disorders.
Overview of the Arizona Articulation Test
The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a widely-used standardized assessment tool designed to evaluate speech sound production skills in children. It is specifically designed to identify errors in articulation and phonological processes, providing valuable information for speech-language pathologists, educators, and parents.
The AAT assesses a child’s ability to produce individual sounds, as well as their proficiency in speech sound combinations. It covers a range of phonemes found in the English language, including vowels, consonants, and consonant clusters. The test consists of a series of pictures, and the child is prompted to name each picture out loud. The examiner then marks whether the child’s articulation is accurate or if any errors or substitutions occur.
The AAT is a norm-referenced assessment tool, meaning that the child’s performance is compared to that of a large sample of children in the same age group. This allows for an objective evaluation of the child’s articulation skills and provides valuable information about their overall speech development.
The test results are typically reported in terms of percentile ranks, which indicate the child’s performance relative to their peers. It also provides information on the specific phonemes or phonological processes that the child may be struggling with. This data allows speech-language pathologists to develop targeted intervention plans to address the child’s specific needs.
The Arizona Articulation Test is widely used in both educational and clinical settings, and its standardized nature ensures consistency and reliability in assessing children’s speech sound production skills. It provides a comprehensive overview of a child’s articulation abilities and helps identify areas that may require further attention and intervention.
Importance of the Arizona Articulation Test
The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a widely used assessment tool in the field of speech-language pathology. It is designed to evaluate the articulatory accuracy of individuals, particularly children, by examining their production of different speech sounds. The test consists of a series of pictures and words, and the examinee is required to name each item. The examiner then records and analyzes the accuracy of the speech sounds produced.
One of the main reasons why the Arizona Articulation Test is important is its role in diagnosing and treating speech sound disorders. By accurately assessing an individual’s articulatory skills, speech-language pathologists can determine the specific areas of difficulty and develop appropriate intervention strategies. The test allows clinicians to identify patterns of errors, such as substitutions, omissions, or distortions of sounds, which can guide the selection of therapy targets and techniques.
Additionally, the Arizona Articulation Test provides a standardized and objective measure of an individual’s speech sound development. It allows for reliable and valid comparisons among different individuals, making it an essential tool for research purposes. The test has established normative data that can be used as a reference for determining whether a person’s articulation skills are within the expected range for their age.
Moreover, the Arizona Articulation Test can be used to monitor progress and evaluate the effectiveness of intervention over time. By re-administering the test at regular intervals, clinicians can track changes in speech sound production and make adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary. This helps to ensure that therapy goals are being met and that the individual is making functional improvements in their ability to produce speech sounds accurately.
In conclusion, the Arizona Articulation Test plays a crucial role in the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of speech sound disorders. Its standardized and objective nature allows for accurate evaluation and comparison, making it an indispensable tool for speech-language pathologists. By using the AAT, clinicians can effectively address individual needs and support the development of clear and intelligible speech in both children and adults.
Administration and Scoring of the Arizona Articulation Test
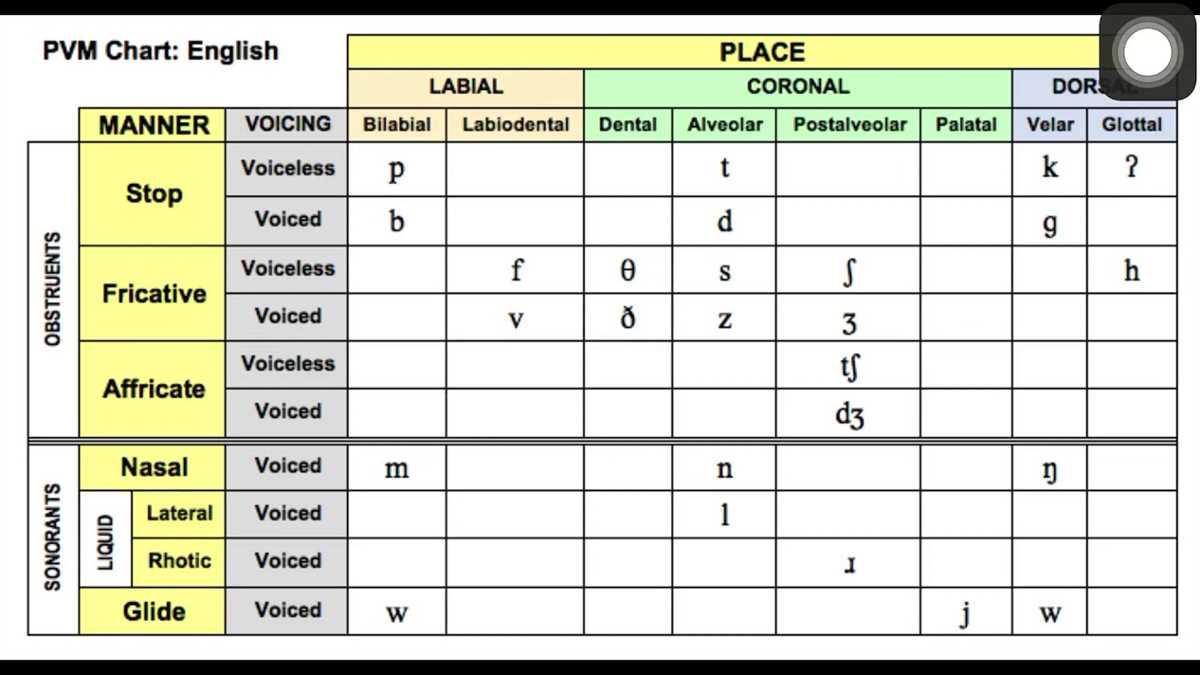
The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a standardized assessment tool used to evaluate children’s speech sound production skills. It is commonly used by speech-language pathologists (SLPs) to identify and diagnose speech disorders in children. The AAT assesses a child’s ability to correctly produce individual phonemes in various word positions and contexts.
Before administering the test, the SLP should familiarize themselves with the administration and scoring procedures outlined in the AAT manual. The manual provides detailed instructions on how to administer the test, including specific guidelines for test administration and scoring criteria. Additionally, it is important for the SLP to establish rapport and create a comfortable testing environment for the child to ensure accurate results.
During the test, the SLP presents a series of pictures, words, or sentences to the child, and the child is asked to repeat or imitate the target sound. The SLP marks the child’s response as correct or incorrect based on specific scoring criteria provided in the manual. The test is typically administered one-on-one in a quiet room to minimize distractions.
The AAT assesses a broad range of speech sounds including consonants, vowels, and consonant clusters in different word positions. The test examines both single sounds and sound combinations to evaluate the child’s overall articulation skills. The SLP records the child’s responses on a scoring sheet or enters them into a computer program for automatic scoring.
After completing the assessment, the SLP analyzes the data to determine the child’s speech sound errors and overall speech intelligibility. The test results can be used to create an individualized treatment plan and set specific speech therapy goals. The AAT is a widely recognized and reliable tool for assessing articulation disorders, providing valuable information for clinicians and researchers in the field of speech-language pathology.
Interpretation and Results of the Arizona Articulation Test
The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a widely used tool for assessing the speech sound production skills of individuals, particularly children. The test evaluates the accuracy of speech sound production by examining the articulation of consonants in various word positions. The results of the AAT help clinicians and speech-language pathologists to diagnose and treat speech disorders.
When interpreting the results of the AAT, several factors should be considered. First, the test provides a percentage score that reflects the overall accuracy of speech sound production. A score of 85% or higher is typically considered within the normal range. Lower scores may indicate the presence of an articulation disorder. However, it is important to note that the AAT only assesses consonant sounds and does not assess other aspects of speech, such as fluency, voice quality, or language skills.
Additionally, the AAT provides specific information about the types of errors made by the individual during the test. These errors can be categorized as substitution, omission, distortion, or addition errors. Substitution errors occur when one sound is consistently replaced by another. Omission errors involve the complete omission of a sound. Distortion errors occur when the sound is produced, but not accurately. Addition errors refer to the insertion of an extra sound or syllable into a word.
The results of the AAT can guide clinicians in developing appropriate treatment plans for individuals with articulation disorders. Therapy may focus on specific sounds or patterns that were identified as problematic during the test. Targeting these areas can help individuals improve their speech sound production and increase overall communication skills.
Advantages and Limitations of the Arizona Articulation Test
The Arizona Articulation Test (AAT) is a widely used assessment tool for evaluating speech sound disorders in children. It offers several advantages that make it a valuable resource for speech-language pathologists:
- Standardization: The AAT is a standardized test, which means that it has been administered to a large sample of individuals to establish norms for comparison. This allows clinicians to accurately assess and compare a child’s speech production abilities with typically developing peers.
- Reliability: The test has been proven to be reliable, meaning that it yields consistent results across different examiners and testing sessions. This reliability enhances the clinical validity of the test and makes it a useful tool in diagnosing and monitoring children with speech sound disorders.
- Comprehensive assessment: The AAT assesses a wide range of speech sounds in various word positions, providing a comprehensive evaluation of a child’s overall speech production abilities. This allows clinicians to identify specific areas of difficulty and tailor intervention programs accordingly.
- Objective scoring: The AAT utilizes a scoring system that allows for objective evaluation of speech production accuracy. This helps to minimize subjective biases and increase the reliability of test results.
Despite its many advantages, the AAT also has limitations that should be considered:
- Limited cultural and linguistic diversity: The AAT was developed and standardized primarily on children from English-speaking, monolingual backgrounds. As a result, it may not be as applicable or accurate when assessing children from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds.
- Limited focus on connected speech: The AAT primarily assesses sounds in single words, which may not fully capture a child’s speech abilities in connected speech contexts. Additional assessment tools or techniques may be needed to evaluate a child’s performance in natural conversational situations.
- Age limitations: The AAT is designed for children between the ages of 2 and 21 years old. It may not be suitable or accurate for evaluating speech sound disorders in younger or older individuals.
- Lack of sensitivity to phonological patterns: The AAT evaluates individual speech sounds, but does not assess the underlying phonological processes that contribute to sound errors. To fully understand a child’s speech sound disorder and develop appropriate intervention strategies, additional assessments may be required.
Despite these limitations, the Arizona Articulation Test remains a valuable tool in the assessment and diagnosis of speech sound disorders in children. Its standardization, reliability, and comprehensive assessment make it a useful resource for clinicians, but it should be used in conjunction with other assessment tools and clinical judgment to ensure accurate and culturally sensitive evaluations.