
In a chemistry classroom, one of the most important topics to understand is bonding. Bonding is the process by which two or more atoms come together to form a chemical compound. It is essential to understand the different types of bonds that can form, as well as the factors that influence bond formation. One popular teaching method for exploring bonding is through the use of POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) activities.
A POGIL activity is a collaborative learning exercise where students work together in small groups to explore a specific topic. In the context of bonding, POGIL activities can help students analyze and interpret data, make predictions, and develop a deeper understanding of the concepts involved. These activities provide students with an opportunity to actively engage with the material, rather than passively receiving information through traditional lectures.
The Bonding POGIL Style Answer Key serves as a valuable resource for both students and teachers. It provides a comprehensive guide to help students navigate through the various POGIL activities and ensure they are on the right track. The answer key contains detailed explanations and solutions to the problems presented in the activities. This allows students to compare their answers and reasoning with the correct ones, enabling them to identify any misconceptions or gaps in their understanding.
Bonding POGIL Style Answer Key: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of chemistry, understanding the concepts of bonding is essential. Bonding POGIL style provides a comprehensive guide to help students master the fundamentals of chemical bonding. This answer key serves as a valuable resource, outlining the correct answers to each question in the bonding POGIL activity.
With this answer key, students can easily review their understanding of various bonding concepts, including ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding. Each question is accompanied by a detailed explanation, allowing students to identify any misconceptions they might have and providing them with the opportunity to improve their knowledge.
The answer key begins with an overview of the different types of bonding and their characteristics. It then dives into specific questions, covering topics such as Lewis structures, electronegativity, and intermolecular forces. The comprehensive nature of the answer key ensures that students gain a deep understanding of bonding concepts, preparing them for future chemistry studies.
Table of Contents:

- Introduction
- Type of Bonding:
- Ionic Bonding
- Covalent Bonding
- Metallic Bonding
- Question 1: Lewis Structures
- Question 2: Electronegativity
- Question 3: Intermolecular Forces
This answer key can be used by teachers as a tool for grading and providing feedback to their students. It ensures consistency in evaluating student responses while also giving teachers insight into common areas of misunderstanding.
Overall, this bonding POGIL style answer key acts as a comprehensive guide, enabling students to reinforce their understanding of bonding concepts and helping teachers in their assessment process. With its detailed explanations and organized structure, it serves as a valuable resource for both students and educators in the field of chemistry.
Understanding Bonding POGIL Style: An Overview
When it comes to learning about bonding in chemistry, POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) style is gaining popularity as an effective method. POGIL is a student-centered approach that encourages active learning through group discussions and problem-solving activities. This style of learning allows students to take ownership of their learning process, promoting critical thinking and deep understanding of the subject matter.
In a typical bonding POGIL activity, students are presented with a set of guided inquiry questions that require them to analyze and interpret bonding concepts. These questions are designed to promote collaboration and discussion among group members, as they work through the activity together. By engaging in cooperative learning, students can share their ideas and perspectives, enhancing their understanding of the material.
One key aspect of bonding POGIL style is the emphasis on process. Rather than focusing solely on finding the correct answers, the process of reasoning and thinking behind the answers is given equal importance. Students are encouraged to think critically, examine evidence, and construct their own understanding of bonding concepts. This approach fosters a deeper comprehension of the subject matter, as students are actively involved in solving problems and making connections.
In order to facilitate the learning process, bonding POGIL activities often incorporate visual aids and models to help students visualize the bonding concepts. These visual representations can make abstract concepts more concrete and accessible, aiding in the comprehension and retention of the material.
Overall, bonding POGIL style offers a dynamic and interactive learning experience for students, promoting a deeper understanding of bonding concepts. By engaging in collaborative problem-solving activities, students develop critical thinking skills and gain a sense of ownership over their learning. This approach not only enhances academic performance but also fosters a lifelong love for learning and inquiry.
The Importance of Bonding in Chemistry
Bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior and properties of substances. At its core, bonding involves the sharing, donation, or transfer of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable configuration. This process forms chemical bonds, which hold atoms together and determine the structure and reactivity of molecules.
One of the key reasons why bonding is important in chemistry is that it allows us to predict and explain the physical and chemical properties of substances. By understanding the types of bonds present in a compound, we can make informed predictions about its boiling point, melting point, solubility, and other properties. For example, substances with strong covalent bonds tend to have higher boiling and melting points, while those with weak intermolecular forces exhibit lower boiling and melting points.
In addition, bonding is crucial for studying the reactivity of substances. Different types of bonds require different amounts of energy to break, which affects how easily a chemical reaction can occur. For example, substances with weak intermolecular forces are more likely to undergo reactions as their bonds can be easily broken. This knowledge is vital in fields such as pharmaceuticals, where understanding the reactivity of different compounds can help in the development of new drugs.
- Bonding helps us understand and predict the properties of substances.
- Different types of bonds have different effects on boiling and melting points.
- Knowledge of bonding is important in studying chemical reactivity.
- Understanding bonding is crucial in fields like pharmaceutical research.
Why POGIL Style Is Effective for Teaching Bonding
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) style is an effective teaching method for explaining the concept of bonding in chemistry. Through POGIL, students actively engage in their learning process, as they work in small groups to explore and analyze bonding scenarios. This collaborative and inquiry-based approach shifts the traditional teacher-centered classroom to a student-centered one, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Active learning: POGIL style promotes active learning, as students are encouraged to form their own hypotheses, design experiments, and analyze data. By actively participating in their learning process, students deepen their understanding of bonding concepts and develop a deeper connection with the material. This hands-on approach allows students to take ownership of their learning, leading to a more meaningful learning experience.
Collaboration: POGIL style emphasizes collaboration among students. Working in small groups, students engage in discussions, share their ideas, and challenge each other’s understanding. Through this collaborative environment, students learn from one another, gaining different perspectives and approaches to problem-solving. This collaboration not only enhances their understanding of bonding but also fosters teamwork and communication skills, which are essential in real-life scientific and professional settings.
Inquiry-based learning: POGIL style utilizes inquiry-based learning, where students actively inquire and investigate bonding concepts. By asking questions, seeking answers, and analyzing data, students develop critical thinking skills and learn to apply their knowledge to real-world situations. This approach encourages students to think outside of the box and explore the underlying principles of bonding, leading to a deeper level of understanding.
In conclusion, POGIL style is an effective method for teaching bonding in chemistry. By promoting active learning, collaboration, and inquiry-based learning, POGIL style engages students in their learning process and enhances their understanding of bonding concepts. This student-centered approach not only helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills but also fosters teamwork and communication skills necessary for future scientific and professional endeavors.
Key Concepts and Definitions in Bonding
Bonding is the process of combining two or more atoms to form a new substance. Understanding the key concepts and definitions in bonding is essential to comprehend how atoms interact and form different types of bonds.
Chemical Bond: A chemical bond is an attraction between two or more atoms that allows the formation of compounds. It involves the sharing, transfer, or redistribution of electrons to achieve stable electron configurations.
Valence Electrons: Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost energy level of an atom. These are the electrons involved in bonding and determine the chemical properties of an atom.
Ionic Bond: An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. It occurs between a metal and a nonmetal and results in the formation of ions.
Covalent Bond: A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons between two atoms. It occurs between two nonmetals and results in the formation of molecules.
Electronegativity: Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond. It plays a crucial role in determining the type of bond that will form between two atoms.
Polarity: Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons in a chemical bond. It arises due to differences in electronegativity between the atoms involved. A polar bond has a positive and negative end, while a nonpolar bond has an even distribution of electrons.
Hydrogen Bond: A hydrogen bond is a special type of chemical bond that occurs between a partially positive hydrogen atom and a highly electronegative atom. It is weaker than ionic or covalent bonds but plays a significant role in many biological processes.
To effectively understand bonding, it is crucial to grasp these key concepts and definitions and apply them in different chemical scenarios. These concepts form the foundation of the study of chemical bonding and help explain the properties and behavior of different substances.
Step-by-Step Approach to Solving Bonding Problems
When it comes to solving bonding problems, it is important to take a step-by-step approach in order to ensure accuracy and understanding. By following a systematic process, you can break down the problem into smaller, more manageable chunks and tackle them one at a time. This approach will help you to identify the key concepts and principles involved in bonding, and ultimately lead you to the correct answer.
The first step in solving a bonding problem is to carefully read and understand the question or prompt. Pay attention to any specific instructions or information provided, and make note of any key terms or concepts that are mentioned. This will give you a clear understanding of what the problem is asking and help you to focus your efforts.
Next, gather all the relevant information and data that is given in the problem. This may include the types of atoms or ions involved, their charges, and the type of bond being formed (ionic, covalent, or metallic). Organize this information in a clear and concise manner, such as creating a table or list.
Once you have all the necessary information, analyze the problem and decide on the appropriate approach to take. Consider what type of bond is being formed and the specific characteristics and properties of that bond. This will help you to determine the appropriate formulas, equations, or principles to apply in order to solve the problem.
With your approach determined, begin solving the problem step by step. This may involve calculating the formal charges of each atom or ion, determining the type and arrangement of bond, or predicting the overall structure of the molecule or compound. Work through each step carefully, checking your work as you go to ensure accuracy. If you encounter any difficulties, refer back to your notes or textbook for additional guidance or examples.
Finally, review and double-check your answer. Make sure that your solution is logical, consistent with the information given, and properly supports your reasoning. If necessary, go back and make any corrections or adjustments as needed. By following this step-by-step approach, you can approach bonding problems with confidence and achieve a correct and thorough understanding of the concepts involved.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Bonding POGIL Style
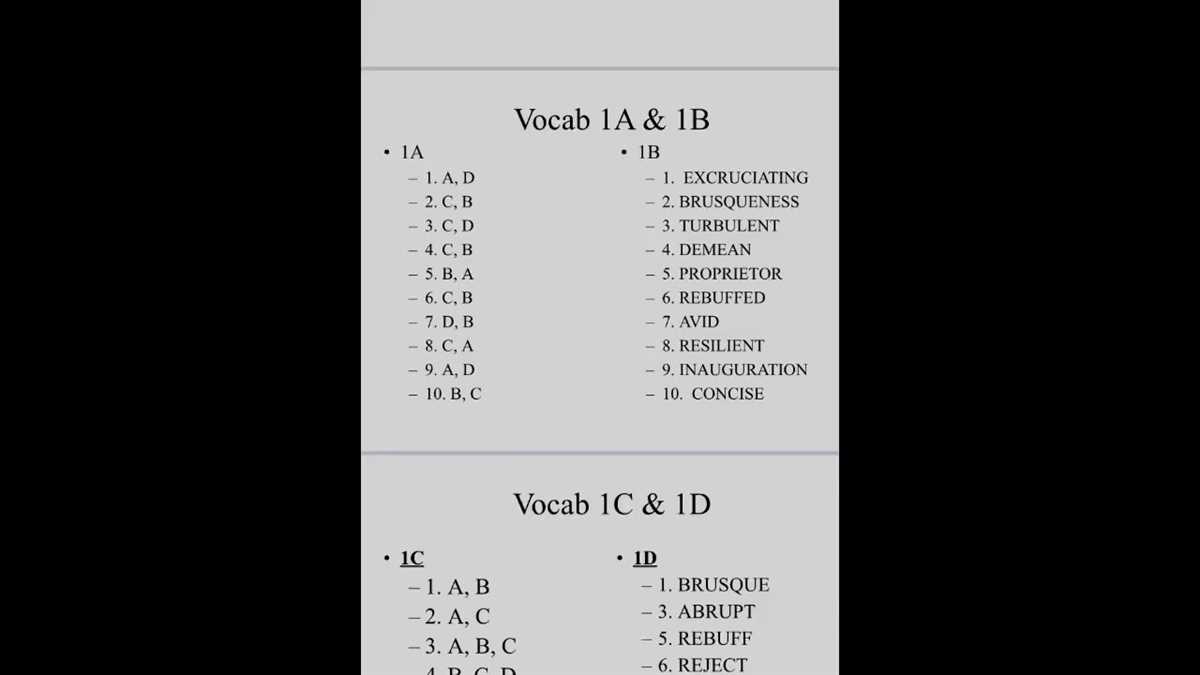
In the process of completing a Bonding POGIL activity, it is common for students to make a few common mistakes. By being aware of these pitfalls, students can avoid them and improve their understanding of bonding concepts. Here are some of the most common mistakes to be mindful of:
1. Not Following Directions
One of the most common mistakes is not following the directions provided in the POGIL activity. It is crucial to read the instructions carefully and follow them step by step. Skipping or rushing through certain steps can lead to incorrect answers and a lack of understanding.
2. Ignoring Visual Clues
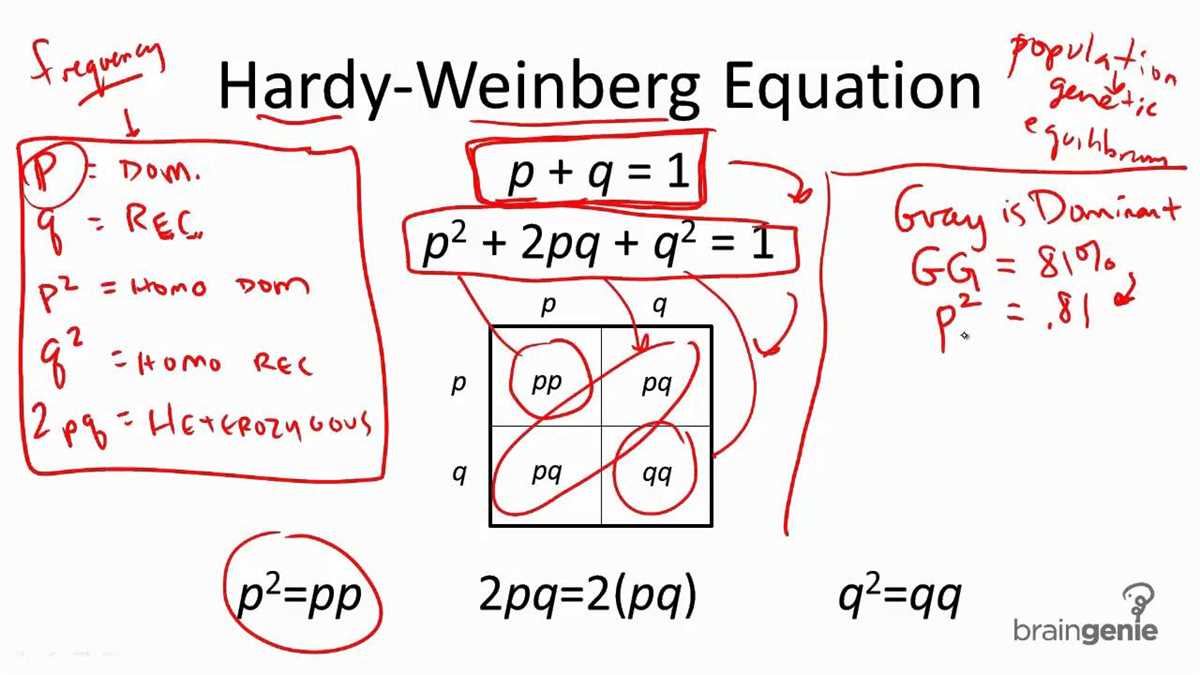
Bonding POGIL activities often include visual aids, such as diagrams or models, to help students visualize bonding processes. A common mistake is to ignore these visual clues and rely solely on written instructions. It is important to pay attention to all the provided information, both visual and written, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
3. Not Discussing with Peers
Another common mistake is not engaging in discussions with peers during the activity. Bonding POGIL activities are designed to promote collaborative learning, and discussions with classmates can help clarify misconceptions, share different perspectives, and deepen understanding. Avoiding these discussions can hinder the learning process.
4. Overlooking Key Concepts
Some students may overlook key concepts or principles while working on a Bonding POGIL activity. It is essential to pay attention to the underlying principles, such as electronegativity, bonding types, and Lewis structures, as they form the foundation for understanding bonding. Ignoring or misunderstanding these concepts can lead to incorrect answers.
5. Not Reflecting on the Process
Lastly, a common mistake is not reflecting on the process after completing a Bonding POGIL activity. Taking the time to reflect on the activity can help identify areas of confusion or areas that need further clarification. It is important to review the activity and assess what was learned and what could be improved for future activities.
By avoiding these common mistakes, students can enhance their learning experience during Bonding POGIL activities and develop a deeper understanding of bonding concepts. Remember to follow directions, pay attention to visual clues, engage in discussions with peers, focus on key concepts, and reflect on the process to make the most out of these collaborative learning activities.