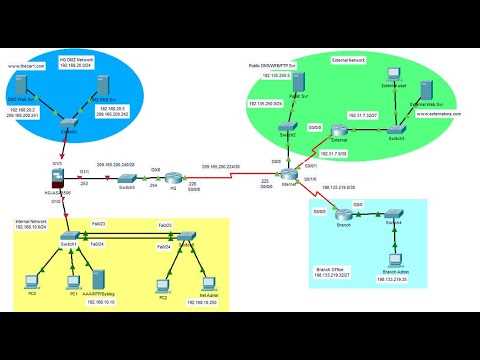
The final exam in CCNA 1 v7 tests your ability to apply networking concepts, configure devices, and troubleshoot network issues. Focus on understanding core concepts such as IP addressing, routing, and switch configuration. This exam demands both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Review key topics like IP subnetting, OSI model, and routing protocols to boost your chances of success.
To approach the exam effectively, break down the content into manageable sections. Start by reviewing the practice questions and labs in each module. Ensure you can configure devices in the command line interface (CLI) and understand the commands needed for tasks like assigning IP addresses and configuring routing tables. Hands-on practice with network simulation tools can help solidify your skills.
When answering questions, pay attention to details such as subnet masks and default gateway configurations. Understanding how to configure routers and switches based on a given network scenario is key. Don’t hesitate to re-check your work, especially when dealing with complex commands or network topologies.
CCNA 1 v7 Final Exam Answers: Practical Insights
When configuring IP addressing, remember that subnetting requires careful attention. Make sure to calculate the correct subnet mask, especially when dealing with Class C networks. For example, in a network with a 255.255.255.0 mask, the first three octets represent the network portion, and the last octet is for hosts. If asked to calculate the number of usable IP addresses, subtract 2 from the total addresses (network and broadcast addresses are not usable).
In routing, always check if the correct routing protocol is enabled. For RIP v2, ensure that the “no auto-summary” command is configured if the network spans multiple subnets. For OSPF, verify that each router has the correct area ID and ensure network types match across interfaces. Remember to configure OSPF on the correct interfaces with the appropriate network statements.
When troubleshooting, focus on the physical layer first–check cables and connections. Use commands like “ping” to test connectivity. If the issue is with routing, confirm that routers are exchanging routing tables by using “show ip route” to verify routes are present and correctly populated.
For VLANs, ensure each switch port is configured correctly. Use “show vlan brief” to see which VLANs are active on the switch. Make sure the correct VLANs are tagged and untagged on the appropriate ports. Also, check trunking configurations between switches. If a trunk link is misconfigured, VLANs won’t propagate properly across the network.
Strategies for Answering Multiple-Choice Questions Correctly
Focus on eliminating obviously incorrect answers first. Often, there will be one or two options that are clearly wrong, allowing you to narrow down your choices quickly.
Look for keywords in the question and answer choices. These clues can guide you toward the correct option, especially when the question is complex or tricky.
Manage Your Time Wisely
Don’t get stuck on one question for too long. If you’re unsure, make your best guess and move on. You can always come back to challenging questions later when you have more time to think.
Use the Process of Elimination
If you’re uncertain, eliminate answers that don’t align with your understanding of the topic. Often, two or three choices can be eliminated right away, making it easier to choose between the remaining options.
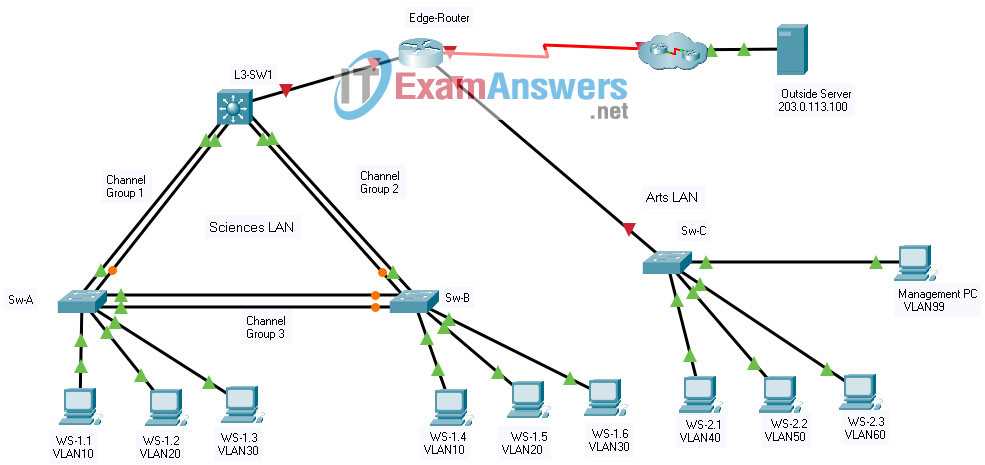
Hands-On Approach to Completing Packet Tracer Tasks
Focus on the task at hand. First, read the instructions carefully to understand the goal. Identify the devices, configurations, and connections required for each step. This will help prioritize actions and avoid unnecessary steps.
1. Set Up the Network Devices

Drag and drop the necessary devices, such as routers, switches, and computers, into the workspace. Ensure each device is placed according to the instructions. Label devices correctly to avoid confusion later.
2. Configure IP Addresses
Assign IP addresses based on the network design. Double-check the subnet mask and gateway settings to ensure proper routing between devices. Use the “FastEthernet” interface when configuring hosts and “GigabitEthernet” for router-to-router connections.
3. Establish Routing
Configure routing protocols as required–static or dynamic. If using dynamic routing, ensure routers are configured with the correct protocol (RIP, OSPF, EIGRP) and verify network interfaces are correctly advertised. For static routing, manually enter routes as per the task’s specifications.
4. Verify Connections and Routing Tables
Use commands like “ping” to test connectivity between devices. Check routing tables on routers using the “show ip route” command to verify that routing protocols are functioning correctly. If any connection fails, check for misconfigured IP addresses or incorrect interfaces.
5. Troubleshoot
If issues arise, follow a systematic troubleshooting approach. Use commands like “show run” to verify configurations, and “show ip interface brief” to ensure interfaces are up. Keep an eye on any error messages in the simulation that could indicate a misconfiguration.
6. Save Progress
Once you’ve completed each task, save your work regularly. This ensures that any completed steps won’t be lost, and you can always return to a previous working state if needed.
By focusing on these core tasks, you can complete the Packet Tracer tasks accurately and efficiently, ensuring that each step is well-understood and properly configured.
Mastering Configuration Commands for Final Exam Success
Begin by practicing common commands like enable, configure terminal, and show to access privileged modes and view device information. These are frequently used during configurations and troubleshooting exercises in the final exam.
For network configuration, familiarize yourself with commands such as ip address, no shutdown, and hostname. These allow you to configure interfaces, enable devices, and assign names. Consistent use of these commands will help you quickly complete tasks in exam scenarios.
Become comfortable with interface commands. Commands like interface gigabitEthernet 0/1 or interface fastEthernet 0/1 will help you access and configure individual interfaces, a common task during the exam.
Practice show running-config and show ip route to check the current configuration and routing table. These commands are invaluable for verifying your setup and troubleshooting issues during the test.
Get used to copy running-config startup-config to save configurations. This simple step ensures your settings remain intact after device reboots, which is often necessary in exam conditions.
Finally, review router ospf or router eigrp commands to configure routing protocols. Understanding how to enable and configure routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP is a key part of network setup in the exam.