
To succeed in assessments related to the study of cells, it’s essential to focus on core principles that form the foundation of the subject. This guide covers the primary themes and concepts necessary to demonstrate a deep understanding of how living organisms function at the microscopic level. By mastering these fundamental areas, you can confidently approach any related academic challenge.
Understanding Basic Structures
The first step in mastering cellular science is recognizing the intricate components that make up a living cell. Each part plays a critical role in maintaining cellular integrity and supporting essential functions such as growth, energy production, and communication. Key areas to review include:
- Plasma membrane: regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
- Nucleus: controls genetic material and cellular activities.
- Mitochondria: produce energy through cellular respiration.
Cellular Communication
Understanding how cells communicate with each other is vital for grasping complex biological processes. The signaling mechanisms that allow cells to coordinate their activities are crucial in both health and disease. Focus on:
- Signal transduction pathways: how external signals lead to cellular responses.
- Receptors: proteins that bind to specific molecules to initiate a cellular action.
Energy Transformation and Function
Energy is central to all life processes, and understanding how cells convert energy is key. This includes the processes of converting nutrients into usable energy and storing that energy for later use. Important areas include:
- ATP synthesis: the process by which cells produce energy.
- Photosynthesis and respiration: energy conversion in plant cells versus animal cells.
Genetic Material and Inheritance
The study of heredity and genetic material is essential for understanding traits and how they are passed from one generation to the next. Pay special attention to:
- DNA structure: the foundation of genetic information.
- Replication: how cells copy their genetic material before division.
Cellular Reproduction

Cell division is a cornerstone of cellular function, driving growth, repair, and reproduction. Knowing the differences between various types of cell division, such as mitosis and meiosis, is crucial. Key concepts include:
- Mitosis: a process of producing identical cells for growth and repair.
- Meiosis: reduction division for the formation of reproductive cells.
Common Topics for Study

In preparation for any related academic challenge, focus on the most commonly tested areas, including:
- Fundamentals of cell structure and function.
- Energy transformations within the cell.
- Genetic processes and inheritance patterns.
By revisiting these core principles, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to excel in your studies and demonstrate a thorough understanding of life at the cellular level.
Key Concepts for Academic Assessments in Cellular Science
To excel in assessments related to the study of living organisms at the microscopic level, it’s important to master the fundamental principles that govern how cells function. This section highlights essential themes that are frequently tested and crucial for understanding key biological processes and structures within the body.
Understanding Cellular Components
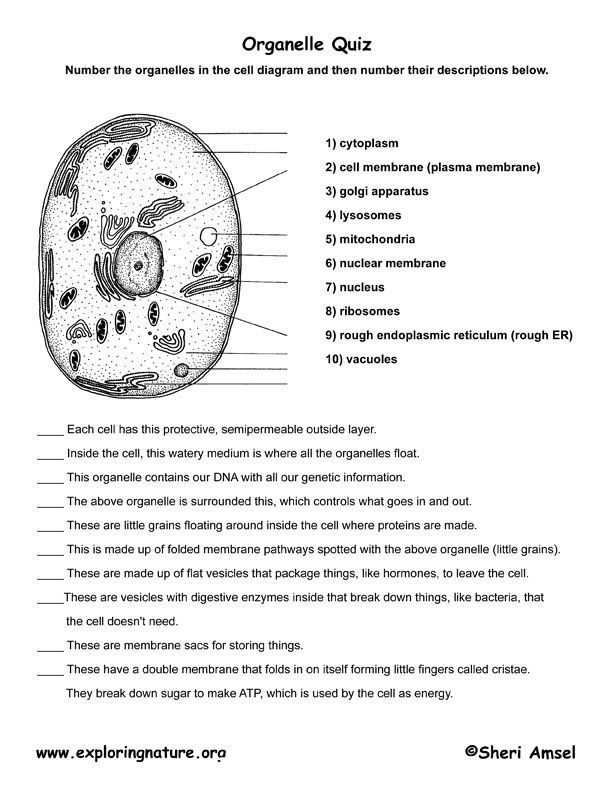
Grasping the core components of a living organism’s basic unit is critical for comprehending how life operates. These elements work together to maintain cellular health, structure, and function. Focus on:
- Plasma membrane: controls the movement of substances into and out of the unit.
- Nucleus: houses genetic material, directing cellular activities.
- Mitochondria: responsible for energy production through metabolic processes.
Cellular Reproduction and Division
One of the most significant biological processes is the division of cells, as it allows organisms to grow, repair tissue, and reproduce. It is essential to understand both the mechanisms and the stages of this process. Key topics include:
- Mitosis: how cells replicate to create identical copies.
- Meiosis: the process responsible for generating reproductive cells.
Genetic Information and Inheritance
Genetic material plays a crucial role in passing traits from one generation to the next. Mastery of DNA replication and the principles of inheritance is vital for understanding how traits are inherited and how genetic information is transmitted. Study areas to review:
- DNA structure: the blueprint for all living organisms.
- Replication: how genetic material is copied for cell division.
Metabolism and Energy Transfer
Energy production and distribution are fundamental to all living processes. Understanding how cells transform nutrients into usable energy is essential for comprehending cellular function. Focus on:
- ATP production: the primary energy currency within cells.
- Respiration and Photosynthesis: key processes for energy generation in different cell types.
Common Topics and Study Areas
When preparing for academic challenges in the field of cellular science, emphasize the following concepts for a thorough understanding:
- Basic structures and functions of cells.
- The role of energy in cellular activities.
- Genetic material and inheritance mechanisms.