
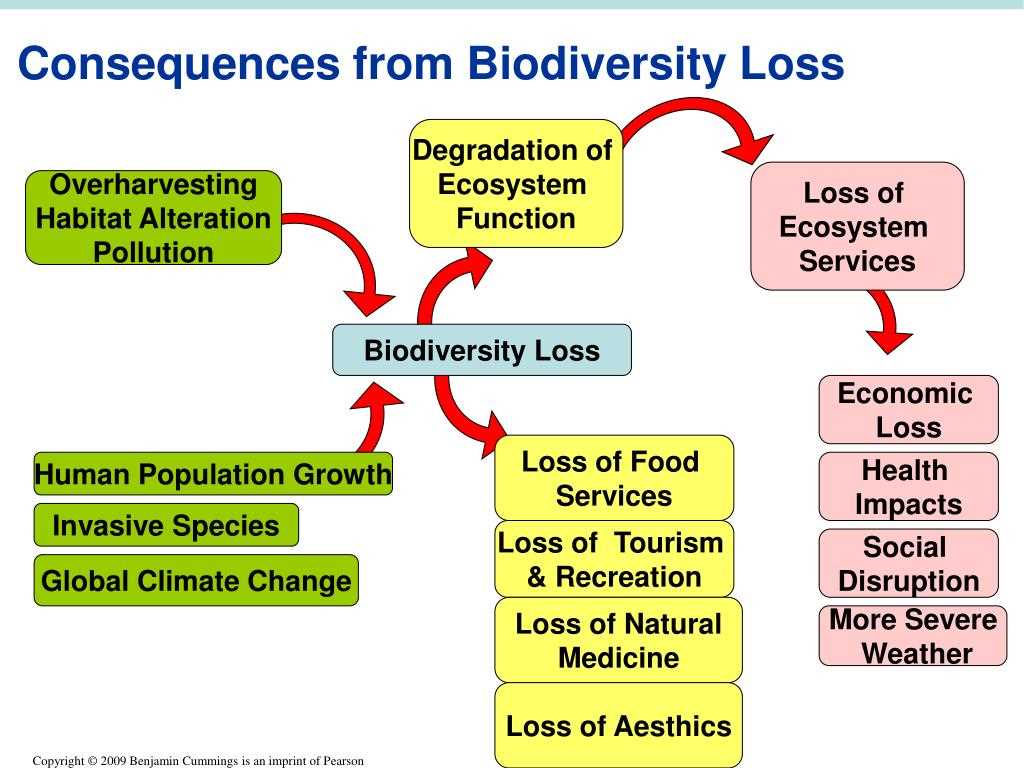
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms, including genes, species, ecosystems, and ecological processes found on Earth. It is the result of billions of years of evolution and is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and the sustainability of life on our planet. Biodiversity provides us with resources, such as food, medicine, and materials for shelter, and contributes to our economic well-being and cultural identity. However, human activities, such as habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of natural resources, and climate change, are causing a rapid loss of biodiversity worldwide.
In order to protect and conserve biodiversity, it is important to understand the factors that contribute to its loss and the strategies that can be implemented to mitigate these impacts. Chapter 5 of the textbook “Biodiversity and Conservation” provides an answer key to the questions and exercises presented throughout the chapter. This key allows students to check their understanding of the material and ensures that they are able to apply the concepts and principles discussed in the chapter.
The answer key covers a range of topics related to biodiversity and conservation, including the value of biodiversity, threats to biodiversity, conservation strategies, and the role of individuals and communities in protecting biodiversity. It provides detailed explanations and examples to help students grasp the concepts and apply them to real-world situations. By using the answer key, students can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of biodiversity and the actions that can be taken to preserve it.
Chapter 5 Biodiversity and Conservation Answer Key: Exploring the Key Concepts
In Chapter 5 of the biodiversity and conservation curriculum, students are introduced to key concepts related to biodiversity and conservation. By understanding these concepts, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of biodiversity and the need for conservation efforts.
The Key Concepts

- Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including different species, genes, and ecosystems. It is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and provides numerous benefits to humans, such as food, medicine, and ecological services.
- Species: A species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. It is the basic unit of biodiversity and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Understanding species is important for conservation efforts as it allows scientists to identify and protect endangered species.
- Genetic Diversity: Genetic diversity refers to the variety of genes within a species. It is important for the survival and adaptability of species, as it allows them to respond to changes in their environment. Loss of genetic diversity can make species more vulnerable to diseases and other threats.
- Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment. It includes interactions between living organisms (such as plants, animals, and microorganisms) and non-living elements (such as air, water, and soil). Ecosystems provide essential services, such as nutrient cycling, water purification, and climate regulation.
- Conservation: Conservation refers to the sustainable use and management of natural resources to ensure their long-term viability. It involves protecting biodiversity, maintaining ecosystem services, and promoting sustainable development. Conservation efforts can include activities like habitat restoration, species conservation, and sustainable resource extraction.
These key concepts provide a foundation for understanding the importance of biodiversity and the need for conservation. By exploring these concepts, students can develop a deeper understanding of the ecological and societal value of biodiversity and the role they can play in preserving it for future generations.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms on Earth, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. It is crucial for maintaining the stability and functioning of ecosystems and plays a vital role in supporting human life. The preservation of biodiversity is essential for the survival and well-being of all species, including humans.
One of the key reasons why biodiversity is important is because it provides ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans obtain from ecosystems. These include the provision of food, water, and medicine; the regulation of climate and disease; and the purification of air and water. Biodiversity is crucial for the functioning of these services. For example, diverse plant and animal species help to pollinate crops, control pests, and maintain nutrient cycles in the soil.
Biodiversity also contributes to the resilience of ecosystems. It enables ecosystems to adapt to changes and disturbances, such as climate change or natural disasters. The more diverse an ecosystem is, the better it can withstand and recover from these events. Additionally, biodiversity provides a form of insurance against unforeseen events. If one species or habitat is lost, there are still many others that can fulfill similar ecological roles. This redundancy is important for maintaining the overall stability and functioning of ecosystems.
In conclusion, biodiversity is of utmost importance for the well-being of both ecosystems and humans. It provides essential ecosystem services, contributes to the resilience of ecosystems, and ensures the long-term sustainability of life on Earth. It is therefore crucial to prioritize the conservation and protection of biodiversity for the benefit of present and future generations.
Threats to Biodiversity
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, is facing numerous threats that are causing the decline of species and ecosystems. Human activities play a major role in the loss of biodiversity, and it is crucial to address these threats in order to conserve and protect the natural world for future generations.
Habitat Loss: One of the primary threats to biodiversity is habitat loss. When natural habitats are destroyed or disturbed, it can have devastating effects on the species that depend on them. Deforestation, urbanization, and conversion of land for agriculture are some of the main causes of habitat loss.
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for timber, agriculture, and development is a major driver of habitat loss. This not only destroys the homes of countless species, but also contributes to climate change and the loss of important ecosystem services.
- Urbanization: The expansion of cities and infrastructure leads to the destruction of natural habitats, fragmentation of ecosystems, and displacement of wildlife. Urban areas are often devoid of the biodiversity found in natural ecosystems.
- Agricultural Conversion: The conversion of land for agriculture, particularly for the production of crops and livestock, results in the destruction of natural habitats and loss of biodiversity. Intensive farming practices can also have negative impacts on soil fertility, water quality, and wildlife populations.
Pollution and Climate Change: Pollution from industrial activities, improper waste disposal, and the use of harmful chemicals poses significant threats to biodiversity. Pollution can contaminate water bodies, soil, and air, leading to the death of aquatic and terrestrial species. Climate change, caused by the emission of greenhouse gases, is also a major threat to biodiversity as it alters ecosystems and disrupts the life cycles of many species.
Overexploitation: The overexploitation of natural resources, such as overfishing and hunting, is another major threat to biodiversity. Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish populations and disrupt marine ecosystems, while excessive hunting can lead to the extinction of species.
In conclusion, the threats to biodiversity are numerous and interconnected. It is essential to address these threats through sustainable and conservation efforts in order to protect and preserve the incredible variety of life on our planet.
Conservation Strategies
Conservation is a critical aspect of biodiversity preservation and plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. To effectively conserve biodiversity, various strategies and approaches are implemented.
Habitat Conservation: One of the primary strategies in biodiversity conservation is the protection and preservation of natural habitats. This includes the conservation of forests, wetlands, grasslands, and other natural landscapes. By safeguarding these habitats, it ensures the survival and well-being of countless species that rely on them for sustenance and shelter.
Species Conservation: Another important strategy in biodiversity conservation is the preservation of endangered and threatened species. This involves implementing measures to protect these species from extinction, such as habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and legal protections. By focusing on conserving specific species, it helps maintain the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem.
Invasive Species Management: Invasive species pose a significant threat to biodiversity by outcompeting native species and disrupting ecosystems. Managing invasive species is a crucial conservation strategy that involves monitoring and controlling their spread. This can include the removal of invasive species, implementing quarantine measures, and promoting public awareness to prevent the introduction of new invasive species.
Sustainable Resource Management: The sustainable use of natural resources is another vital conservation strategy. This involves employing practices that ensure the long-term availability of resources without depleting them. Sustainable resource management includes responsible fishing, forestry, agriculture, and mining practices. By promoting sustainable resource management, it helps protect biodiversity by minimizing the negative impacts of resource extraction on ecosystems.
Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in biodiversity conservation is an effective strategy for long-term success. By involving communities in conservation efforts, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards protecting biodiversity. This can be achieved through education and awareness programs, establishing community-based conservation initiatives, and providing economic incentives for conservation practices.
In conclusion, conservation strategies are essential tools in preserving biodiversity. By implementing habitat conservation, species conservation, invasive species management, sustainable resource management, and community involvement, we can ensure the continued existence and health of our planet’s diverse ecosystems.
Case Studies in Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity conservation is crucial in order to protect the variety of living organisms and their ecosystems. Numerous case studies have been conducted to assess the effectiveness of conservation measures and to develop strategies for preserving biodiversity. These case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities of conservation efforts.
The Case of the Galapagos Islands
The Galapagos Islands, located in the Pacific Ocean, are a famous case when it comes to biodiversity conservation. These islands are home to a unique range of species found nowhere else on Earth. However, due to factors such as invasive species and human activity, the biodiversity of the Galapagos Islands has been threatened. Through various conservation initiatives, including the establishment of the Galapagos National Park and the implementation of strict regulations, efforts have been made to protect and restore the delicate ecosystems of the islands. These measures have proven effective in preserving the unique biodiversity of the Galapagos Islands.
The Case of the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest is another significant case study in biodiversity conservation. It is the largest tropical rainforest in the world and is home to countless species of plants, animals, and insects. Deforestation, primarily driven by agricultural expansion and logging, poses a severe threat to the Amazon’s biodiversity. Conservation efforts in the region have focused on establishing protected areas, empowering local communities, and promoting sustainable land-use practices. These initiatives aim to prevent further deforestation and promote the conservation of the Amazon’s rich biodiversity.
In conclusion, case studies in biodiversity conservation provide valuable insights into the challenges and successes of preserving the variety of life on Earth. The cases of the Galapagos Islands and the Amazon rainforest demonstrate the importance of establishing protected areas, implementing strict regulations, and involving local communities in conservation efforts. Through these initiatives, it is possible to protect and restore biodiversity and ensure the long-term survival of our planet’s ecosystems.
Evaluating Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in protecting biodiversity and preserving ecosystems. However, evaluating the effectiveness of these efforts is essential to ensure that resources are being allocated efficiently and that conservation goals are being met.
There are several key factors to consider when evaluating conservation efforts:
- Monitoring and data collection: Collecting data on the target species or ecosystems is essential to understand their status and track any changes over time. This data can help assess the impact of conservation efforts and determine whether they are having a positive effect.
- Measurable indicators: Establishing measurable indicators, such as population size or habitat quality, can help determine whether conservation efforts are achieving their intended outcomes.
- Local engagement and involvement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for their long-term success. Local perspectives and knowledge can contribute valuable insights and help tailor conservation strategies to specific contexts.
- Economic impact: Assessing the economic impact of conservation efforts is important to understand their sustainability. Understanding the economic benefits and costs can help prioritize and justify conservation initiatives.
Overall, evaluating conservation efforts is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, assessment, and adaptation. It is essential to regularly review and adjust conservation strategies based on the data and feedback collected. By doing so, we can ensure that our conservation efforts are effective, efficient, and contributing to the long-term preservation of biodiversity.