Understanding and managing anxiety and depression are crucial for maintaining our mental and emotional well-being. Chapter 5 Lesson 1 of the comprehensive guide on dealing with anxiety and depression provides essential answers and guidance to help individuals navigate through these challenging mental health conditions.
Whether one is personally experiencing anxiety and depression or seeking to support a loved one, this lesson offers valuable insights that can make a significant difference. It explores various aspects of anxiety and depression, including their causes, symptoms, and the impact they can have on our daily lives.
A key focus of this lesson is on coping mechanisms and strategies that can be employed to effectively alleviate anxiety and depression. The answers provided in this chapter are based on evidence-based practices and proven techniques. By implementing these strategies, individuals can develop healthier coping mechanisms and pave the way for a more balanced and happy life.
Understanding Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are two common mental health conditions that can significantly impact a person’s daily life and overall well-being. It is important to understand these conditions in order to provide support and seek appropriate treatment.
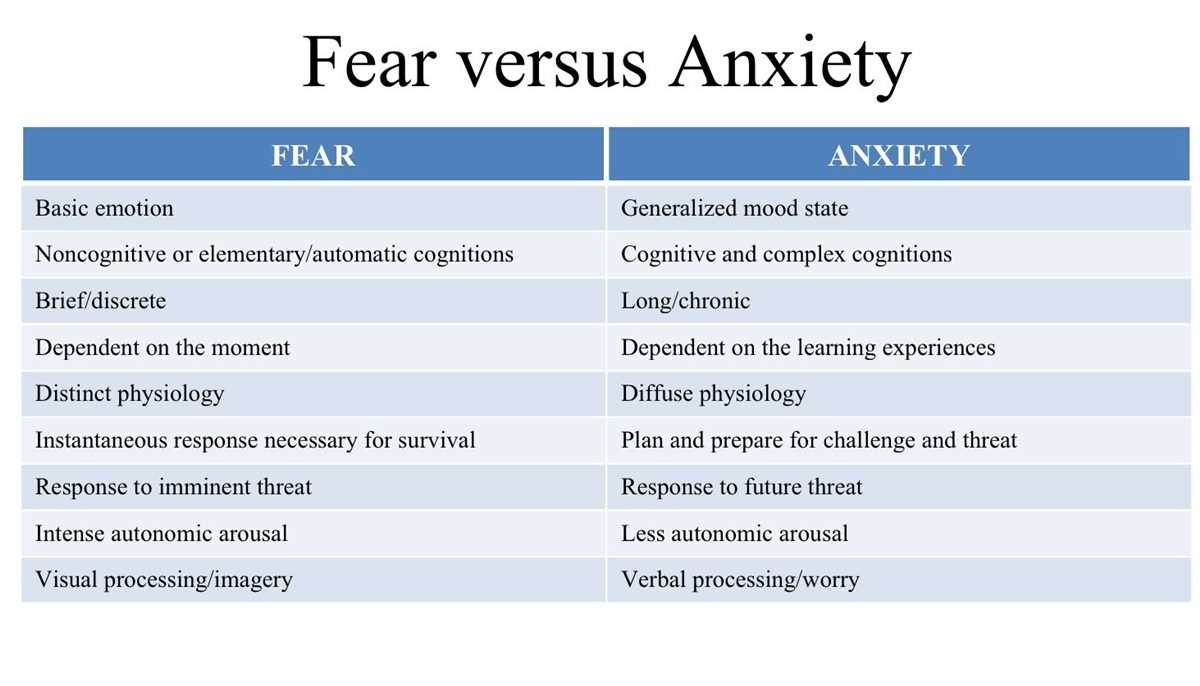
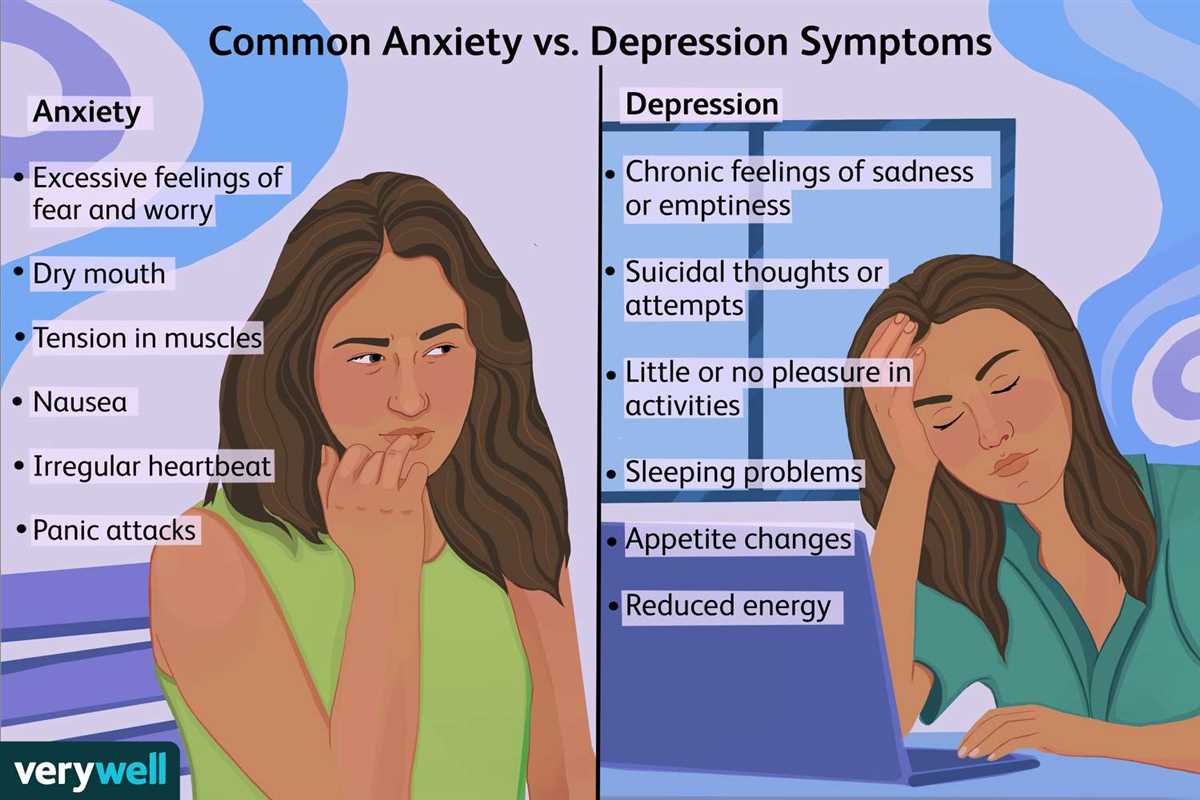
Anxiety: Anxiety is characterized by persistent and excessive worrying, fear, and anticipation of future events. It can manifest in physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shortness of breath. Anxiety disorders can range from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. People with anxiety may experience difficulty in concentration, restlessness, and irritability, making it challenging for them to engage in everyday activities.
Depression: Depression is a mood disorder that affects how a person feels, thinks, and handles daily activities. It is characterized by a persistent feeling of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, and a lack of energy. Depression can also cause physical symptoms such as changes in appetite and sleep patterns, difficulty in concentrating, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, and suicidal thoughts. Major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and postpartum depression are some of the different forms of depression that individuals may experience.
Treatment and Support: Both anxiety and depression can be treated and managed with a combination of therapy, medication, and support. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, is often used in the treatment of anxiety and depression. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines may also be prescribed to help manage symptoms. Additionally, having a strong support system of family, friends, and mental health professionals can provide the necessary guidance and understanding for individuals dealing with anxiety or depression.
Self-Care: In addition to professional help, practicing self-care is crucial for individuals with anxiety and depression. This can involve engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies. Developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as deep breathing exercises or journaling, can also help manage symptoms. It is important for individuals to prioritize their mental health by setting boundaries, seeking help when needed, and practicing self-compassion.
In conclusion, anxiety and depression are complex mental health conditions that can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives. By understanding the symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and practicing self-care, individuals can take steps towards managing and overcoming these conditions to live healthier and happier lives.
What are Anxiety and Depression?
Anxiety and depression are two common mental health disorders that can have a significant impact on a person’s life. They are often experienced together and can be debilitating if left untreated.
Anxiety is characterized by excessive worry, fear, and uneasiness. It can manifest in various forms such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. People with anxiety may constantly anticipate negative outcomes and have difficulty controlling their racing thoughts. Physical symptoms such as restlessness, shortness of breath, and rapid heartbeat are also common.
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities. It can affect a person’s energy levels, appetite, and sleep patterns. Depression can make it difficult to function and enjoy life, often leading to social withdrawal and feelings of isolation. It can also be accompanied by physical symptoms such as changes in appetite and unexplained aches and pains.
Both anxiety and depression are complex conditions that can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, and life experiences. It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of anxiety or depression, as these disorders can be effectively treated with therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Causes of Anxiety and Depression

Anxiety and depression are complex mental health conditions that can have various underlying causes. While each individual may have a unique combination of factors contributing to their anxiety or depression, there are some common causes that are often observed.
One major cause of anxiety and depression is genetics. Research suggests that individuals with a family history of these conditions are more likely to experience them themselves. Certain genes may make an individual more susceptible to developing anxiety or depression in response to stress or other triggers. Additionally, imbalances in brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, are also believed to play a role in anxiety and depression.
Environmental factors
- Stressful life events: Traumatic experiences, such as the loss of a loved one, abuse, or a major life change, can trigger anxiety and depression in susceptible individuals.
- Chronic stress: Prolonged exposure to stress, such as a demanding job, financial difficulties, or relationship problems, can contribute to the development of anxiety and depression.
- Childhood experiences: Adverse experiences during childhood, such as neglect, abuse, or parental substance abuse, can increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression later in life.
- Social environment: Factors like social isolation, lack of social support, or being in an unsupportive or abusive relationship can also contribute to anxiety and depression.
Psychological factors
- Negative thinking patterns: People who tend to have pessimistic or negative thinking patterns may be more prone to anxiety and depression.
- Personality traits: Certain personality traits, such as being highly self-critical, perfectionistic, or having low self-esteem, can increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression.
- Previous mental health conditions: Individuals who have had previous episodes of anxiety or depression are more likely to experience them again in the future.
It is important to note that anxiety and depression are multi-faceted conditions, and the underlying causes can vary from person to person. Identifying and understanding these causes can be crucial in developing an effective treatment plan and providing appropriate support for those affected.
Common Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are two separate mental health conditions, but they can often occur together and share some common symptoms. These symptoms can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily functioning and overall well-being. It is essential to recognize and understand these symptoms to seek appropriate help and support.
Anxiety Symptoms:
- Excessive worrying and feeling tense or on edge
- Racing thoughts and inability to concentrate
- Restlessness and irritability
- Physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and trembling
- Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep
- Panic attacks characterized by sudden and intense fear
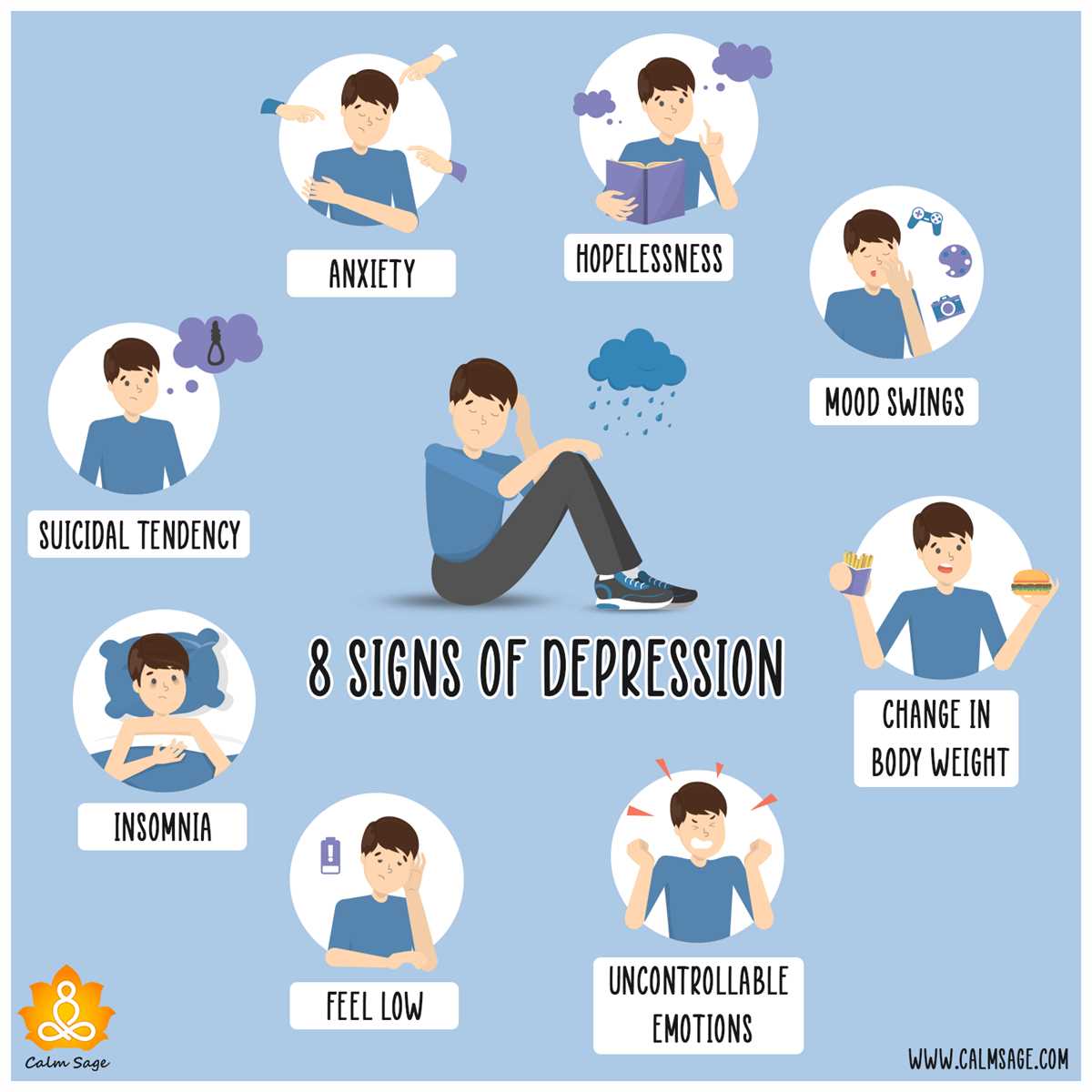
Depression Symptoms:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed
- Significant changes in appetite and weight
- Low energy and fatigue
- Trouble concentrating and making decisions
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or helplessness
- Thoughts of death or suicide
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and duration from person to person. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to reach out to a healthcare professional or mental health provider for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
How to Deal with Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are common mental health disorders that can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. It’s important to recognize the signs and symptoms of these conditions and seek help when needed. Here are some strategies and techniques that can help individuals manage anxiety and depression.
1. Seek Professional Help: If you’re experiencing anxiety or depression, it’s important to reach out to a mental health professional. They can provide you with an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan that may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
2. Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. These techniques promote a sense of calmness and relaxation, allowing individuals to better manage their emotions.
3. Engage in Regular Physical Exercise: Regular physical exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on mental health. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, or dancing can help reduce anxiety and depression symptoms.
4. Establish a Supportive Network: Surrounding yourself with supportive and understanding individuals can make a significant difference in managing anxiety and depression. Building a strong network of friends, family, or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and offer emotional support during difficult times.
5. Manage Stress: Finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial in dealing with anxiety and depression. This can include practicing time management, setting realistic goals, and engaging in stress-reducing activities such as hobbies, journaling, or spending time in nature.
6. Challenge Negative Thoughts: Negative thinking patterns can worsen symptoms of anxiety and depression. It’s important to challenge and reframe negative thoughts by focusing on positive aspects of life, practicing gratitude, and seeking out evidence to support positive beliefs.
7. Take Care of Yourself: Self-care is essential in managing anxiety and depression. This can include getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment. Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being is crucial for overall mental health.
By implementing these strategies and seeking professional help, individuals can effectively manage their anxiety and depression and improve their overall well-being. It’s important to remember that everyone’s journey is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, it’s essential to find the methods and techniques that work best for you.
Seeking Professional Help for Anxiety and Depression
Therapists and Counselors: One of the primary ways to seek professional help for anxiety and depression is through therapy or counseling. Therapists and counselors are trained experts who can provide guidance and support in a safe and confidential environment. They can help you identify and address the root causes of your anxiety and depression, develop coping strategies, and work towards developing healthier thought patterns and behaviors.
Psychiatrists and Psychologists: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage symptoms of anxiety and depression. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health and can prescribe medication to help alleviate symptoms. Psychologists, on the other hand, focus on therapy and do not prescribe medication. It may be beneficial to consult with both a psychiatrist and psychologist to receive comprehensive care.
Support Groups: Support groups can also be a valuable resource for individuals dealing with anxiety and depression. These groups provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, offer support, and learn from others who are going through similar struggles. Support groups may be facilitated by a mental health professional or led by peers who have firsthand experience with anxiety and depression.
Choosing a Professional: When seeking professional help for anxiety and depression, it is essential to find a professional who is the right fit for you. Consider factors such as their expertise, approach to therapy, and your comfort level. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek out multiple professionals until you find the one that feels right for you.
Remember: Seeking professional help for anxiety and depression is a brave and important step towards improving your mental health. There is no shame in asking for support, and it can make a significant difference in your overall well-being. You don’t have to face these challenges alone – there are professionals ready to help you on your journey to recovery.
Tips for Supporting Someone with Anxiety and Depression
Supporting someone with anxiety and depression can be challenging, but your presence and understanding can make a significant difference. Here are some helpful tips:
- Be a good listener: Listening is one of the most important things you can do for someone with anxiety and depression. Allow them to express their thoughts and feelings without judgment or interruptions. Offer your full attention and validate their experiences.
- Show empathy: Understand that anxiety and depression are real and can be debilitating for the person experiencing them. Try to put yourself in their shoes and imagine what they might be going through. Offer reassurance and support, letting them know that you are there for them.
- Educate yourself: Learn more about anxiety and depression to better understand the challenges your loved one is facing. This knowledge can help you provide appropriate support and guidance.
- Encourage professional help: If the person is open to it, encourage them to seek professional help. Offer to help them find resources, accompany them to appointments, or provide transportation if needed.
- Be patient: Recovery takes time, and there may be setbacks along the way. It’s crucial to be patient and not push the person to “get over” their anxiety and depression. Offer support and understanding as they navigate their journey towards healing.
- Offer practical assistance: Help with everyday tasks like cooking, cleaning, or running errands can alleviate some of the stress and pressure for someone with anxiety and depression. Even small gestures can make a big difference.
- Encourage self-care: Remind your loved one of the importance of self-care. Encourage them to engage in activities they enjoy, practice relaxation techniques, and prioritize their physical and mental well-being.
- Check in regularly: Keep in touch with your loved one regularly and let them know that you are available to support them. Regular check-ins can provide a sense of connection and offer an opportunity for them to share their feelings or concerns.
Remember, every person’s experience with anxiety and depression is unique, so it’s essential to be sensitive and responsive to their individual needs. By offering support, understanding, and encouragement, you can be a vital source of comfort and strength for someone navigating these challenges.