
Welcome to the chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet Answers. In this article, we will explore the concept of covalent bonding and its various aspects. Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding that occurs between atoms when they share electrons. Unlike ionic bonding, where electrons are transferred from one atom to another, covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons. This sharing allows atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration and form molecules.
In this worksheet, we will cover various topics related to covalent bonding, including Lewis structures, molecular geometry, and the properties of covalent compounds. We will also provide detailed answers to the accompanying questions to help you solidify your understanding of these concepts. By the end of this worksheet, you will have a clear understanding of covalent bonding and be able to apply this knowledge to solve problems.
Whether you are a student studying chemistry or a professional in the field, this chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet Answers will serve as a valuable resource. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of covalent bonding!
The Basics of Covalent Bonding: A Guide
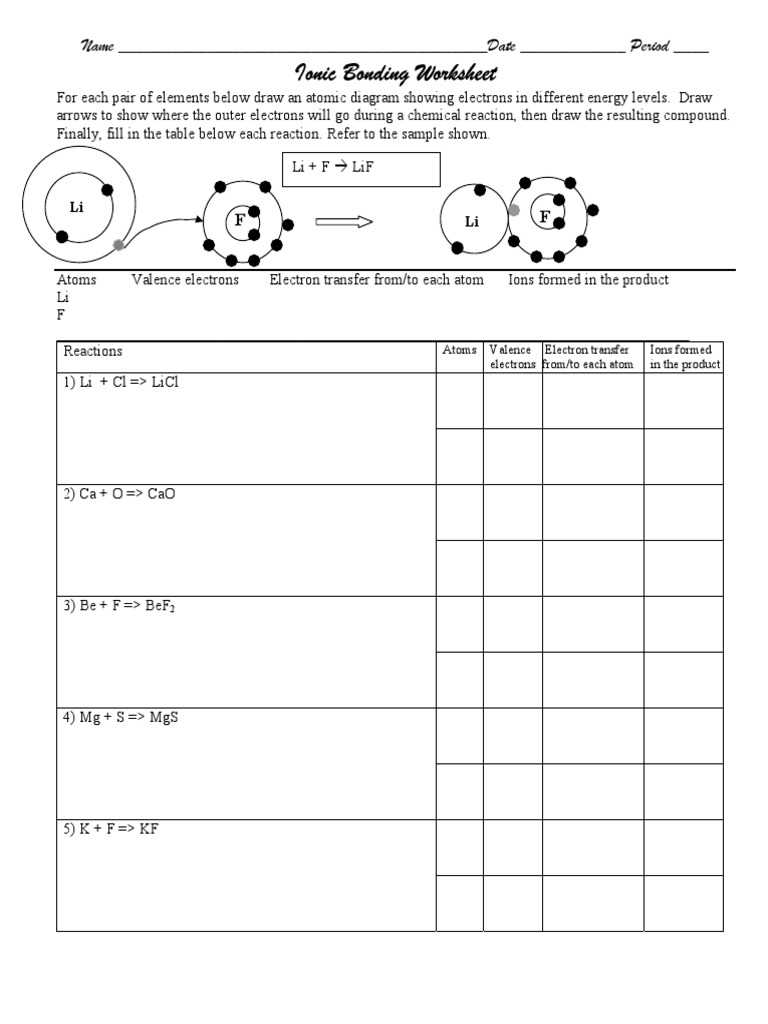
Covalent bonding is one of the fundamental concepts in chemistry. It is a type of chemical bonding that involves the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms. This allows atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration by filling their outermost electron shells. Covalent bonding is typically observed between nonmetallic elements, such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen.
In a covalent bond, each atom contributes one or more electrons to the shared electron pair. These electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a strong bond that holds the atoms together. The shared electrons are often represented using Lewis dot structures, where each dot represents a valence electron. The number of dots surrounding an atom in the Lewis structure corresponds to the number of electrons it shares in a covalent bond.
Covalent bonds can be classified as either polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativities between the atoms involved. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not shared equally, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. This creates a dipole, or a separation of positive and negative charges within the molecule. Nonpolar covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve equal sharing of electrons and do not create dipoles.
In summary, covalent bonding plays a vital role in the formation of molecules by allowing atoms to share electrons and achieve stability. It can result in polar or nonpolar bonds, depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved. Understanding the basics of covalent bonding is crucial for studying and predicting the chemical behavior of substances.
Understanding Covalent Bonding: Key Concepts and Definitions
Covalent bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. In a covalent bond, the atoms are held together by the shared electrons, which are attracted to the positive nuclei of both atoms. This type of bonding is typically found between nonmetal atoms.
Electronegativity is a key concept in covalent bonding. It is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. The difference in electronegativity between two atoms determines the type of covalent bond formed. If the electronegativity difference is small, a nonpolar covalent bond is formed, where electrons are shared equally between the atoms. If the electronegativity difference is large, a polar covalent bond is formed, where electrons are shared unequally and one atom has a partial negative charge while the other has a partial positive charge.
Another important concept in covalent bonding is the octet rule. This rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons. This is known as the octet rule because most atoms are most stable when they have eight valence electrons, similar to noble gases.
The Lewis structure is a way to represent covalent bonding using dots and lines. Each dot represents a valence electron, and each line represents a covalent bond. The Lewis structure helps visualize the bonding arrangement and the distribution of electrons in a molecule or compound.
In summary, understanding covalent bonding involves concepts such as electronegativity, polar and nonpolar covalent bonds, the octet rule, and the use of Lewis structures. These concepts help explain how atoms form covalent bonds and how electrons are shared between them to create stable and balanced chemical structures.
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet: Overview and Importance

The Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the concept of covalent bonds and their significance in chemistry. This worksheet is an essential resource for students studying chemical bonding and related topics.
Covalent bonding occurs when two nonmetal atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The worksheet covers various aspects of covalent bonding, such as Lewis structures, molecular formulas, and bonding theories. It also explores the properties and characteristics of covalent compounds, including their physical and chemical properties.
The worksheet includes numerous exercises and problems that allow students to practice their understanding of covalent bonding concepts and apply them to real-life scenarios. By working through these exercises, students can develop their problem-solving skills and gain a deeper grasp of the subject matter.
Key Concepts Covered in the Worksheet:
- Definition and examples of covalent bonding
- Comparison of covalent bonding with other types of chemical bonding
- Lewis dot structures and molecular formulas
- Electronegativity and polarity in covalent compounds
- Bonding theories, including Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory
The Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet is an essential tool for students to build a strong foundation in covalent bonding and its applications in chemistry. It provides a comprehensive overview of the topic and offers ample opportunities for practice and reinforcement of the key concepts.
Exploring Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet Answers
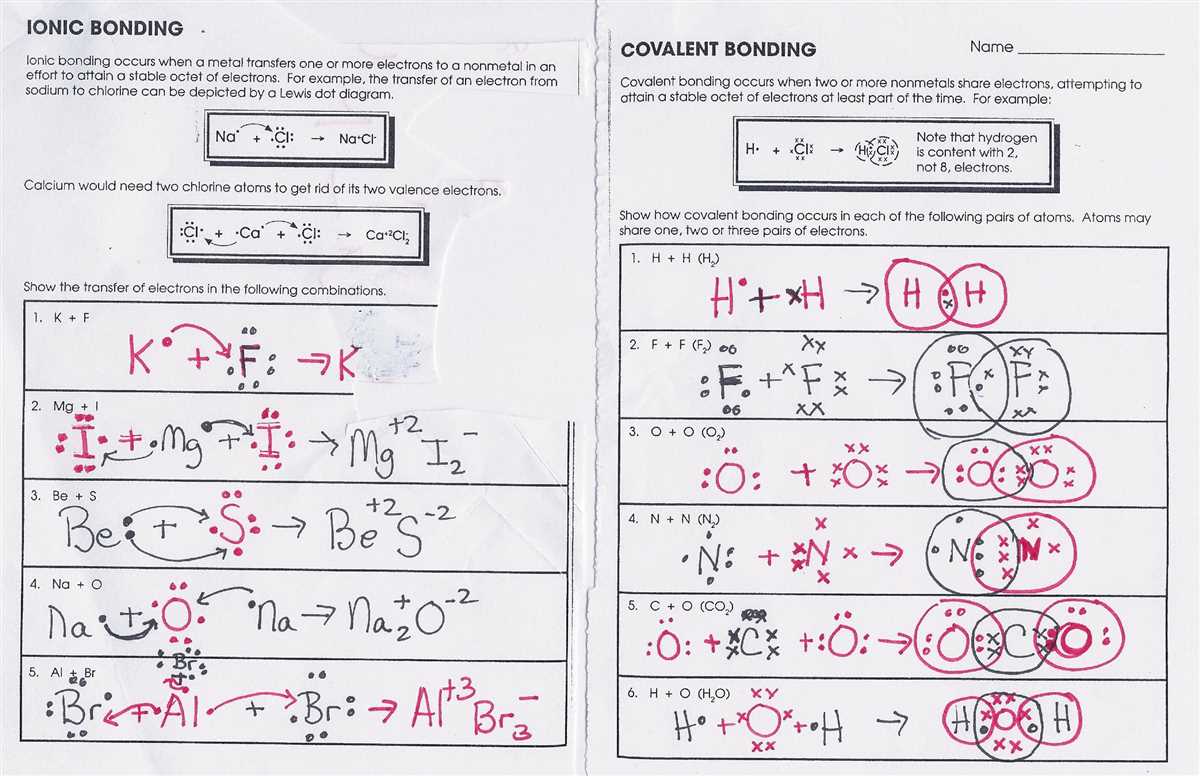
In Chapter 8 of the chemistry textbook, students are introduced to the concept of covalent bonding. Covalent bonds occur when two atoms share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. This chapter provides a thorough exploration of covalent bonding, including its definition, properties, and examples of compounds formed through this type of bond.
One of the key concepts covered in this chapter is the Lewis structure, which is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom and the bonds that it forms. The Lewis structure allows students to visually understand how electrons are shared between atoms to form covalent bonds. The worksheet associated with this chapter provides practice problems for students to draw Lewis structures for various molecules.
The answers to the covalent bonding worksheet provide students with a helpful resource to check their work and ensure they have correctly drawn the Lewis structures. These answers also serve as a guide for students who may be struggling with understanding the concepts presented in the chapter. By referring to the provided answers, students can identify any mistakes they may have made and gain a better understanding of how to correctly draw Lewis structures.
Overall, the exploration of Chapter 8 covalent bonding worksheet answers allows students to solidify their understanding of covalent bonds and Lewis structures. Through the practice problems and their corresponding answers, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their ability to accurately represent covalent bonds. This chapter provides an important foundation for further study of chemical bonding and the understanding of complex molecules.
Common Challenges and Mistakes in Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet
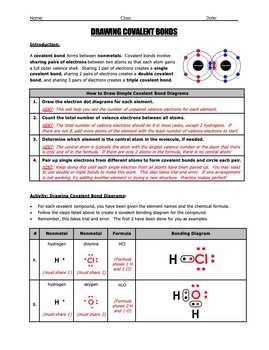
Chapter 8 of the covalent bonding worksheet can present several challenges for students. Understanding the concept of covalent bonds and how they form between nonmetal atoms can be confusing. One common mistake is thinking that covalent bonding only occurs when two atoms share one electron. In reality, covalent bonding involves the sharing of electron pairs, with each atom contributing one or more electrons.
Another challenge is identifying the correct number of shared electron pairs in a covalent bond. Students may mistakenly think that the number of shared electron pairs is equal to the number of available valence electrons for each atom. However, it is essential to consider the octet rule, which states that most atoms strive to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons.
Some common mistakes students make include:
- Incorrectly drawing Lewis dot structures by not representing all valence electrons for each atom.
- Not considering the formal charge of each atom when determining the most stable Lewis dot structure.
- Confusing the terms “polar covalent bond” and “nonpolar covalent bond” and not understanding the factors that determine the polarity of a bond.
- Misconceptions about the strength of covalent bonds and how bond length and bond energy are related.
In order to overcome these challenges and avoid common mistakes, students should practice drawing Lewis dot structures and determining the number of shared electron pairs for different covalent compounds. They should also understand the factors that determine the polarity of a bond, such as differences in electronegativity between the atoms involved.
By familiarizing themselves with these concepts and practicing problem-solving, students can develop a solid understanding of covalent bonding and successfully complete the Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Worksheet.
Tips and Strategies for Mastering Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Concepts
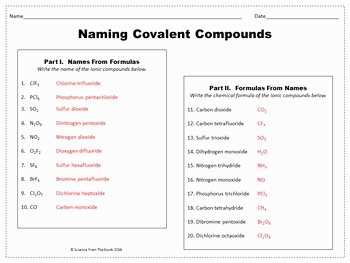
Chapter 8 of your chemistry textbook focuses on covalent bonding, a key concept in understanding the nature of chemical compounds. Covalent bonds occur when two atoms share electrons in a way that allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. This chapter covers topics such as Lewis dot structures, molecular shapes, bond polarity, and the intermolecular forces present in covalent compounds.
To successfully master the concepts presented in Chapter 8, it is important to employ effective study strategies and techniques. Here are some tips to help you excel in your understanding of covalent bonding:
- Review Lewis dot structures: Understanding how to draw Lewis dot structures is crucial in determining the number and arrangement of electrons in covalent compounds. Practice drawing Lewis dot structures for different molecules and ions to reinforce your understanding of this fundamental concept.
- Master molecular shapes: Molecular geometry plays a significant role in determining the physical and chemical properties of covalent compounds. Familiarize yourself with the various molecular shapes and their corresponding bond angles. Use molecular models or online simulators to visualize and manipulate different molecular shapes.
- Understand bond polarity: Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved. Learn how to determine bond polarity using electronegativity values and the concept of dipole moments. Practice identifying polar and nonpolar covalent bonds to enhance your skills in this area.
- Recognize intermolecular forces: Covalent compounds exhibit different types of intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding. Familiarize yourself with the characteristics and strength of each intermolecular force. Use examples and real-life applications to solidify your understanding of these concepts.
- Practice problem-solving: Regularly solve practice problems and exercises related to covalent bonding. Work through a variety of problems that require you to apply the concepts covered in the chapter. This will help you develop problem-solving skills and reinforce your understanding of the material.
- Seek additional resources: If you find yourself struggling with specific concepts or need further clarification, don’t hesitate to seek additional resources. Consult your textbook’s accompanying resources, such as online tutorials or interactive quizzes. Additionally, consider reaching out to your instructor or forming study groups with classmates for collaborative learning.
By following these tips and strategies, you will be well-equipped to master the concepts presented in Chapter 8 of your chemistry textbook. Remember to practice regularly and seek assistance when needed. With dedication and perseverance, you can confidently navigate the complexities of covalent bonding and excel in your chemistry studies.