
Welcome to this comprehensive review for your upcoming chemical bonding test! In this article, we will cover the key concepts and principles related to chemical bonding that you need to know for the exam. Whether you are a high school student preparing for a chemistry test or a college student revisiting the fundamentals, this review will help you solidify your understanding of chemical bonding.
Chemical bonding is a crucial topic in chemistry as it explains how atoms come together to form compounds. Understanding chemical bonding allows us to predict the properties and behavior of substances, which is essential in many scientific and industrial applications. This review will cover the different types of chemical bonds, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, as well as their respective properties and characteristics.
Throughout this review, we will explore topics such as Lewis dot structures, electronegativity, valence electrons, and molecular geometry. These concepts play a fundamental role in understanding how atoms bond and arrange themselves in molecules. By mastering these concepts, you will be able to analyze and predict the stability, reactivity, and physical properties of various substances.
Understanding Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand how atoms combine to form molecules. It refers to the attractive forces that hold atoms together in a chemical compound. By studying chemical bonding, scientists are able to explain the properties and behaviors of different substances.
One of the key types of chemical bonding is called covalent bonding. This occurs when atoms share electrons in order to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Covalent bonds are typically formed between nonmetal atoms, and they can result in the formation of molecules or polyatomic ions. The strength of a covalent bond depends on factors such as the number of shared electrons and the distance between the bonded atoms.
Another important type of chemical bonding is ionic bonding. This occurs when there is a transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. Positive ions, called cations, are formed when an atom loses electrons, while negative ions, called anions, are formed when an atom gains electrons. These oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other, forming an ionic bond. Ionic compounds, such as table salt (NaCl), have high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
- Chemical bonding involves attractive forces that hold atoms together in compounds.
- Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons, while ionic bonding involves a transfer of electrons.
- Understanding chemical bonding helps explain the properties and behaviors of substances.
Types of Chemical Bonding
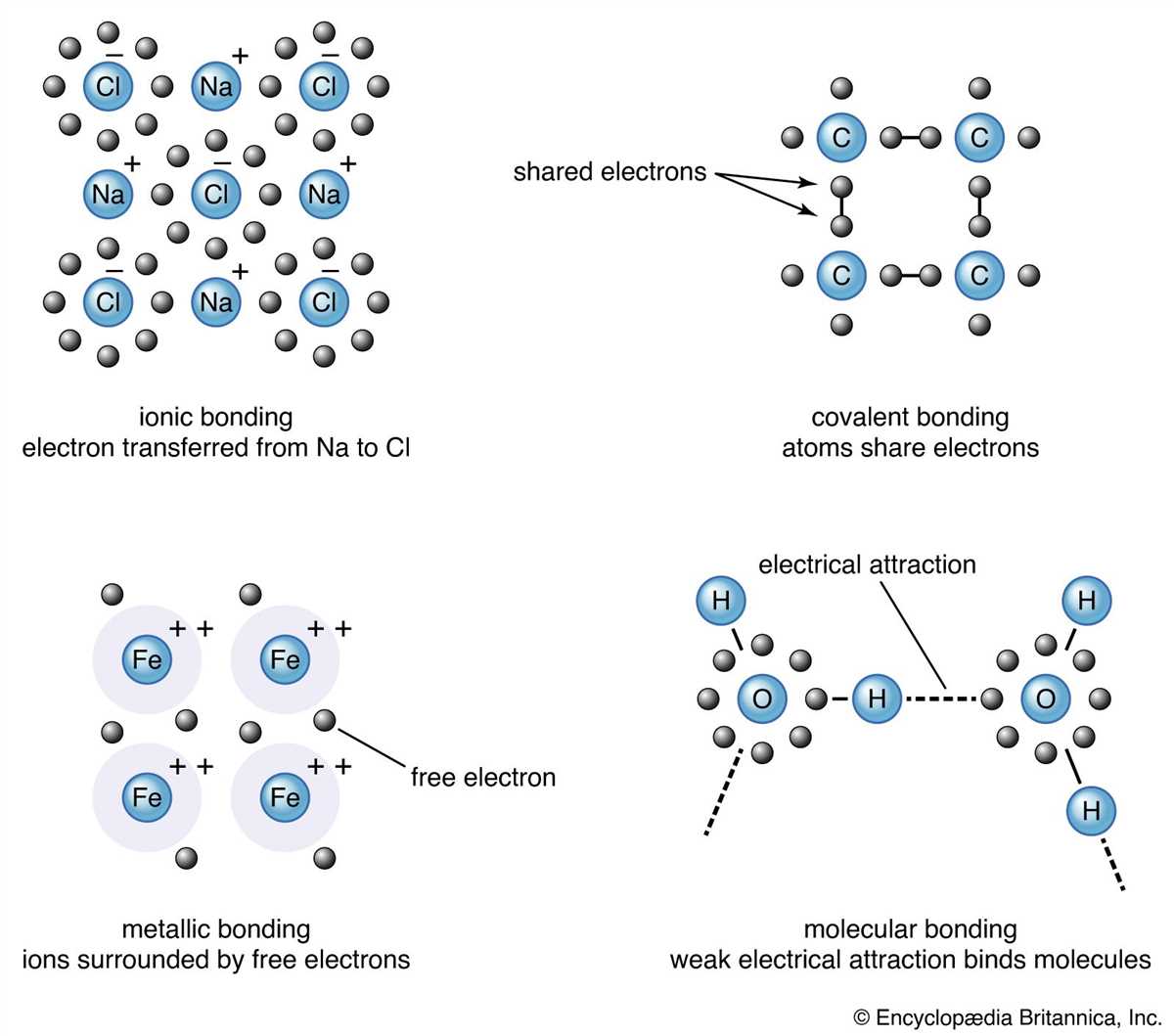
In chemistry, chemical bonding refers to the process of combining two or more atoms to form a molecule. There are three main types of chemical bonding: ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding. Each type of bonding involves a different level of electron sharing or transfer between atoms.
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of ions. In this type of bonding, one atom becomes positively charged (cation) by losing electrons, while the other atom becomes negatively charged (anion) by gaining electrons. The attraction between these opposite charges creates an ionic bond. Ionic bonds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals.
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. In this type of bonding, both atoms contribute one or more electrons to the shared electron pair. The shared electrons form a bond that holds the atoms together. Covalent bonds are typically formed between nonmetals.
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is found in metallic elements and alloys. In this type of bonding, metal atoms share their valence electrons freely, forming a “sea” of delocalized electrons. The positive metal ions are surrounded by this sea of electrons, which allows them to move freely, making metals good conductors of electricity and heat. Metallic bonding gives metals their unique properties such as malleability and ductility.
- Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms.
- Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Metallic bonding involves the sharing of valence electrons in a sea of delocalized electrons.
Understanding the different types of chemical bonding is essential in predicting and explaining the properties and behavior of compounds and materials.
Key concepts in chemical bonding
Chemical bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that refers to the attractive forces that hold atoms together in compounds. Understanding the key concepts of chemical bonding is crucial for understanding the nature of matter and the behavior of substances.
1. Ionic bonding: Ionic bonding occurs when atoms gain or lose electrons to form charged ions. This type of bonding is typically seen between metals and nonmetals. In an ionic bond, the metal atom loses electron(s) to form a positive ion, while the nonmetal atom gains electron(s) to form a negative ion. These oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other and held together by electrostatic forces.
2. Covalent bonding: Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons to form a stable electron configuration. This type of bonding is typically seen between nonmetals. In a covalent bond, two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons create a bond between the atoms, holding them together. Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms.
3. Metallic bonding: Metallic bonding occurs between metal atoms in a lattice structure. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of metal atoms are delocalized and free to move throughout the structure. This creates a “sea” of electrons that holds the metal atoms together. Metallic bonding is responsible for the unique properties of metals, such as their conductivity and malleability.
4. Intermolecular forces: Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction between molecules. These forces are weaker than chemical bonds but still play a significant role in determining the physical properties of substances. Examples of intermolecular forces include dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces.
5. Lewis dot structures: Lewis dot structures are diagrams that show the arrangement of valence electrons in an atom or molecule. These structures are useful for understanding the bonding and predicting the molecular geometry of compounds. In a Lewis dot structure, the valence electrons are represented as dots around the symbol of the element.
- Key concepts in chemical bonding include ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding, as well as intermolecular forces and Lewis dot structures.
- Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, while covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons.
- Metallic bonding involves the delocalization of electrons in a lattice structure.
- Intermolecular forces are weaker than chemical bonds but still influence the properties of substances.
- Lewis dot structures are diagrams that show the arrangement of valence electrons in atoms and molecules.
Common questions about chemical bonding

Chemical bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the attraction between atoms to form compounds. It is crucial to understand the principles of chemical bonding to predict the properties and behavior of substances. Here are some common questions about chemical bonding:
What is a chemical bond?
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that enables them to form stable compounds. Atoms can achieve stability by either gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. The type of bond formed depends on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms.
What are the different types of chemical bonds?
There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds involve a transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions. Covalent bonds occur when atoms share electrons to achieve stability. Metallic bonds are found in metals, where electrons are delocalized and move freely throughout the structure.
How do you determine the type of bond formed between atoms?
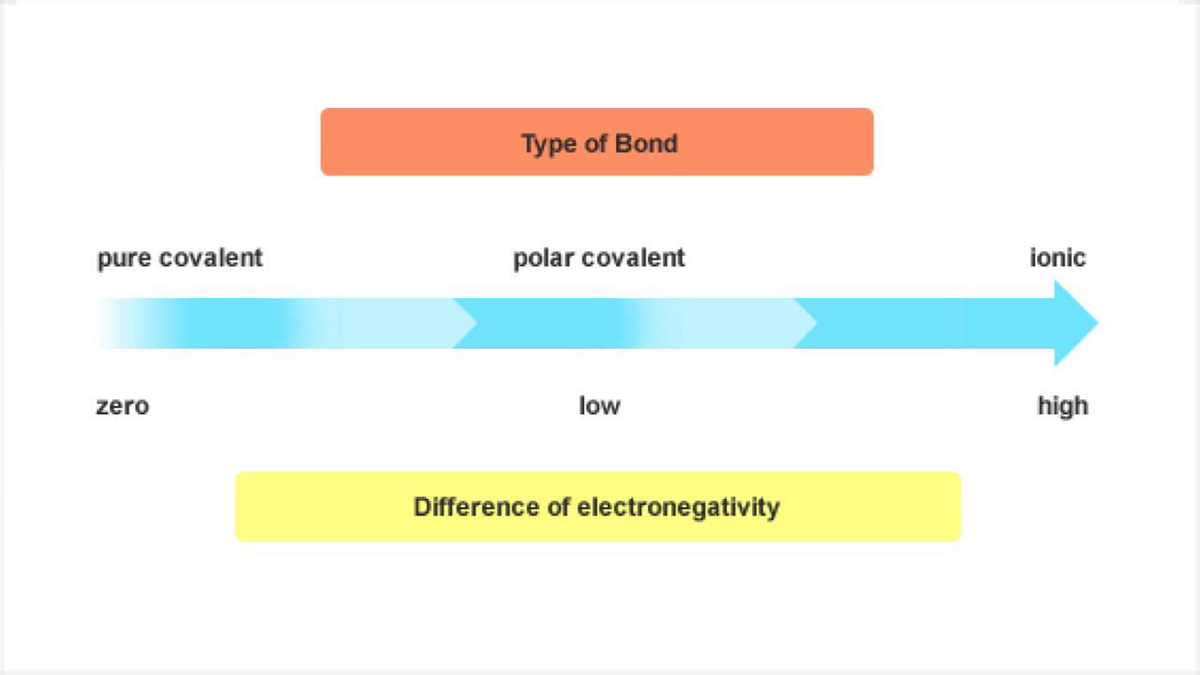
The type of bond formed between atoms can be determined by comparing their electronegativity values. If the electronegativity difference is large, an ionic bond is likely to form. If the electronegativity difference is smaller, a covalent bond is more probable. If the electronegativity difference is negligible, a metallic bond may be present.
What are some examples of compounds with different types of chemical bonds?
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an example of a compound with an ionic bond. Sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl), resulting in the formation of Na+ and Cl- ions that are attracted to each other. Water (H2O) is an example of a compound with a covalent bond, where hydrogen (H) shares electrons with oxygen (O) to form a stable molecule. Copper (Cu) is an example of a metal with metallic bonding, where the delocalized electrons hold the copper ions together in a solid lattice.
Tips for Studying Chemical Bonding

Chemical bonding is an important concept in chemistry, and understanding it is crucial for success on a chemical bonding test. Here are some tips to help you study effectively:
1. Review the basics: Before diving into more complex topics, make sure you have a solid understanding of the basics of chemical bonding, including the different types of chemical bonds (ionic, covalent, and metallic) and the role of electrons in bonding.
2. Take notes: As you study, take detailed notes on the key concepts, definitions, and examples of chemical bonding. Summarize the information in your own words to ensure comprehension and make it easier to review later.
3. Practice with examples: Chemical bonding often involves working with formulas and equations. To solidify your understanding, practice solving problems and working through examples. This will help you become familiar with common patterns and techniques.
4. Use visual aids: Diagrams and illustrations can be incredibly helpful in visualizing the concepts of chemical bonding. Use models, drawings, or online resources to see how atoms and molecules interact and bond together. This can make abstract concepts easier to understand and remember.
5. Collaborate with others: Studying with classmates or forming study groups can be beneficial, as you can discuss concepts, explain ideas to each other, and work through problems together. Collaboration can help reinforce your understanding and fill in any gaps in your knowledge.
6. Test yourself: Regularly test your knowledge by completing practice quizzes or working through past exam questions. This will help you identify areas where you need to improve and reinforce what you have already learned.
7. Seek help if needed: If you are struggling to understand certain concepts or need clarification, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher, classmates, or online resources. Understanding chemical bonding can be challenging, but with the right support, you can overcome any obstacles.
By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding of chemical bonding and increase your chances of success on a chemical bonding test. Remember to stay organized, practice regularly, and seek help when needed. Good luck!
Preparing for the Chemical Bonding Test
As the chemical bonding test approaches, it is important to have a solid plan for studying and preparing. Here are some key steps to help you succeed on the test:
- Review your notes: Go through your class notes and make sure you understand the key concepts and principles of chemical bonding. Pay attention to any examples or explanations given by your teacher as they may be similar to the questions on the test.
- Practice problems: Work through a variety of practice problems to reinforce your understanding of chemical bonding concepts. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more challenging ones. This will help you identify any areas where you need more practice.
- Collaborate with classmates: Form a study group with your classmates and review the material together. Discussing the concepts and problem-solving strategies can deepen your understanding and provide different perspectives on the material.
- Use additional resources: Utilize textbooks, online resources, and study guides to supplement your class notes. These resources can provide additional explanations and practice problems to reinforce your knowledge.
- Review previous tests or quizzes: Look over any previous tests or quizzes on chemical bonding to identify areas where you may have struggled. Focus on these areas during your study sessions to ensure you have a solid understanding.
- Create flashcards: Create flashcards with key terms, definitions, and examples related to chemical bonding. Use these flashcards to test your knowledge and review important information.
- Get enough rest: It is important to get enough rest before the test. A good night’s sleep can improve your focus, concentration, and overall performance.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Preparing for the chemical bonding test requires a combination of reviewing class notes, practicing problems, collaborating with classmates, utilizing additional resources, and reviewing previous tests or quizzes. Creating flashcards and getting enough rest are also important aspects of test preparation. By following these steps, you can improve your understanding of chemical bonding and increase your chances of success on the test.