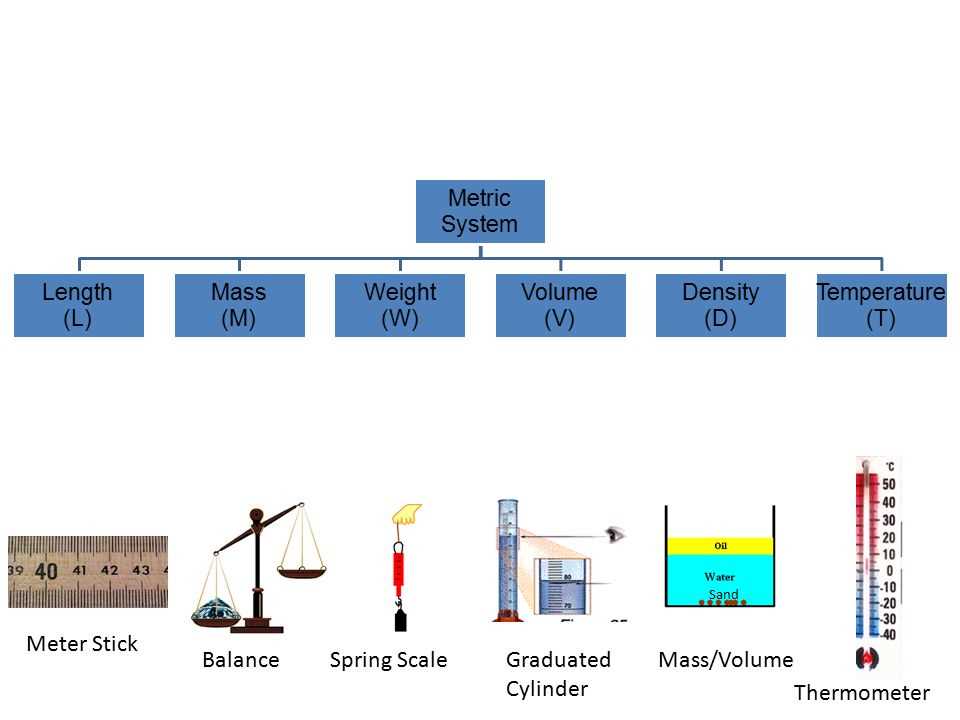
Welcome to our guide for Chemquest 7, where we will be discussing the concepts of density, mass, and weight. In this article, we will provide you with the answer key to the Chemquest 7 worksheet, which will help you understand and practice these key concepts in chemistry. Density, mass, and weight are fundamental properties of matter, and understanding them is essential for various applications in science and everyday life.
In Chemquest 7, you will learn about the relationship between mass and volume, as well as how to calculate density and weight. Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, while volume is the amount of space occupied by the object. Density is the mass per unit volume, and it is commonly used to characterize and compare the properties of different materials. Weight, on the other hand, refers to the force exerted by gravity on an object, and it can vary depending on the location of the object.
By completing the Chemquest 7 worksheet and using the answer key provided, you will be able to practice calculating density, mass, and weight for various objects and substances. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of these concepts and how they are related to one another. Understanding density, mass, and weight is crucial in many scientific disciplines, such as physics and chemistry, and is also useful in everyday situations, such as cooking or determining the appropriate amount of material needed for a construction project.
What is Chemquest 7?
Chemquest 7 is a specific activity or assignment that focuses on the concept of density, mass, and weight in the field of chemistry. It is designed to enhance understanding and knowledge in these areas through various tasks and questions.
In Chemquest 7, students are typically presented with different scenarios and situations where they need to apply their understanding of density, mass, and weight to solve problems and answer questions. This activity allows students to practice calculating density, mass, and weight using the appropriate formulas and units.
Chemquest 7 focuses on the following key concepts:
- The definition and calculation of density
- The relationship between mass and weight
- The use of density to determine unknowns
- Converting units of mass and weight
- Problems related to floating and sinking
Overall, Chemquest 7 serves as a valuable learning tool for students to reinforce their understanding of density, mass, and weight in the field of chemistry. It provides them with opportunities to apply their knowledge and develop problem-solving skills in real-life situations.
Understanding Density
Density: Definition and Formula

Density is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry that measures the compactness of a substance. It is defined as the mass per unit volume of a material. The formula for calculating density is density = mass/volume. In other words, it is the amount of mass packed into a given volume of space. Density is usually expressed in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) or kilograms per liter (kg/L).
To calculate the density of a material, you need to know its mass and volume. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, usually measured in grams or kilograms. Volume, on the other hand, is the amount of space occupied by an object, usually measured in cubic centimeters or liters. By dividing the mass by the volume, you can determine the density of the material.
Importance of Density
Density is an important property of substances as it can provide valuable information about their physical and chemical characteristics. It can help identify and distinguish between different materials, as every substance has a unique density. For example, water has a density of 1 g/cm3, which means that a given volume of water will have a mass of 1 gram. This property allows scientists to identify and differentiate water from other liquids based on its density.
Density also plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of substances in different environments. Objects with lower density than a fluid will float in it, while objects with higher density will sink. This principle is utilized in various applications, such as determining the buoyancy of ships and submarines or designing flotation devices. Additionally, density can also affect other physical properties, including the ability to conduct heat and electricity, the melting and boiling points, and the solubility of substances.
Measuring Density
There are several methods to measure the density of a substance. The most common method is using a density bottle or pycnometer, which involves measuring the mass of an empty bottle, filling it with the substance, and measuring the mass again. The difference in mass is then divided by the volume of the bottle to determine the density. Another method is the displacement method, where an object is submerged in a fluid, and the change in fluid volume is used to calculate the density. Other techniques, such as using a hydrometer or a densitometer, can also be employed depending on the substance and the accuracy required.
Overall, understanding density is crucial in various fields of science, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. By grasping the concept of density and its applications, scientists and engineers can better comprehend the properties and behaviors of different substances, leading to advancements in technology, industry, and our overall understanding of the natural world.
Definition of Density
Density is a physical property of matter that describes the amount of mass of a substance contained in a given volume. It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object or substance by its volume. The unit of density is typically grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) for solids and liquids, or grams per liter (g/L) for gases. Density can also be expressed in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) for larger quantities.
The concept of density is based on the idea that matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms or molecules that are closely packed together. The density of a substance is determined by the arrangement and spacing of these particles. Materials with a higher density have particles that are more closely packed together, while those with a lower density have particles that are more spread out.
The density of a substance is often used to determine its physical properties and behavior. For example, a substance with a higher density will sink in a substance with a lower density in a process known as buoyancy. Additionally, the density of a substance can affect its ability to conduct heat and electricity, as well as its solubility in other substances.
Understanding density is important in various fields, such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. It is used to characterize and compare different materials, determine the composition of mixtures, and analyze the behavior of fluids and gases. By measuring the density of a substance, scientists and engineers can make predictions about its properties and how it will interact with other substances or materials.
Calculating Density
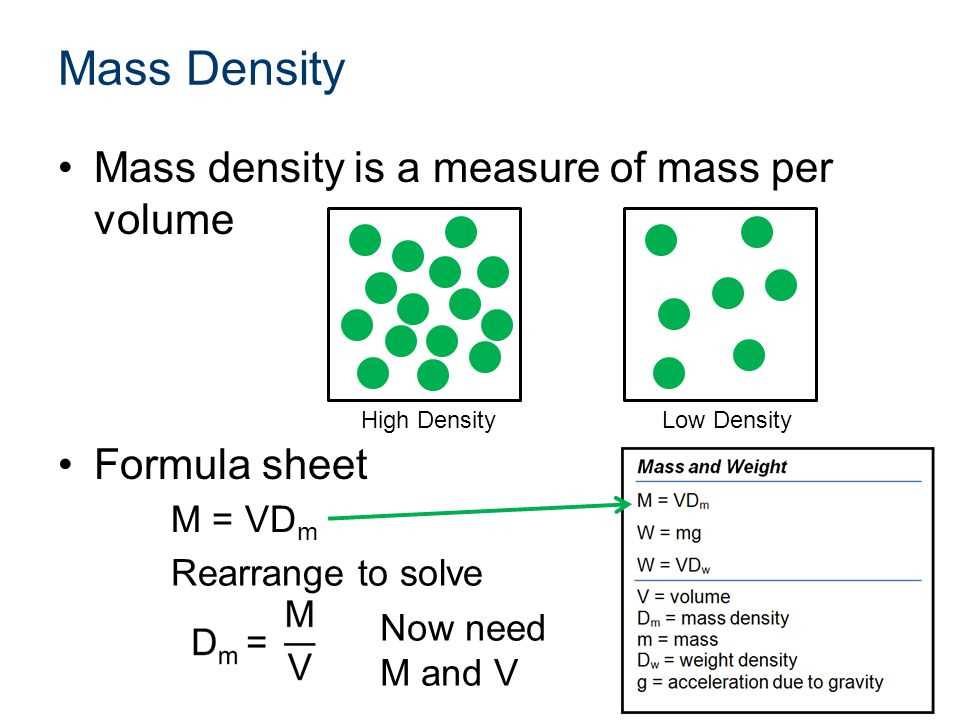
Density is a fundamental property of matter that describes how much mass is contained in a given volume. It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. The formula for density is:
Density = Mass / Volume
In order to calculate the density of an object, you first need to measure its mass and volume. Mass is typically measured using a balance or scale, while volume can be determined using various methods such as measuring the dimensions of an object or using displacement techniques. It is important to use consistent units for both mass and volume in order to obtain an accurate density calculation.
Once you have the mass and volume measurements, you can plug them into the density formula to obtain the density value. The resulting density value will have units of mass per unit volume, such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per liter (kg/L).
Density is an important property in many scientific fields, especially in the study of materials and substances. It can help identify unknown substances, determine the purity of a material, and understand the physical properties of different substances. By calculating and comparing the densities of different materials, scientists can gain insights into their composition and behavior.
In summary, calculating density involves dividing the mass of an object by its volume. It is an important property that helps us understand the characteristics of different substances and materials. By accurately measuring mass and volume and using consistent units, we can calculate the density of an object and gain valuable insights into its properties.
The Formula for Calculating Density
Density is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry that is used to describe the amount of mass in a given volume. It is an important property of matter and has practical applications in various fields, such as engineering, materials science, and geology. The formula for calculating density is relatively simple and can be expressed mathematically.
The formula for calculating density is: density = mass / volume. In other words, density is equal to the mass of an object divided by its volume. This formula can be used to determine the density of various substances, including solids, liquids, and gases.
To calculate the density of an object, you need to know its mass and volume. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is typically measured in grams or kilograms. Volume, on the other hand, is a measure of the amount of space that an object occupies and is usually measured in cubic centimeters or cubic meters.
Once you have the mass and volume of an object, you can simply divide the mass by the volume to find the density. The resulting value will be in units such as grams per cubic centimeter or kilograms per cubic meter, depending on the units used for mass and volume.
It is important to note that density is an intensive property, which means it does not depend on the size or amount of the substance. For example, a small piece of iron and a large block of iron will have the same density because the ratio of mass to volume is the same for both objects.
In summary, the formula for calculating density is a fundamental tool for understanding the physical properties of substances. By knowing the mass and volume of an object, you can determine its density and gain insights into its characteristics and behavior.
Measuring Mass

Measuring mass is an essential part of scientific research and everyday life. Mass is a fundamental property of matter that represents the amount of substance in an object. It is commonly measured in units such as grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
To accurately measure mass, a balance or scale is used. A balance typically consists of a pan where the object being measured is placed and a beam or display that shows the mass. The object is compared to a set of standard weights to determine its mass. A scale, on the other hand, measures the force exerted by an object due to its mass.
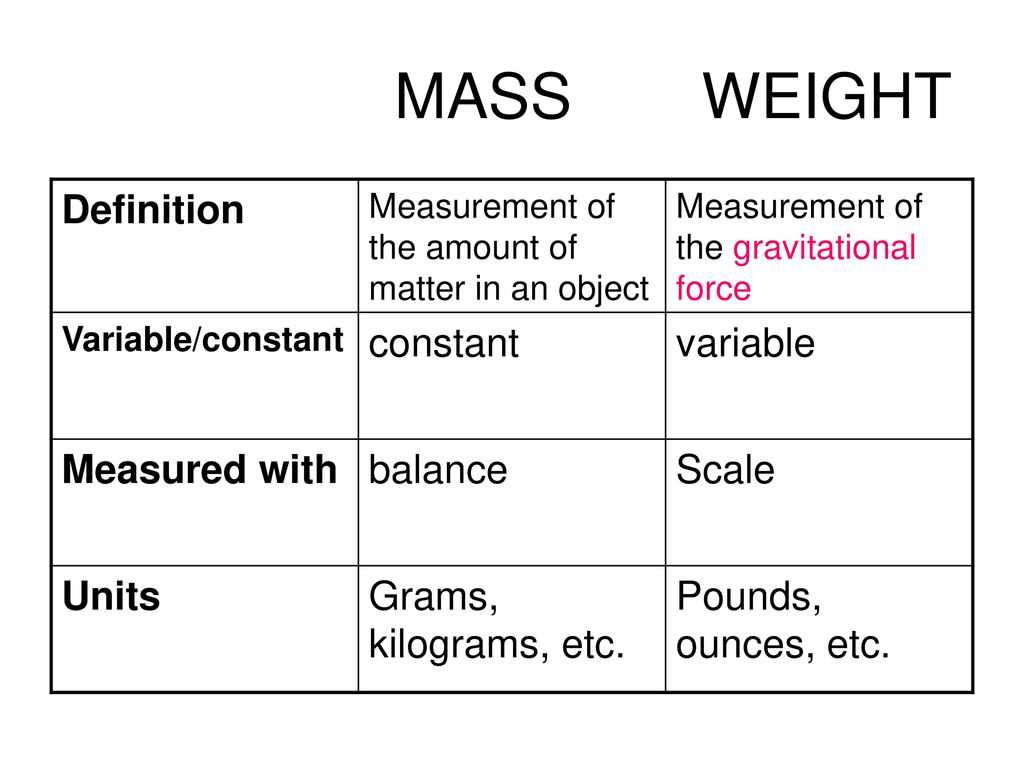
When measuring mass, it is important to distinguish it from weight. While mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains, weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Weight can vary depending on the location, but mass remains constant. This distinction is particularly important when conducting experiments or analyzing data.
In scientific research, measuring mass accurately is crucial for various applications. It is used in chemistry to determine the quantity of substances in a reaction, in physics to calculate momentum and gravitational force, and in biology to weigh specimens and measure biomass. Additionally, mass measurements are essential in fields such as astronomy, engineering, and manufacturing.
Overall, measuring mass plays a significant role in various disciplines and everyday life. It allows scientists to understand the properties of matter, perform accurate experiments, and make informed decisions. Whether it’s in the laboratory, the kitchen, or in industries, having precise mass measurements is essential for ensuring accuracy and reliability in scientific investigations and practical applications.
Methods for Measuring Mass
Measuring mass is an essential part of many scientific experiments and everyday tasks. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, and it can be measured using various methods. Here, we will discuss some common methods for measuring mass.
Balances: In a laboratory setting, balances are often used to measure mass accurately. These devices consist of a pan on one side and a mass standard on the other. The object whose mass needs to be measured is placed on the pan, and weights are added or removed from the mass standard until the balance beam is level. The mass of the object is then determined by the sum of the weights added or removed.
Electronic Scales: In everyday life, electronic scales are commonly used to measure mass. These scales work by using sensors that detect the amount of force applied by an object. The force is converted into an electrical signal, which is then displayed as the mass of the object on a digital screen. Electronic scales are often more convenient and precise than traditional balances.
- Spring Scales: Spring scales are another common tool used to measure mass. They consist of a coiled spring attached to a hook or hanging platform. When an object is hung from the spring, it stretches proportional to the force exerted by the object. The stretching of the spring is then used to determine the mass of the object.
- Water Displacement Method: This method is used when measuring the mass of irregularly shaped objects. The object is submerged in a container of water, and the change in water level is measured. By using the principle of displacement, the mass of the object can be calculated based on the volume of water displaced.
Conclusion: Measuring mass accurately is crucial in various scientific and everyday situations. Balances, electronic scales, spring scales, and the water displacement method are some of the common methods used to measure mass. Each method has its advantages and is suitable for different types of objects or situations. It is important to choose the appropriate method based on the specific requirements of the measurement.
Exploring Weight
In conclusion, understanding weight is crucial in the field of chemistry. Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity, and it can be calculated by multiplying an object’s mass by the acceleration due to gravity. Weight is measured in newtons (N) and is different from mass, which is the amount of matter in an object and is measured in kilograms (kg).
Weight can vary depending on the gravitational pull of a celestial body. For example, an object that weighs 10 N on Earth would weigh less on the moon due to its lower gravitational pull. Additionally, weight can be influenced by factors such as altitude, as the gravitational pull decreases with distance from the Earth’s surface.
It is important to differentiate between weight and density, as they are not the same. Density is the amount of mass per unit volume, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. While an object’s weight can change depending on its location, its density remains constant.
Overall, weight plays a significant role in various applications, including determining the buoyancy of objects in fluids, calculating the pressure exerted by objects on surfaces, and understanding the behavior of objects in different gravitational environments. By understanding weight and its relationship with mass and density, scientists can make accurate predictions and conduct experiments that contribute to advancements in fields such as physics, engineering, and chemistry.