A unit test is an assessment given to students to evaluate their understanding of a specific topic or unit of study. In the case of a circles unit test, students are assessed on their knowledge of various concepts related to circles, including circumference, radius, diameter, central angle, and area.
The test typically consists of a combination of multiple-choice, short answer, and problem-solving questions that require students to apply their understanding of circle properties and formulas. This type of assessment allows teachers to gauge the level of mastery their students have achieved in the study of circles and identify areas where further instruction or review may be necessary.
Preparing for a circles unit test involves studying and reviewing key concepts, formulas, and problem-solving strategies. It is important for students to understand the relationships between different circle properties and how to apply them in various scenarios. Practice problems and sample questions can be helpful in reinforcing understanding and building confidence before the test.
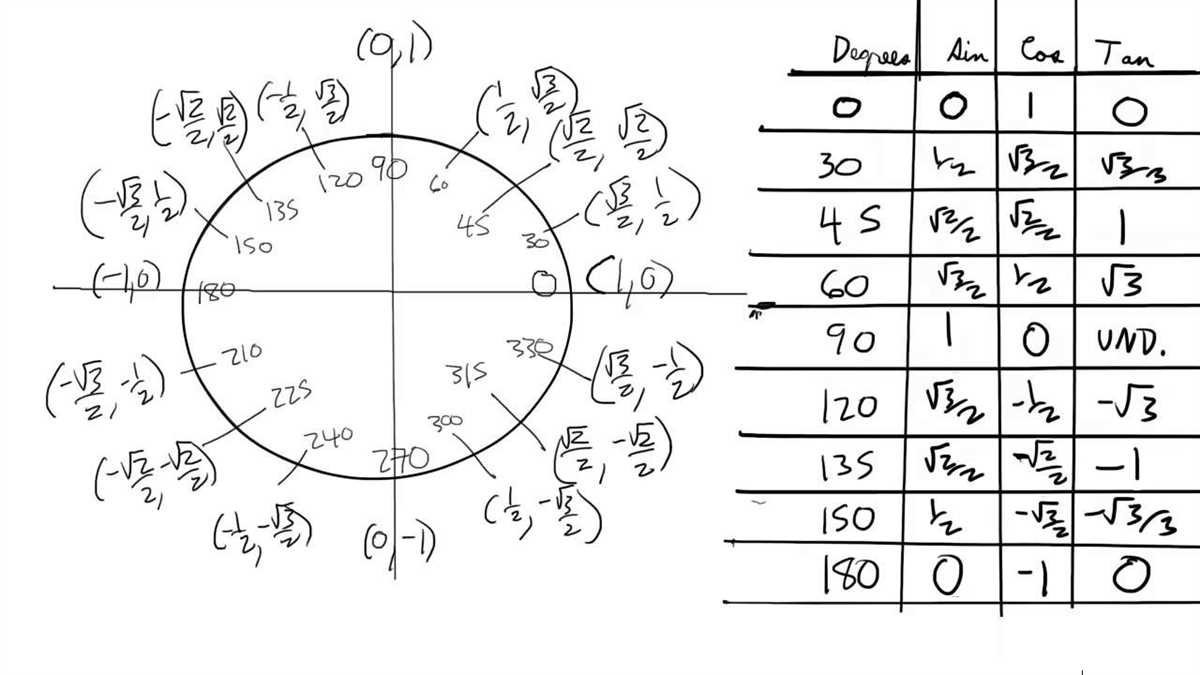
Understanding circles
When it comes to geometry, circles are one of the fundamental shapes that we study. A circle is defined as a perfectly round shape with all points on its boundary equidistant from the center. Understanding circles is important in various fields such as mathematics, architecture, and engineering.
Properties of circles: There are several key properties that help us understand circles better. One of the most important properties is the radius, which is the distance between the center of the circle and any point on its boundary. The diameter, on the other hand, is the distance across the circle passing through the center. Another important property is the circumference, which is the distance around the circle. The formula to calculate the circumference is C = 2πr, where π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
Parts of a circle: A circle can be divided into different parts to aid in its study. The sector is a region bounded by two radii and an arc, while the chord is a straight line segment connecting two points on the circle. The tangent is a line that intersects the circle at exactly one point, and the secant is a line that intersects the circle at two points. Understanding these different parts helps us analyze and solve problems related to circles.
Applications of circles: The study of circles has practical applications in various fields. In mathematics, circles are used in trigonometry, coordinates, and calculus. In architecture, circles are used in designing round structures such as domes and arches. Engineers also use circles in areas such as bridge construction and road curves. Circles are also prevalent in everyday life, from the wheels of a bicycle to the shape of a dinner plate.
In conclusion, understanding circles is essential in geometry and has practical applications in various fields. By knowing the properties and parts of a circle, we can apply this knowledge to solve problems and analyze real-world situations. Circles are not just a mathematical concept but a fundamental shape that plays a significant role in the world around us.
The equation of a circle

A circle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that consists of all the points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. The equation of a circle is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the coordinates of the center of the circle and the distance from the center to any point on the circle’s circumference.
The general equation of a circle in the coordinate plane is (x – h)² + (y – k)² = r², where (h, k) represents the coordinates of the center of the circle, and r represents the radius. This equation is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
To find the equation of a circle, you need to know the coordinates of its center and the length of its radius. Once you have this information, you can plug the values into the equation (x – h)² + (y – k)² = r² and simplify to obtain the final equation of the circle.
The equation of a circle can be useful in various applications, such as geometry, physics, and engineering. It allows us to describe the properties and relationships of circles in a precise and mathematical way. By manipulating the equation, we can determine the distance between two circles, find points of intersection between circles and other geometric objects, and analyze the behavior of objects moving in circular paths.
In summary, the equation of a circle is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the coordinates of the center of the circle and the distance from the center to any point on the circle’s circumference. It is derived from the Pythagorean theorem and can be used to describe and analyze various properties and relationships of circles in different contexts.
Calculating the circumference of a circle
Calculating the circumference of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry. The circumference is defined as the distance around the outer boundary of a circle. It is an important measurement that is used in various applications, such as engineering, architecture, and physics.
To calculate the circumference of a circle, you can use the formula C = 2πr, where C represents the circumference, π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, and r is the radius of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its outer boundary.
Using this formula, you can easily find the circumference of a circle given its radius. For example, if the radius of a circle is 5 units, you can substitute the value into the formula: C = 2π(5) = 10π units. If you need a numerical approximation, you can substitute the value of π with its decimal approximation, such as 3.14, to get an approximate value for the circumference.
It is important to remember that the circumference is always greater than the diameter of a circle. The diameter is the distance across the circle, passing through its center. In fact, the circumference is exactly π times the diameter, or C = πd, where d represents the diameter. This relationship between the circumference and diameter is another way to calculate the circumference of a circle.
In conclusion, calculating the circumference of a circle is a straightforward process using the formula C = 2πr or C = πd. It is an essential concept in geometry and has numerous practical applications in various fields.
Calculating the area of a circle

The area of a circle can be calculated using the formula A = πr^2, where A represents the area and r represents the radius of the circle.
To calculate the area, you need to know the radius of the circle. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. Once you have the value for the radius, you can plug it into the formula and solve for the area.
For example:
- If the radius of a circle is 5 units, the formula becomes A = π * 5^2.
- By squaring the radius (5^2 = 25) and then multiplying by π (approximately 3.14), you can find the area of the circle.
- In this case, the area of the circle would be 3.14 * 25 = 78.5 square units.
It’s important to note that the value for π is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed exactly as a fraction or a decimal. The commonly used approximation for π is 3.14, but for more accurate calculations, you can use more decimal places.
In summary, calculating the area of a circle involves using the formula A = πr^2, where A represents the area and r represents the radius. By plugging in the value for the radius and performing the necessary calculations, you can determine the area of the circle.
Properties of circles
A circle is a two-dimensional figure that consists of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. Understanding the properties of circles is essential in various fields, including mathematics, geometry, and engineering.
One of the fundamental properties of a circle is its radius, which is the distance from the center point to any point on the circle’s circumference. The radius is denoted by the letter ‘r’. The diameter of a circle is the distance between two points on the circle’s circumference that passes through the center point. The diameter is related to the radius by the equation: diameter = 2 * radius.
Another important property of a circle is its circumference, which is the distance around the circle. It is calculated using the formula: circumference = 2 * π * radius, where ‘π’ is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. The area of a circle is the measure of the region enclosed by the circle. It is given by the formula: area = π * (radius)^2.
Circles also have several important angles associated with them. The central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle and whose sides pass through two points on the circle. The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the arc it subtends. Another angle associated with a circle is the inscribed angle, which is an angle formed by two chords that intersect on the circle. The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Overall, the properties of circles play a crucial role in various mathematical and practical applications. Whether it’s calculating the circumference of a wheel, designing circular structures, or understanding the geometrical relationships of circular objects, a solid understanding of circle properties is essential.
Solving problems involving circles

Circle is a fundamental shape in geometry that has many real-life applications. From calculating the area of a circular garden to finding the circumference of a tire, solving problems involving circles requires understanding of various formulas and properties.
One of the key concepts in solving problems related to circles is the use of the radius and diameter. The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference, while the diameter is the distance across the circle passing through the center. These measurements are crucial for calculating the area, circumference, and other properties of circles.
Formulas for solving problems involving circles:

- Area of a circle: The area of a circle can be calculated using the formula A = πr^2, where A represents the area and r represents the radius of the circle.
- Circumference of a circle: The circumference of a circle can be calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where C represents the circumference and r represents the radius of the circle.
- Arc length: The length of an arc can be calculated using the formula L = θ/360 * 2πr, where L represents the length, θ represents the angle of the arc in degrees, and r represents the radius of the circle.
- Sector area: The area of a sector can be calculated using the formula A = θ/360 * πr^2, where A represents the area, θ represents the angle of the sector in degrees, and r represents the radius of the circle.
These formulas allow us to solve a wide range of problems involving circles, such as finding the area of a circular field, the circumference of a bicycle wheel, or the length of an arc in a clock face. By understanding and applying these formulas, we can confidently tackle problems that require circle measurements and properties.
Overall, solving problems involving circles requires a solid understanding of circle properties, measurements, and the use of specific formulas. By practicing and applying these concepts, you can develop proficiency in solving a variety of circle-related problems and enhance your mathematical skills.
Q&A:
How do you find the diameter of a circle?
To find the diameter of a circle, you can either measure the distance across the circle passing through its center, or you can use the formula: diameter = 2 * radius.
What is the formula for finding the circumference of a circle?
The formula for finding the circumference of a circle is: circumference = 2 * π * radius. The value of π, or pi, is approximately 3.14159.
How do you find the area of a circle?
To find the area of a circle, you can use the formula: area = π * radius^2. The value of π, or pi, is approximately 3.14159.
What is the relationship between the radius and diameter of a circle?
The radius of a circle is half of its diameter. This means that if the diameter is 10 units, the radius would be 5 units.
How do you find the circumference of a circle if you know the radius?
If you know the radius of a circle, you can find the circumference using the formula: circumference = 2 * π * radius. Simply substitute the value of the radius into the formula to calculate the circumference.
What is the formula for the circumference of a circle?
The formula for the circumference of a circle is C = 2πr, where C is the circumference and r is the radius of the circle.
How do you find the area of a circle?
The formula for finding the area of a circle is A = πr^2, where A is the area and r is the radius of the circle.