In the study of chemistry, understanding the classification of matter is essential. Matter can be classified into different categories based on its properties and composition. This webquest answer key will provide a comprehensive overview of the classification of matter, exploring the various categories and their characteristics.
One of the primary ways to classify matter is by its state or phase. Matter can exist in three main states – solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but can change shape, and gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume. Understanding the properties and behavior of each state is crucial in many areas of chemistry and physics.
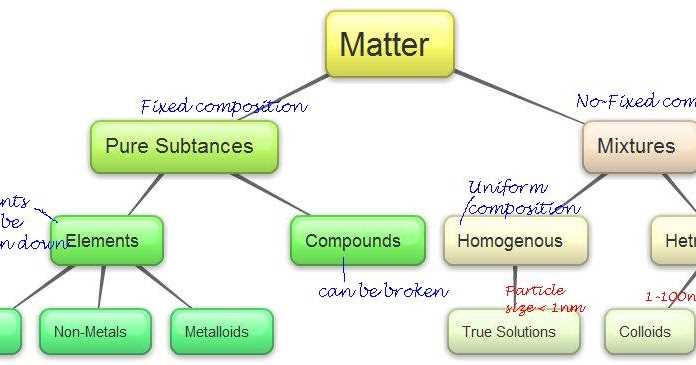
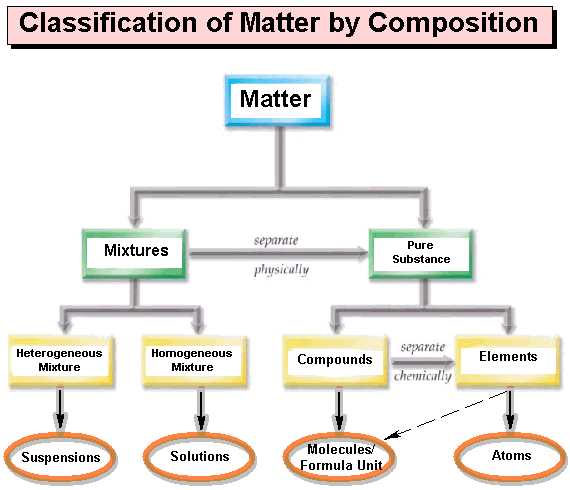
Another way to classify matter is by its composition. Pure substances and mixtures are the two main categories. Pure substances have a defined composition and cannot be separated into other substances by physical means. They can be further classified into elements and compounds. Elements are made up of only one type of atom, while compounds consist of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together. On the other hand, mixtures are a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical means.
Classification of Matter Webquest Answer Key
In the Classification of Matter Webquest, we explored the different types of matter and how they can be classified. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It can be categorized into two main types: pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are further divided into elements and compounds.
Elements: Elements are the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances. They are made up of only one type of atom. In the webquest, we learned about several elements such as oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, and gold. Each element has its own unique atomic symbol and atomic number.
Compounds: Compounds are substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined in specific ratios. They can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions. In the webquest, we explored examples of compounds such as water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Compounds have their own unique chemical formulas.
Mixtures: Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are physically mixed together. They can be separated using physical methods such as filtration or evaporation. In the webquest, we learned about two main types of mixtures: homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition, while heterogeneous mixtures have an uneven distribution of substances.
Classification of Matter Chart:
| Type of Matter | Composition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Element | One type of atom | Oxygen (O) |
| Compound | Two or more elements chemically combined | Water (H2O) |
| Homogeneous Mixture | Uniform composition | Saltwater |
| Heterogeneous Mixture | Uneven distribution of substances | Salad dressing |
Understanding the classification of matter is important in chemistry as it helps us identify and differentiate between different types of substances. It allows us to predict their properties and behavior. By studying the composition and structure of matter, scientists can make new discoveries and develop new materials for various applications.
Understanding the Basics of Matter
Matter is all around us and makes up everything in the universe. It is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter can exist in different forms such as solids, liquids, and gases. Understanding the basics of matter is crucial in many scientific fields, including chemistry and physics.
One key concept in understanding matter is the distinction between physical and chemical properties. Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the substance, such as color, shape, or density. Chemical properties, on the other hand, describe how a substance undergoes a change or reaction with other substances, such as flammability or reactivity.
All matter is composed of atoms, which are the smallest units of matter that retain the properties of an element. Atoms combine to form molecules, which are the building blocks of matter. Elements are pure substances made up of only one type of atom, while compounds are substances made up of two or more different atoms combined in a fixed ratio.
There are several ways to classify matter. One classification system is based on its physical state: solid, liquid, or gas. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container, and gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume. Another classification system is based on its composition, distinguishing between pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are uniform throughout and cannot be separated by physical means, while mixtures are a combination of two or more substances that can be separated.
The study of matter is fundamental to our understanding of the world around us. By understanding the basics of matter, scientists can better explore its properties and behavior, leading to advancements in various fields of science and technology.
States of Matter and their Properties
The states of matter are the different forms in which matter can exist. Matter can exist as a solid, liquid, or gas, depending on the arrangement and movement of its particles. Each state of matter has unique properties that distinguish it from the others.
Solid: Solids have a fixed shape and volume. The particles in a solid are tightly packed together and have very little movement. They vibrate in place but do not move around freely. Solids have a high density and are not easily compressed.
Liquid: Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container. The particles in a liquid have more movement than those in a solid. They can slide past one another, allowing the liquid to flow. Liquids have a lower density than solids and are not easily compressed.
Gas: Gases have no definite shape or volume. The particles in a gas have the most movement and are far apart from each other. They move freely and rapidly in all directions, filling the space available to them. Gases have a low density and are easily compressed.
These three states of matter can also undergo phase changes. For example, a solid can melt to become a liquid, and a liquid can evaporate to become a gas. These phase changes involve the addition or removal of energy, typically in the form of heat.
In summary, solids, liquids, and gases have different properties due to the arrangement and movement of their particles. Understanding these states of matter and their properties is essential in many scientific and everyday applications.
Classification of Matter based on Composition
Matter is classified based on its composition, meaning the types and amounts of substances that make it up. The two main categories of matter based on composition are pure substances and mixtures.
Pure Substances
A pure substance consists of only one type of molecule or atom. It cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Pure substances are further classified into two types: elements and compounds.
- Elements: Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. They are made up of only one type of atom. For example, oxygen and gold are elements.
- Compounds: Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. The elements in a compound are always present in a specific ratio. For example, water (H2O) is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Mixtures
A mixture consists of two or more substances physically combined. Unlike pure substances, mixtures can be separated into their individual components by physical means. Mixtures are further classified into two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous.
- Homogeneous Mixtures: Homogeneous mixtures are uniform in composition throughout. The components are evenly distributed, and it is difficult to distinguish the different substances in the mixture. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include saltwater and air.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: Heterogeneous mixtures are not uniform in composition and have distinct phases or regions with different properties. The components of a heterogeneous mixture are not evenly distributed, and the different substances can be visibly separated. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include salad dressing and granite.
Understanding the classification of matter based on composition is essential in various fields, including chemistry and materials science. It allows scientists to categorize and study different types of matter, which helps in understanding their properties and behavior.
Classifying Matter using the Periodic Table
When it comes to classifying matter, the Periodic Table is an essential tool. It provides a systematic way to organize and categorize the different elements found in nature. The elements on the Periodic Table are classified based on their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. The atomic number determines an element’s chemical properties and its position on the Periodic Table.
The Periodic Table is divided into rows, called periods, and columns, called groups or families. Each element is assigned a unique symbol that consists of one or two letters, such as H for hydrogen and O for oxygen. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom.
Elements in the same group or family have similar properties due to their similar electron configurations. For example, all elements in Group 1A, also known as the alkali metals, have one valence electron and are highly reactive. Elements in the same period have the same number of energy levels.
The Periodic Table also provides information about the physical and chemical properties of elements, as well as their respective atomic masses. The atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of an element, taking into account their abundance in nature.
- The Periodic Table allows chemists and scientists to predict the behavior of elements and their compounds based on their position.
- It helps identify trends and patterns in elemental properties, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
- Elements on the Periodic Table can be classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids based on their physical and chemical properties.
- Metals are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals are generally dull, brittle, and poor conductors. Metalloids have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
Overall, the Periodic Table is an indispensable tool for scientists in classifying and understanding the properties of the various elements in the universe. It provides a comprehensive framework for organizing matter and studying its fundamental building blocks.
Applications and Importance of Classification of Matter
Classification of matter is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that helps us understand and organize the materials around us. Here are some important applications and the significance of classification of matter:
1. Understanding chemical reactions:
Classification of matter allows us to identify different substances and understand how they interact and react with each other. It helps us predict and explain the outcomes of chemical reactions, including the formation of new substances and the release or absorption of energy.
2. Designing and improving products:

Classification of matter is crucial in product design and development. By classifying different materials and their properties, scientists and engineers can choose the most suitable materials for specific applications. For example, understanding the properties of metals, plastics, and ceramics helps in designing products with desired strength, conductivity, or flexibility.
3. Environmental monitoring and remediation:
Classification of matter plays a significant role in monitoring and remediation of environmental issues. By identifying and categorizing pollutants, scientists can determine their sources, effects, and appropriate remediation methods. Understanding the classification of pollutants helps in developing strategies to prevent and mitigate environmental damage.
4. Pharmaceutical research and development:
Classification of matter is essential in the field of pharmaceuticals. It helps in identifying and classifying different drugs based on their chemical composition and properties. This knowledge aids in the development of new medicines, understanding their therapeutic effects, and ensuring their safety and efficacy.
5. Education and scientific research:
Classification of matter forms the foundation of chemistry and physics education. It provides a systematic way to study and understand the properties and behavior of different substances. It also allows scientists to categorize and organize their research findings, making it easier to communicate and build upon existing knowledge.
In conclusion, the classification of matter is crucial for various practical applications. It helps us understand chemical reactions, design and improve products, monitor and remediate environmental issues, develop pharmaceuticals, and advance scientific research. By organizing and categorizing different materials, we can better comprehend their properties, interactions, and potential uses, leading to advancements in various fields.