The Colligative Properties Gizmo is an online simulation that allows students to explore the effects of solute concentration on colligative properties, such as boiling point elevation and freezing point depression. This interactive tool is designed to help students understand the concept of colligative properties and how they can be used to determine the concentration of solute in a solution.
With the Colligative Properties Gizmo, students can experiment with different solutes and observe how their presence affects the properties of a solution. They can vary the concentration of the solute and measure changes in boiling and freezing points. This hands-on approach allows students to develop a deeper understanding of the relationship between solute concentration and colligative properties.
In addition to exploring the effects of solute concentration, the Colligative Properties Gizmo also provides answers to common questions and prompts students to think critically about the underlying concepts. It includes pre-laboratory questions to help guide students’ thinking and post-laboratory questions to assess their understanding. This interactive tool can be used as a standalone activity or as part of a larger lesson on colligative properties.
Overall, the Colligative Properties Gizmo is a valuable educational tool that helps students explore the relationship between solute concentration and colligative properties. By engaging in hands-on experimentation and answering thought-provoking questions, students can develop a deeper understanding of this important topic in chemistry.
Understanding Colligative Properties

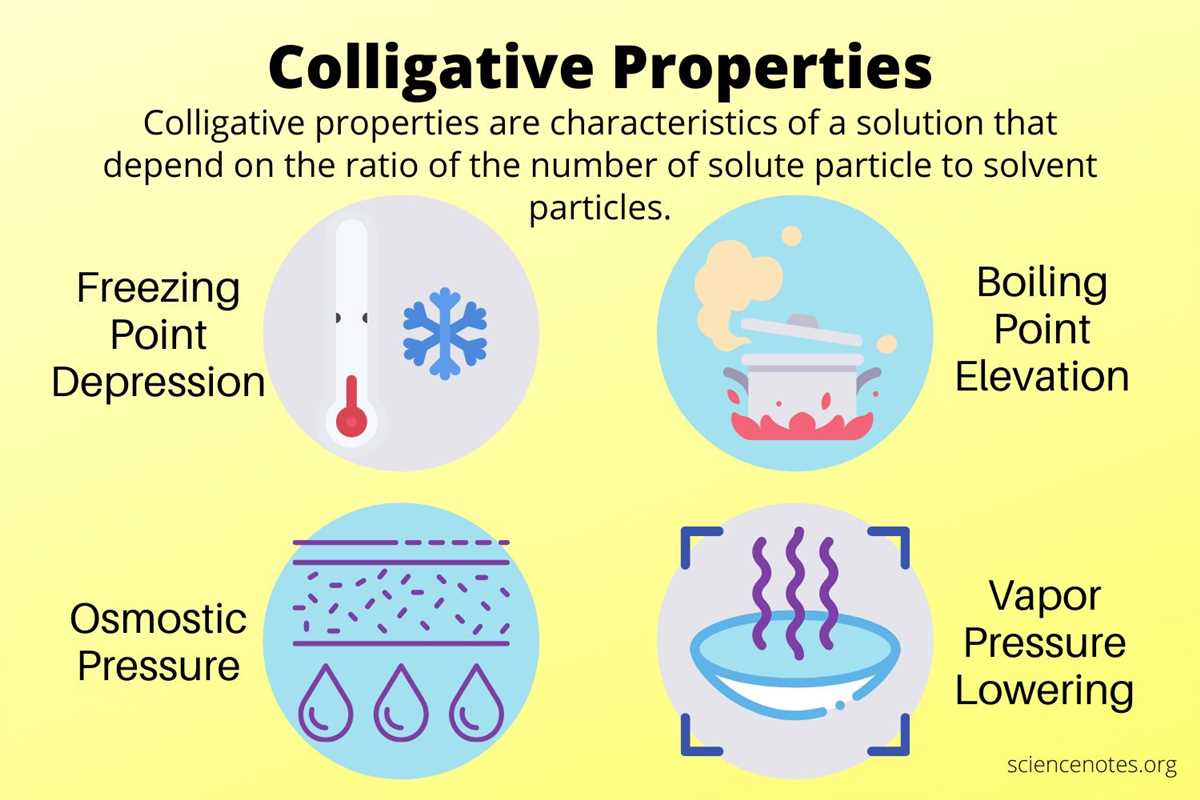
Colligative properties are properties of a solution that depend on the number of solute particles present, rather than the specific identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, osmotic pressure, and vapor pressure lowering. By understanding colligative properties, we can better comprehend how solute particles affect the physical properties of a solution.
Boiling point elevation is a colligative property that occurs when a nonvolatile solute is added to a solvent. The boiling point of the solvent increases, as the presence of solute particles disrupts the formation of the solvent’s vapor at the surface. This phenomenon is used in everyday life, such as when adding salt to water to cook pasta, where the higher boiling point of the saltwater allows the pasta to cook at a higher temperature.
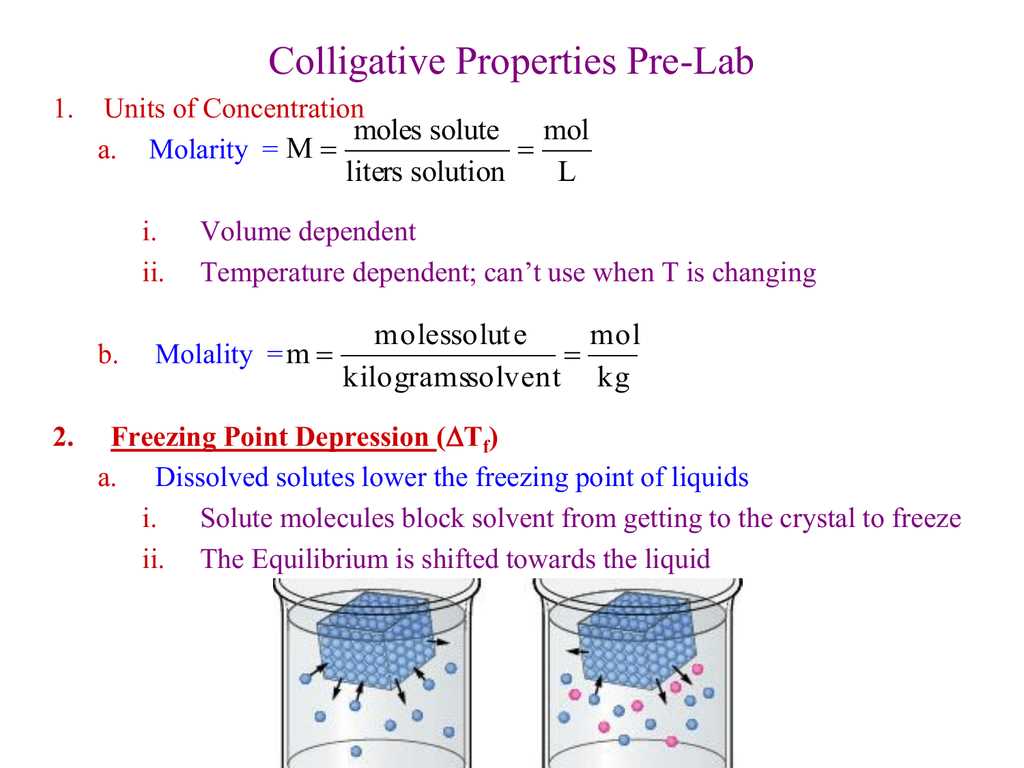
Freezing point depression is another colligative property that arises when a solute is added to a liquid. The freezing point of the liquid decreases, as the solute particles interfere with the formation of the solvent’s solid lattice structure. This principle is utilized in antifreeze solutions, where the addition of chemicals lowers the freezing point of the liquid, protecting it from freezing in cold temperatures.
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property that describes the pressure required to stop the flow of solvent across a semipermeable membrane, due to differences in solute concentration. It plays a crucial role in biological systems, such as the movement of water in and out of cells, as well as in industrial applications like reverse osmosis for water purification.
Vapor pressure lowering is the final colligative property, which occurs when a solute is added to a liquid and reduces the vapor pressure of the liquid. The presence of solute particles exerts a partial pressure, making it harder for the solvent molecules to escape into the gas phase. This concept is significant in applications like controlling humidity and in the design of refrigeration systems.
In conclusion, colligative properties provide valuable insight into the behavior of solutions and the effects of solute particles on their physical properties. Understanding these properties allows us to explain various phenomena in everyday life, as well as develop practical applications in fields such as chemistry, biology, and engineering.
What Are Colligative Properties?
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that are influenced by the number of solute particles present, rather than the chemical nature of the solute. These properties depend on the concentration of solute particles and include properties such as boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure.
Boiling point elevation occurs when the presence of solute particles in a solvent increases the boiling point of the solution compared to the pure solvent. This happens because the solute particles disrupt the regular arrangement of solvent molecules, making it more difficult for them to escape as vapor. As a result, the solution needs to be heated to a higher temperature in order for the vapor pressure to match that of the surrounding environment.
Freezing point depression, on the other hand, happens when the presence of solute particles lowers the freezing point of a solution compared to the pure solvent. The solute particles interfere with the formation of the regular lattice structure of the solvent during freezing, preventing the solvent from solidifying at its normal freezing point. Consequently, the solution needs to be cooled to a lower temperature in order for solidification to occur.
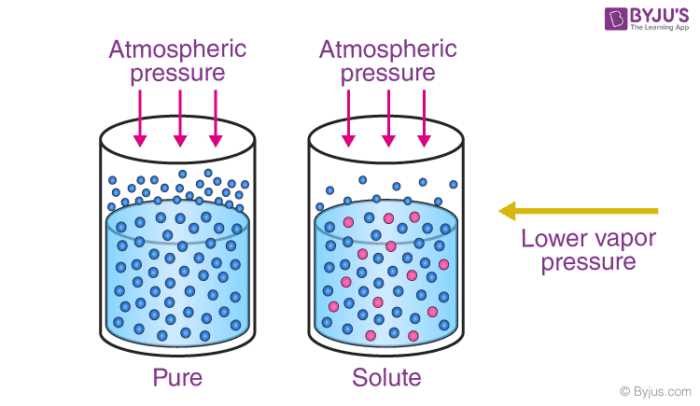
Vapor pressure lowering refers to the phenomenon where the presence of solute particles decreases the vapor pressure of a solution compared to the pure solvent. This occurs because the solute particles occupy space at the liquid surface, reducing the number of solvent molecules available to escape as vapor. As a result, the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by the solvent molecules as they pass through a semipermeable membrane to equalize the concentration of solute particles on both sides of the membrane. This pressure increases as the concentration of solute particles in the solution increases.
In conclusion, colligative properties are a set of physical properties of solutions that are affected by the concentration of solute particles. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure. Understanding these properties is important in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Importance of Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are of great importance in various fields of science and industry. These properties, which depend on the number of solute particles rather than their nature, play a vital role in understanding and predicting the behavior of solutions.
One of the key applications of colligative properties is in determining the molecular weight of an unknown compound. By measuring the colligative properties, such as freezing point depression or boiling point elevation, we can calculate the molar mass of the solute. This information is crucial in characterizing and identifying unknown substances, particularly in fields such as pharmaceuticals and forensic science.
Colligative properties also have practical implications in everyday life. For example, adding salt to icy roads lowers the freezing point of water, preventing the formation of ice and making the roads safer for driving. Similarly, antifreeze solutions used in car engines exhibit a lower freezing point, protecting the engine from damage during extreme cold weather conditions.
In industrial processes, colligative properties are utilized to enhance efficiency and optimize production. For instance, in the manufacturing of plastics, the addition of solutes can significantly lower the melting point of the polymer, making it easier to process and shape. Additionally, the osmotic pressure of solutions is a vital factor in osmosis, which is essential for processes such as water purification and desalination.
Overall, colligative properties play a crucial role in various scientific disciplines and industries. Understanding and manipulating these properties allow us to predict and control the behavior of solutions, leading to advancements in fields ranging from medicine to manufacturing.
Exploring the Relationship between Solutes and Solvents

Solutes and solvents are two crucial components in the study of solutions and chemistry as a whole. A solute refers to a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, while a solvent is a substance in which solutes are dissolved. The relationship between solutes and solvents is fundamental and plays a significant role in various scientific and practical applications.
One important aspect of the relationship between solutes and solvents is the effect they have on each other’s physical properties. When a solute is dissolved in a solvent, it can alter the boiling point, freezing point, and vapor pressure of the solvent. This phenomenon, known as colligative properties, is dependent on the concentration of the solute in the solution. For example, the presence of a solute can lower the freezing point of a solvent, allowing it to remain in a liquid state at lower temperatures.
Colligative properties are extensively studied and have numerous practical applications. For instance, the understanding of colligative properties is crucial in determining the appropriate antifreeze concentration for car engines. By lowering the freezing point of the coolant, antifreeze prevents the engine from freezing in cold temperatures. Additionally, the use of salt to melt ice on roads during winter is another example of how the relationship between solutes and solvents can be applied in real-life situations.
Moreover, the interaction between solutes and solvents is important in chemical reactions. The solvent provides a medium for reactions to occur, allowing solutes to react and form new compounds. Different solvents can have varying effects on the rate and outcome of chemical reactions. For example, polar solvents like water are often used in acid-base reactions due to their ability to dissolve ionic compounds and facilitate ionization. On the other hand, nonpolar solvents like benzene are commonly used in organic reactions, where they enhance the solubility of nonpolar compounds.
In summary, the relationship between solutes and solvents is a critical aspect of chemistry. The presence of solutes can significantly impact the physical properties of solvents, as observed through colligative properties. This understanding has practical applications in various fields, from automotive engineering to winter maintenance. Additionally, solvents play a vital role in facilitating chemical reactions by providing a suitable medium for solutes to react. Overall, exploring and understanding the relationship between solutes and solvents is essential for advancements in scientific research and everyday life.
Determining Colligative Properties with Gizmo

The Colligative Properties Gizmo is a powerful tool that allows students to explore and determine various colligative properties of solutions. Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles present, rather than the specific nature of the solute.
One of the main colligative properties explored by the Gizmo is freezing point depression. Freezing point depression is the phenomenon where the freezing point of a solvent decreases when a solute is added to it. With the Gizmo, students can experiment with different solutes and solvents to observe how the freezing point changes as the concentration of the solute increases.
Another colligative property that can be determined with the Gizmo is boiling point elevation. Boiling point elevation occurs when the boiling point of a solvent increases when a non-volatile solute is added. By adjusting the concentration of the solute, students can observe how the boiling point of a solution changes compared to the pure solvent.
The Gizmo also allows students to explore osmotic pressure, which is another important colligative property. Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop osmosis, the process of solvent molecules moving through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. By manipulating the concentration of solutes on either side of a semi-permeable membrane, students can observe the flow of solvent molecules and determine the osmotic pressure.
In conclusion, the Colligative Properties Gizmo provides an interactive and hands-on way for students to explore and determine various colligative properties of solutions. By experimenting with freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure, students can develop a deeper understanding of the relationship between solute concentration and these colligative properties.
Common Colligative Properties Gizmo Answers
Colligative properties are a set of physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of particles present, regardless of their identity. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure. The Colligative Properties Gizmo allows students to explore these properties and understand how they are affected by the concentration of solute.
One common colligative property that can be explored with the Gizmo is freezing point depression. This property states that adding a solute to a solvent will lower the freezing point of the solution compared to the pure solvent. The Colligative Properties Gizmo allows students to see this phenomenon in action by varying the concentration of the solute and observing how it affects the freezing point of the solution.
Another interesting colligative property that can be studied with the Gizmo is osmotic pressure. This property is related to the movement of solvent particles across a semipermeable membrane to equalize the concentration on both sides. The Colligative Properties Gizmo enables students to investigate this process by controlling the concentration of solute in the solution and observing the resulting osmotic pressure.
In conclusion, the Colligative Properties Gizmo provides a hands-on learning experience for students to understand and explore common colligative properties. By manipulating the concentration of solute and observing the resulting changes in freezing point and osmotic pressure, students can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying principles behind these properties.
Practical Applications of Colligative Properties
Colligative properties have numerous practical applications in various fields. Some of these applications are:
- Antifreeze: Colligative properties are utilized in the production of antifreeze. By adding antifreeze to a liquid, the freezing point of the liquid is lowered, preventing it from freezing at low temperatures. This property becomes crucial in places where low temperatures can damage or disrupt the functioning of engines or pipelines.
- Preservation of Food: Colligative properties, particularly the boiling point elevation, are used in food preservation. By increasing the boiling point of the liquid surrounding the food, it takes longer for the liquid to evaporate, extending the shelf life of the food.
- Osmosis in Living Organisms: Colligative properties, such as osmotic pressure, play a vital role in the movement of fluids in living organisms. Osmosis allows for the movement of water across cell membranes, maintaining balance and proper functioning of cells.
- Pharmaceutical Formulations: Colligative properties are crucial in the formulation of medications. For example, the addition of solutes to solutions affects their freezing point, allowing for the production of injectable drugs that remain in a liquid state at low temperatures.
- Chemical Separations: Colligative properties, particularly the vapor pressure lowering, are used in distillation techniques to separate different components of a mixture by exploiting the differences in boiling points caused by the presence of solutes.
In conclusion, colligative properties have significant practical applications in various fields ranging from automotive engineering to pharmaceuticals. By understanding and utilizing these properties, scientists and engineers can develop innovative solutions and products that improve our everyday lives.
Q&A:
What are the practical applications of colligative properties?
Colligative properties have several practical applications in various fields. For example, in the food industry, colligative properties are used to determine the freezing point depression of ice cream, which helps in the production process and improves the texture and taste of the final product. In the medical field, colligative properties are used to determine the osmolarity of solutions used in intravenous therapy, which ensures that the solutions have the appropriate concentration for effective treatment. Colligative properties are also used in antifreeze solutions for cars, where the lowering of the freezing point helps prevent the engine coolant from freezing in cold climates. Additionally, colligative properties are important in determining the boiling point of solutions, which is utilized in cooking and in the distillation of alcoholic beverages.
How do colligative properties affect the freezing point of a solution?
Colligative properties, such as freezing point depression, lower the freezing point of a solution compared to the pure solvent. This is because when solute particles are added to a solvent, they disrupt the crystal lattice structure of the solvent and make it more difficult for the solvent molecules to arrange themselves into a solid. As a result, a solution with a lower freezing point is formed. The extent of freezing point depression depends on the concentration of the solute particles in the solution. More solute particles lead to a greater depression of the freezing point.
What is the significance of colligative properties in determining the concentration of solute in a solution?
Colligative properties, such as osmotic pressure and boiling point elevation, can be used to determine the concentration of solute in a solution. By measuring these properties and knowing the properties of the pure solvent, it is possible to calculate the concentration of the solute using mathematical equations. This is particularly useful when dealing with volatile or non-volatile solutes that may be difficult to directly measure. Colligative properties provide a practical and indirect method of determining the concentration of solute in a solution.
How are colligative properties essential in industrial applications?
Colligative properties play a crucial role in various industrial applications. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, colligative properties are used to determine the suitable concentration of active ingredients in medications to ensure their effectiveness and proper dosing. In the automotive industry, colligative properties are utilized in the formulation of antifreeze solutions to prevent engine coolant from freezing in cold temperatures. Colligative properties are also important in the production of chemicals, as they help determine the freezing and boiling points of various solutions, which aids in the purification process. Overall, colligative properties are essential in ensuring the quality and functionality of products in various industrial sectors.