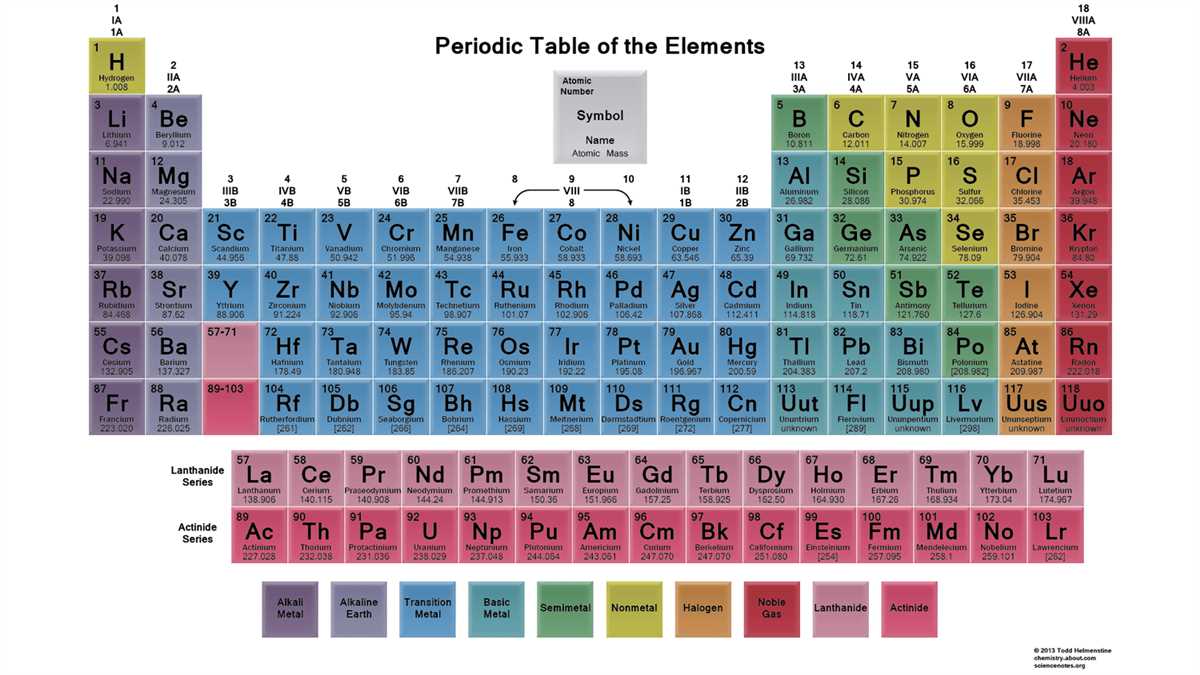
Understanding the periodic table is a fundamental element of studying chemistry. With its 118 elements arranged in a specific order, the periodic table provides a wealth of information about each element’s properties and characteristics. One helpful tool in deciphering the periodic table is color coding. By assigning different colors to different groups of elements, color coding can make it easier to identify patterns and relationships within the table.
Color coding the periodic table answer key is a valuable resource for students and researchers alike. By providing a clear visual representation of the different groups of elements, this answer key helps to organize and simplify the abundance of information found within the periodic table. Each color corresponds to a specific group or category of elements, making it easier to identify similarities and differences between elements.
One common color coding system in the periodic table assigns different colors to the main groups, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. For example, alkali metals such as lithium, sodium, and potassium are colored red, while noble gases like helium, neon, and argon are colored green. This color coding system allows students to quickly identify and memorize the main groups of elements and their properties.
What is Color Coding in the Periodic Table?
Color coding in the periodic table is a visual representation technique used to organize and categorize elements based on their properties. Each element is assigned a specific color or combination of colors, which helps users quickly identify and understand the characteristics of each element. This color-coded system aids in learning and memorizing the periodic table, making it an effective educational tool.
The color coding scheme used in the periodic table is based on various factors, including the element’s atomic number, atomic mass, electron configuration, and chemical properties. Different colors are used to represent different groups of elements, such as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases, and lanthanides/actinides.
The color coding system in the periodic table allows users to easily distinguish between different groups of elements and identify trends and patterns in their properties. For example, all elements in the same group have similar chemical properties and behave in a similar manner. By using color coding, it becomes easier to understand the periodic trends, such as the increase in atomic size and reactivity as you move down a group, or the decrease in atomic size and increase in electronegativity as you move across a period.
This color-coded approach to organizing the periodic table provides a visual representation that aids in comprehension and simplifies the study of elements. It allows students and researchers to quickly locate and compare elements, understand their properties, and identify relationships between different elements. By using color coding, the periodic table becomes a powerful tool for scientists to study and explore the vast world of chemistry.
Understanding the Basics
When it comes to understanding the periodic table and its color coding, it’s important to start with the basics. The periodic table is a chart that organizes all known elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring patterns of chemical properties. Each element is represented by a unique symbol and can be found in specific groups and periods on the table. The color coding of the periodic table helps to visually distinguish between different categories of elements and provides valuable information about their properties.
The key to understanding the color coding of the periodic table lies in recognizing the different types of elements and their characteristics. For example, elements in the alkali metal group, such as lithium and sodium, are typically colored red. These elements are highly reactive and easily lose their outermost electron to form positive ions. On the other hand, elements in the alkaline earth metal group, like magnesium and calcium, are often colored yellow. These elements are also reactive, but not as much as alkali metals. They have two valence electrons and tend to lose both to form divalent cations.
Other groups of elements in the periodic table have their own distinctive colors. Transition metals, which include metals like iron and copper, are typically colored blue. These elements have variable valence states, forming different ions with different charges. Nonmetals, such as oxygen and nitrogen, are often colored green. They tend to gain or share electrons to complete their valence shells and form negative ions. Finally, noble gases, like helium and neon, are usually colored purple. These elements have full valence shells and are known for their low reactivity.
To fully understand and utilize the color coding of the periodic table, it is important to study the properties and characteristics of each element within the different groups. This knowledge can help scientists and students alike to make predictions about chemical behavior, understand trends, and identify similarities and differences between elements. Overall, the color coding of the periodic table serves as a visual tool to aid in the understanding and organization of the vast array of elements in the universe.
Importance of Color Coding in the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a visual representation of the elements, organized in a specific order based on their atomic number and electron configuration. To make it easier to read and understand, color coding is commonly used in the periodic table. This visual aid helps to highlight patterns and trends, making it an important tool for chemists, students, and researchers alike.
Effective Organization: Color coding allows for the effective organization of elements in the periodic table. By assigning different colors to groups of elements with similar properties, it becomes easier to identify and remember their characteristics. For example, the noble gases are typically color-coded in yellow, which helps to distinguish them from other elements.
Highlighting Patterns: The use of color in the periodic table allows for the clear visualization of patterns and trends in element properties. For instance, elements within a group or period often share similar colors, indicating their similar chemical properties or atomic structure. This visual representation helps chemists and researchers to quickly identify and analyze these patterns.
Visual Memorization: Color coding assists in the memorization of the periodic table. By associating specific colors with certain elements or groups, individuals can create visual cues that aid in remembering the information. This is particularly beneficial for students who are learning about the periodic table for the first time and need a visual aid to help them grasp the concepts.
Enhanced Comprehension: The use of color in the periodic table enhances comprehension by providing a visual representation of complex information. The colors help to differentiate between metals, non-metals, and metalloids, as well as distinguish between different states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) at room temperature. This visual clarity aids in understanding the properties and characteristics of each element.
Universal Language: Color coding in the periodic table serves as a universal language for scientists around the world. Regardless of language barriers, the use of color allows researchers from different countries and backgrounds to easily communicate and discuss the elements, their properties, and their relationships. This facilitates collaboration and the sharing of scientific knowledge.
In conclusion, color coding is an essential tool in the periodic table. It aids in effective organization, highlights patterns, enhances memorization, improves comprehension, and serves as a universal language for scientists. By using color, the periodic table becomes more accessible and user-friendly, making it an invaluable resource in the field of chemistry.
How is the Periodic Table Color Coded?

The periodic table is a visual representation of the elements arranged in order of atomic number. To make it easier to read and understand, the periodic table is color coded based on certain properties of the elements. This color coding system helps to categorize and group similar elements together for easier identification.
One common color coding system used for the periodic table is based on the element’s classification as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. Metals are represented in blue, nonmetals in red, and metalloids in green. This color coding helps to quickly identify and differentiate between the different types of elements. For example, in the first row of the periodic table, hydrogen is colored in white to indicate that it is not a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid.
The periodic table is also color coded to represent different groups or families of elements. For example, the noble gases are colored in purple, the alkali metals in pink, and the alkaline earth metals in orange. This color coding helps to easily identify elements that have similar properties and react similarly in chemical reactions. It also allows for quick recognition of certain patterns and trends within the periodic table.
In addition to color coding, some periodic tables also use symbols, numbers, or other visual cues to provide additional information about the elements. For example, the atomic number and atomic weight of each element are often included in the table. This additional information helps to provide a more comprehensive understanding of each element and its characteristics.
Overall, the color coding of the periodic table helps to make it more visually appealing and easier to interpret. It allows for quick recognition of certain properties and patterns, which can be especially helpful for students and scientists studying the elements and their properties.
Benefits of Using a Color Coded Periodic Table
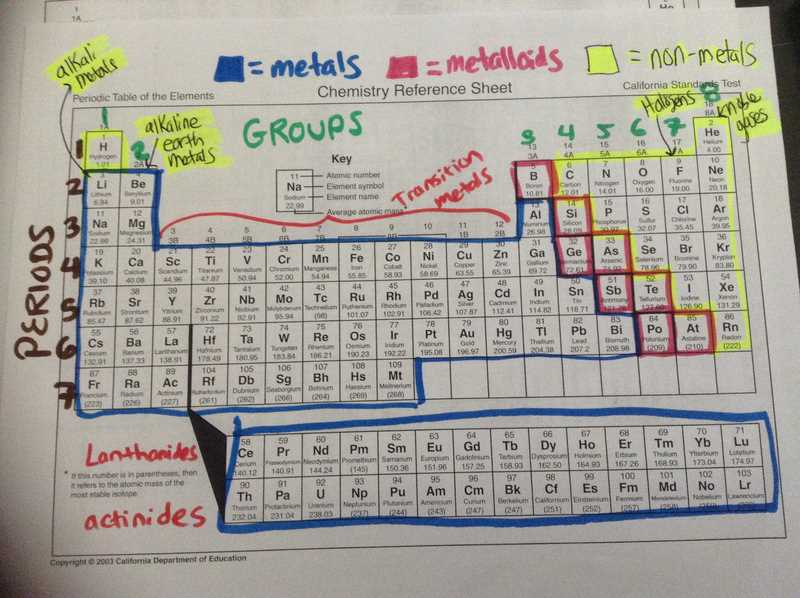
A color coded periodic table provides several benefits that can aid in the understanding and study of chemical elements. By using different colors to represent different groups or categories of elements, it allows for easier visual identification and comprehension of their properties. This visual representation can make it easier for students and researchers to locate specific elements and understand their relationship to other elements in the table.
Improved organization and categorization: The color coding of the periodic table helps to organize the elements into distinct groups based on their properties. For example, metals may be represented by a specific color, while nonmetals are assigned a different color. This organization allows for easier identification of elements belonging to a certain group and helps users recognize patterns and trends in the periodic table.
Faster information retrieval: With a color coded periodic table, finding specific information about an element becomes quicker and more efficient. The use of colors allows users to visually scan the table and identify the desired element or category without having to rely solely on text or numerical data. This can be especially useful in educational settings, where students can quickly locate elements for experiments or research purposes.
Enhanced learning and comprehension: The visual nature of a color coded periodic table can greatly enhance the learning experience. By associating specific colors with different elements or groups, it becomes easier for individuals to remember and understand the properties and characteristics of those elements. This visual representation can also aid in the development of mental models and concepts related to the periodic table, making it easier to grasp complex concepts and relationships between elements.
Facilitation of data analysis: When working with the periodic table, color coding can make it easier to discern patterns and trends in the arrangement of elements. By visually representing properties such as atomic number, symbol, or atomic mass, color coded periodic tables allow users to quickly identify relationships and similarities between elements. This can be especially useful in chemistry research or experiments that require the analysis of multiple elements and their properties.
In summary, a color coded periodic table offers numerous benefits that can significantly aid in the understanding, organization, and retrieval of information related to chemical elements. Whether used in educational settings or scientific research, the use of colors can enhance learning, facilitate data analysis, and make the study of the periodic table more efficient and accessible.
Applications of a Color Coded Periodic Table

Color coding the periodic table has numerous applications and benefits. Some of the key applications include:
- Facilitating Understanding: A color coded periodic table helps in visualizing the trends and patterns in elements more easily. By assigning different colors to different groups or categories, it becomes simpler to identify similarities and differences among elements.
- Enhancing Teaching and Learning: Color coding the periodic table can be a valuable educational tool. It aids in simplifying complex information, making it more accessible and understandable for students. Teachers can utilize a color coded periodic table to engage students in interactive learning activities, quizzes, and games.
- Research and Analysis: Scientists and researchers can benefit from a color coded periodic table by quickly identifying elements with specific properties. For example, if they are studying elements with similar reactivity or atomic mass, color coding can help identify and group them together, simplifying the analysis process.
- Chemical Industry: Color coding can be useful for professionals working in the chemical industry. It can assist in identifying elements and their properties, aiding in the formulation of new compounds and materials.
- Promoting Safety: Color coding also plays a crucial role in promoting safety within scientific laboratories. By using different colors to distinguish hazardous and non-hazardous materials, potential risks can be minimized, ensuring a safer work environment.
In conclusion, color coding the periodic table enhances understanding, aids in teaching and learning, facilitates research and analysis, benefits the chemical industry, and promotes safety. It is a valuable tool that simplifies complex information, making it more accessible and useful for various applications. By utilizing a color coded periodic table, scientists, educators, and professionals can benefit from a visual representation that enhances their understanding and improves their work.
Q&A:
What is a color-coded periodic table?
A color-coded periodic table is a visual representation of the chemical elements arranged in a tabular format, where each element is assigned a specific color based on its characteristic properties or properties of its compounds.
What is the purpose of a color-coded periodic table?
The purpose of a color-coded periodic table is to provide an easy way to visually identify and distinguish different elements and their properties. It helps in understanding trends, patterns, and relationships between elements, such as their atomic numbers, atomic weights, electron configurations, and chemical properties.
What are the applications of a color-coded periodic table?
The applications of a color-coded periodic table are varied. It is used in educational settings to teach students about the elements and their properties. It is also used by researchers and scientists to study and analyze the behavior and characteristics of different elements. Additionally, it can be used by professionals in fields such as chemistry, physics, and materials science to aid in their work and research.
How can a color-coded periodic table be helpful in science education?
A color-coded periodic table is helpful in science education as it makes learning about the elements and their properties more engaging and visually appealing. It allows students to easily identify and memorize elements based on their colors, which aids in retaining information. It also helps in understanding the periodic trends and relationships between elements, which are fundamental concepts in chemistry.