
Constitutions play a pivotal role in defining the power structure and guiding the governance of a nation. They lay the foundation for the legal and political framework of a country, enshrining the rights and responsibilities of its citizens. While every constitution is unique to a particular nation, there are certain features that can be compared across different constitutions. This answer key aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the similarities and differences between various constitutions around the world.
One important aspect to consider when comparing constitutions is the way in which power is distributed. Some constitutions establish a unitary system where power is concentrated at the national level, while others adopt a federal structure with power shared between the national and regional governments. Another key area of comparison is the separation of powers. Constitutions often outline the division of power between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government, with some employing a strict separation of powers and others allowing for a certain degree of overlap.
The protection of individual rights is another crucial aspect of any constitution. Many constitutions contain a bill of rights that guarantees fundamental rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial. The extent to which these rights are protected and the mechanisms available for their enforcement can vary greatly. Additionally, some constitutions also incorporate provisions for affirmative action, which aim to address historical inequalities and promote equal opportunities for marginalized groups.
Key similarities between constitutions
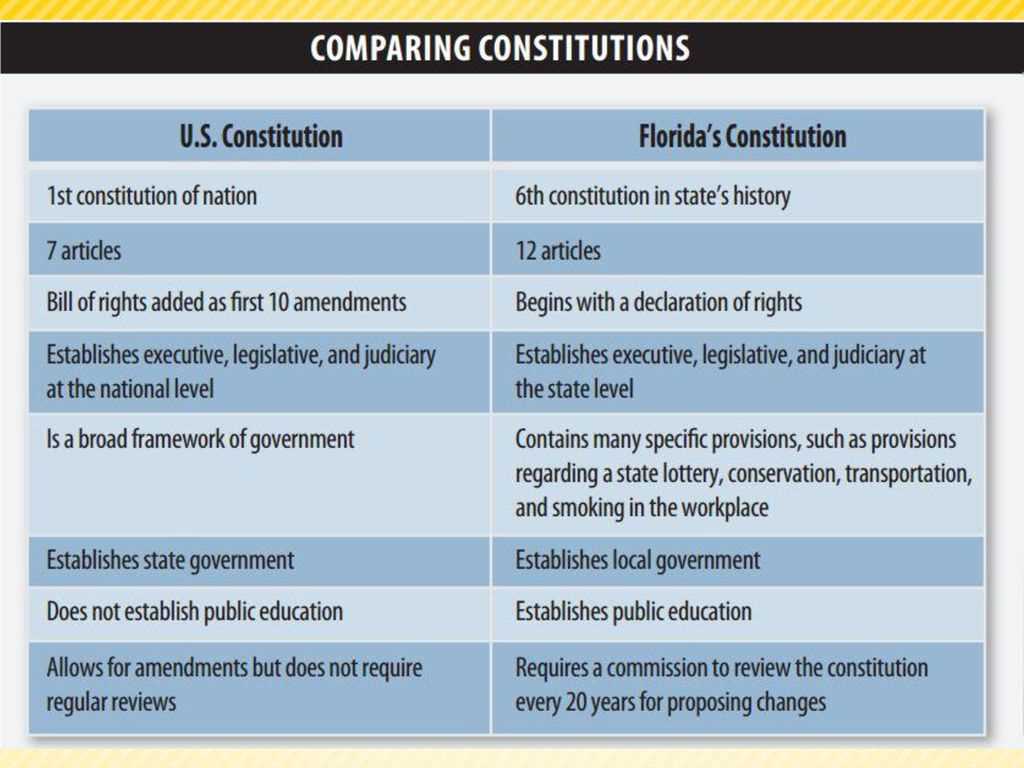
The constitutions of different countries may vary in their specific provisions and structures, but there are several key similarities that can be found across many constitutions around the world. These similarities are often influenced by the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law.
One key similarity between constitutions is the establishment of a system of government with separate branches and a system of checks and balances. This ensures that no single branch of government has too much power and provides a mechanism for power-sharing and accountability. Most constitutions also establish a head of state and a legislature, which is responsible for making and passing laws.
- Protection of fundamental rights: Another important similarity between constitutions is the protection of fundamental rights and freedoms. Constitutions often include provisions that guarantee freedom of speech, religion, and assembly, as well as the right to due process and equality before the law. These rights are considered essential for a democratic society and are protected by the constitution.
- Establishment of a legal framework: Constitutions also establish a legal framework for the country, including the establishment of a judicial system. This ensures that there is an independent and impartial judiciary that can interpret and apply the law. The constitution often outlines the structure and jurisdiction of the courts, as well as the appointment and tenure of judges.
- Amendment procedures: Most constitutions also provide a mechanism for amending or revising the constitution. This allows for the constitution to be adapted and updated over time to reflect the changing needs and values of society. The process for amending the constitution is often more difficult than passing regular legislation, requiring a supermajority or popular vote.
Overall, while constitutions may differ in their specific provisions and structures, they share key similarities in terms of the establishment of a government system, the protection of fundamental rights, and the establishment of a legal framework. These similarities reflect the core principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law that are important for the functioning of a just and equitable society.
Basic Structure
The basic structure of a constitution establishes the framework and fundamental principles of a country’s governance. It outlines the roles and powers of the different branches of government, defines the rights and responsibilities of citizens, and sets clear rules and procedures for governing the nation. Constitutions typically consist of several key elements that provide the foundation for a country’s legal and political system.
1. Preamble: The preamble is an introductory statement that sets forth the goals and aspirations of a nation and its people. It often articulates the principles of justice, liberty, equality, and democracy that the constitution seeks to uphold.
2. Fundamental Rights and Freedoms: Constitutions guarantee certain fundamental rights and freedoms to citizens, such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly. These rights are considered essential for the protection and well-being of individuals and are typically enshrined in the constitution to ensure their permanence and enforceability.
3. Separation of Powers: Constitutions establish a system of separation of powers, dividing the government into independent branches with distinct functions and powers. This separation aims to prevent the concentration of power in any one branch and provides a system of checks and balances to maintain accountability.
4. Structure of Government: Constitutions outline the structure of government, including the composition and powers of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This section may also establish the qualifications and procedures for selecting government officials.
5. Amendment Process: Constitutions typically include provisions for amending the document to accommodate the changing needs and dynamics of society. The amendment process varies across constitutions, but it usually requires a supermajority or special majority of the legislative body or approval through a referendum.
6. Protection of Constitution: Constitutions often include mechanisms to protect and uphold the constitution itself. This may involve establishing a constitutional court or other independent body to interpret and adjudicate constitutional matters and ensure the constitution’s integrity is maintained.
These elements collectively form the basic structure of a constitution and provide the framework for a country’s governance. The overall structure and content of a constitution vary from one country to another, reflecting the unique historical, cultural, and political context of each nation.
Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are the basic rights and freedoms that individuals possess and are protected by the constitution of a country. These rights are essential for the dignity and well-being of every person, and they often form the foundation of a democratic society. They are typically categorized into civil and political rights, economic and social rights, and cultural and collective rights.
Civil and political rights include the right to life, liberty, and security of person; the right to equality before the law; freedom of speech, religion, and assembly; and the right to participate in the political process. These rights ensure that individuals are treated fairly and have the freedom to express their opinions and beliefs without fear of persecution or discrimination. They are crucial for maintaining individual liberty and promoting a just society.
Economic and social rights encompass the right to work and receive fair wages, the right to adequate housing and healthcare, and the right to education. These rights are essential for ensuring that every individual has access to basic necessities and can live a dignified life. They aim to reduce poverty, inequality, and social exclusion by providing equal opportunities and resources for all members of society.
Cultural and collective rights recognize the rights of minority groups, indigenous peoples, and communities to preserve their cultural identity, language, and heritage. These rights acknowledge the importance of cultural diversity and promote the inclusion and participation of all individuals in society. They are essential for maintaining social cohesion and fostering mutual respect and understanding among different groups.
Overall, fundamental rights are the backbone of a democratic society, ensuring the protection and well-being of individuals and promoting equality, justice, and freedom. They play a crucial role in upholding human dignity and guaranteeing that every person can live a life of dignity and respect.
Separation of Powers
The principle of separation of powers is a fundamental concept in the field of constitutional law, ensuring that no single branch of government has absolute power. It is founded on the idea that dividing power between different branches–legislative, executive, and judicial–creates a system of checks and balances that prevents the abuse of power and protects individual liberties.
The legislative branch, also known as the Congress or Parliament, is responsible for making laws. This branch consists of elected representatives who represent the people’s interests and draft and pass legislation. They have the power to propose and debate bills, vote on legislation, and oversee the actions of the executive branch.
The executive branch, led by the President or Prime Minister, is responsible for implementing and enforcing the laws. They have the power to execute and administer laws, manage the day-to-day operations of the government, and make decisions on behalf of the country. However, their actions are subject to oversight and scrutiny by the legislative branch and can be challenged by the judicial branch.
The judicial branch, headed by the courts, is responsible for interpreting and applying the laws. They have the power to hear and decide legal cases, provide legal guidance, and ensure that the laws are in accordance with the constitution. The judiciary acts as a check on the other branches by reviewing the constitutionality of their actions and resolving disputes between them.
In summary, the principle of separation of powers ensures that no branch of government becomes too powerful, promoting a balance of power and protecting the rights and freedoms of individuals. It is a crucial element of a democratic system and serves as a safeguard against tyranny and abuse of power.
System of checks and balances
The system of checks and balances is an important feature of many constitutions around the world. It is designed to ensure that no one branch of government becomes too powerful and to protect the rights and liberties of the citizens. The system consists of a series of checks and balances among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government. This system ensures that each branch has some degree of power over the others, helping to prevent abuse of power and maintain a balance of power.
One example of the system of checks and balances is the power of the executive branch to veto legislation passed by the legislative branch. This allows the executive to prevent laws from being enacted, but the legislative branch can override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote. This check ensures that the executive branch does not have unlimited power to make laws and that there is a mechanism for the legislative branch to challenge the executive’s decisions.
The system of checks and balances also includes the power of the judicial branch to interpret laws and determine their constitutionality. This power allows the judiciary to check the actions of both the legislative and executive branches. If a law is deemed unconstitutional, the judiciary can strike it down, preventing the other branches from enforcing it. This check is essential for protecting the rights and liberties of the citizens and ensuring that the government operates within the bounds of the constitution.
In conclusion, the system of checks and balances plays a crucial role in maintaining a balance of power and protecting the rights of citizens in many constitutions. It ensures that no one branch of government becomes too powerful and provides mechanisms for the different branches to check and balance each other. This system is a cornerstone of democratic governance and helps to prevent the abuse of power by any one branch of government.
Key differences between constitutions
The constitutions of different countries can vary greatly in terms of structure, content, and the rights and responsibilities they outline for their citizens. While each constitution is unique to its respective country, there are several key differences that can be observed across different constitutions worldwide.
1. Length and specificity: Constitutions can vary in length, with some being relatively short and concise, while others are more detailed and lengthy. Some constitutions may provide specific details on the powers and functions of each branch of government, while others may leave room for interpretation and flexibility.
2. Sources of authority: Constitutions can derive their authority from different sources, such as religious texts, historical documents, or popular sovereignty. Some countries may have a constitution that is rooted in religious principles, while others may emphasize the will of the people as the ultimate source of authority.
3. Amendment process: The process for amending a constitution can also vary. Some constitutions may require a simple majority vote in the legislature, while others may require a supermajority or even a national referendum. The ease or difficulty of amending a constitution can have significant implications for the stability and adaptability of a country’s legal framework.
4. Protections and rights: Constitutions often include provisions that protect the rights and freedoms of citizens. The specific rights and protections outlined can vary, with some constitutions placing a greater emphasis on individual rights, while others may prioritize collective rights or social welfare. The extent and scope of these rights can also vary, depending on the cultural, historical, and political context of a country.
5. Balance of power: Constitutions play a crucial role in establishing the balance of power between different branches of government. Some constitutions may grant significant powers to the executive branch, while others may focus on creating a system of checks and balances between multiple branches. The specific allocation of powers can have a profound impact on the functioning of a country’s government.
In summary, the differences between constitutions can be seen in their length and specificity, sources of authority, amendment process, protections and rights, and balance of power. These differences reflect the unique historical, cultural, and political contexts in which constitutions are crafted and implemented, ultimately shaping the governance and legal systems of different countries.
Source of Authority
The source of authority in a constitution refers to the ultimate power or entity from which the constitution derives its legitimacy and validity. It defines who has the right to make decisions and exercise control over a country’s governance. This can vary significantly between different constitutions.
In some constitutions, the source of authority may be derived from a religious or divine entity. For example, in Iran, the Islamic Republic’s constitution is based on the principle of divine authority, with ultimate power vested in the Supreme Leader who is considered the representative of God on Earth. Similarly, in Saudi Arabia, the Basic Law of Governance is founded on Islamic principles and the authority is vested in the ruling monarchy as custodians of the two holy mosques.
In other constitutions, the source of authority may be based on popular sovereignty, where power is derived from the people. This can be seen in the United States, where the Constitution begins with the phrase “We the People,” emphasizing that the authority of the government is derived from the consent of the governed. The Constitution of India also establishes the authority of the government in the name of the people.
Furthermore, some constitutions may have a combination of different sources of authority. For instance, the Constitution of South Africa recognizes both popular sovereignty and democratic representation, as well as acknowledging the importance of traditional leadership and cultural diversity. It provides for a system of government that reflects the values and aspirations of the diverse South African society.
Ultimately, the source of authority in a constitution plays a crucial role in shaping the legal framework and governance of a country. It defines the relationship between the government and the people, and determines the extent and limitations of power. Different approaches to the source of authority can have significant implications for the rights and freedoms of citizens, as well as the overall stability and legitimacy of a constitution.
Amendment Process
The amendment process is a crucial aspect of any constitution as it allows for the document to be changed and adapted over time. It provides a mechanism for addressing evolving societal needs and ensuring that the constitution remains relevant and responsive to the needs of the people.
Key Features of the Amendment Process:
- The process for amending a constitution varies between different countries, but it generally involves a specific procedure that must be followed.
- Typically, an amendment must be proposed by a legislative body or through a popular initiative, and then it must be ratified by a certain number of states or by the general population through a referendum.
- Amendments can be relatively simple, such as correcting typographical errors, or they can be substantial, such as altering fundamental rights or changing the structure of government.
- The process for amending a constitution is often intentionally difficult in order to ensure that proposed changes have widespread support and are not made impulsively or without careful consideration.
Importance of the Amendment Process:
The amendment process serves as a reflection of the democratic principles upon which a constitution is based. It allows for the voice of the people to be heard and for their values and priorities to be reflected in the constitution’s content and provisions. Furthermore, the ability to amend a constitution ensures that it can adapt to changing circumstances and societal needs. Without a robust amendment process, a constitution may become outdated and ineffective in guiding the governance of a nation.
In conclusion, the amendment process plays a vital role in the effectiveness and relevance of a constitution. By providing a mechanism for change and adaptation, it ensures that the constitution remains a living document that reflects the values and needs of the people. It reinforces the democratic principles upon which a constitution is built and allows for the continuous improvement and development of a nation’s governance framework.