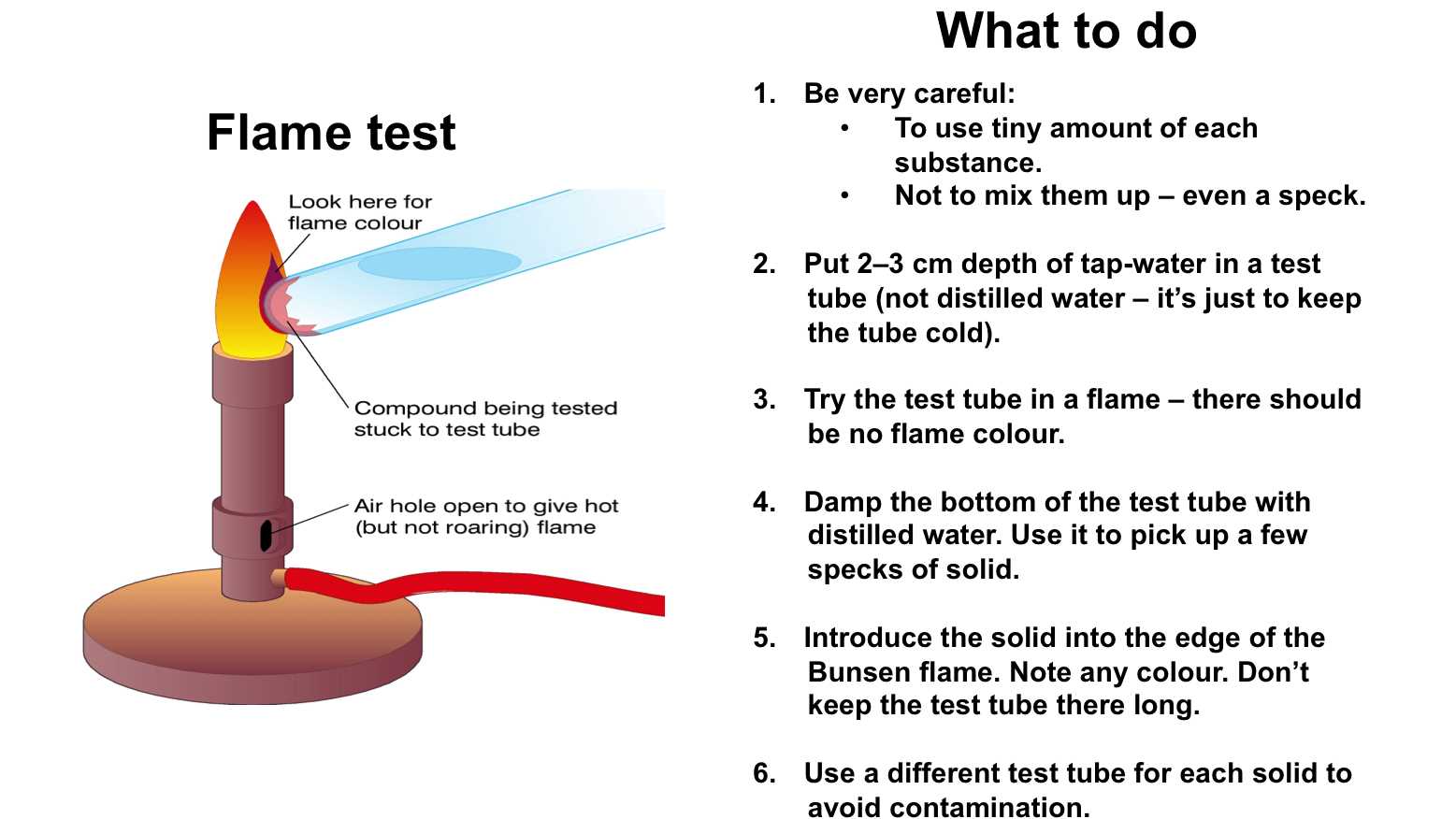
In the study of chemistry, observing how substances react under certain conditions provides valuable insight into their properties. One such method involves using heat to observe the distinct colors emitted by elements when they are exposed to intense temperatures. This process allows scientists to determine the presence of specific metals or compounds based on the color produced during the reaction. It is a fundamental technique used for both educational purposes and practical applications in various scientific fields.
Understanding the Process

When certain metals or salts are heated, they emit characteristic colors. This occurs due to the energy absorbed by the electrons in the atoms, which causes them to move to higher energy levels. As they return to their original state, energy is released in the form of visible light. Different elements release different wavelengths of light, making each color unique to the element it comes from.
Common Elements and Their Colors
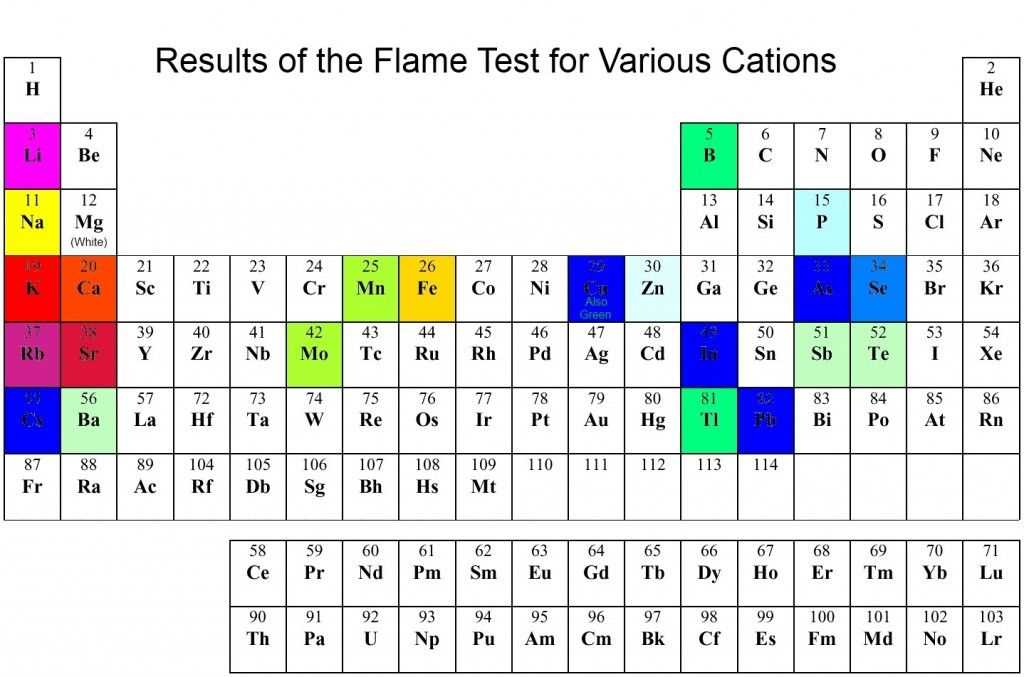
- Sodium: Bright yellow
- Potassium: Light lilac or purple
- Copper: Green or blue
- Calcium: Orange-red
- Barium: Green
Practical Applications and Safety
This technique is not only a valuable tool in chemistry classes but also has real-world applications in fields such as material science and forensic analysis. It helps in identifying unknown substances and can be used for quality control in manufacturing processes. However, proper safety measures must be observed when conducting such reactions, including wearing protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation.
Interpreting Results
The colors produced during heating should be compared to known standards to accurately identify the substances involved. Each reaction provides a unique pattern, allowing for precise conclusions about the composition of the material. Interpretation of the results requires a thorough understanding of the elements involved and the specific conditions under which the reactions occur.
Role of Colors in Chemical Reactions Identifying Elements Through Heat Reactions
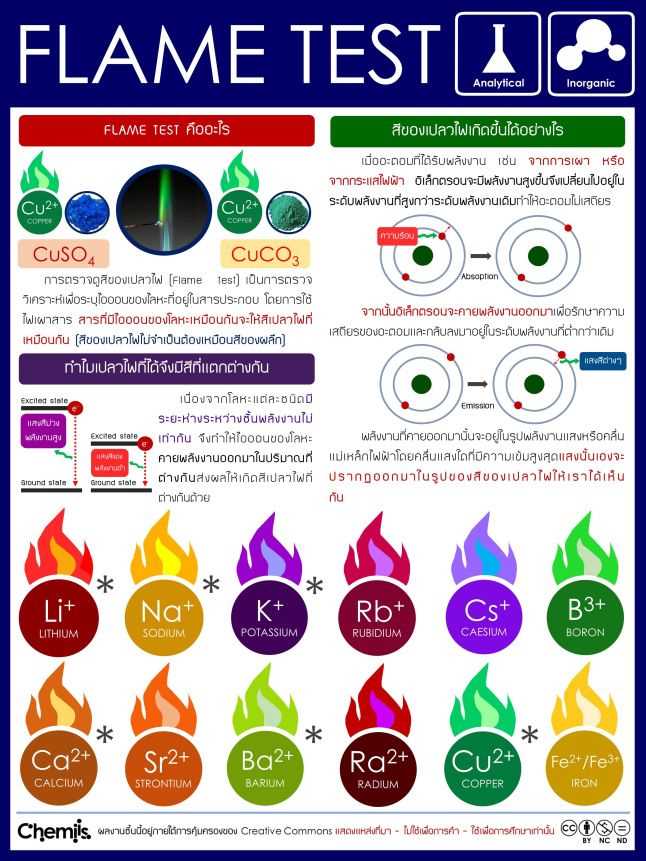
The observation of colors produced during chemical reactions is a critical method for determining the identity of certain elements. When specific materials are exposed to intense heat, they emit distinct shades of light, which can be used to identify their composition. This visual indication helps chemists and students alike understand the properties of various substances, making the process both informative and essential for accurate analysis.
Common Elements and Their Color Indications
Each element reacts uniquely to heat, producing a specific color that serves as its signature. For example, sodium generates a bright yellow hue, while potassium shows a delicate lilac color. These distinctive colors can be used to differentiate between substances and aid in their identification, providing valuable information without the need for complex equipment or analysis.
Proper Heat Exposure Procedures for Safety
While the reaction of materials to heat is fascinating, safety should always be the primary concern. Proper handling of materials and the use of protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, is essential to avoid accidents. Additionally, ensuring a well-ventilated area is crucial to prevent harmful fumes from accumulating. Correct procedures should be followed to ensure both the accuracy of the results and the safety of the individuals involved.
By closely observing the reactions and the colors produced, accurate conclusions can be made regarding the identity of elements involved. These visual cues, when carefully analyzed, provide chemists with the necessary data to determine the specific substances being tested. The ability to interpret these results correctly is a skill that is essential in both educational and professional chemistry settings.