
Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique in molecular biology and genetics. It allows scientists to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. This technique plays a crucial role in various applications, such as genetic testing, forensic analysis, and gene expression studies. To better understand gel electrophoresis, many virtual lab simulations are available online, offering a hands-on experience without the need for physical equipment.
One of the most frequently asked questions regarding gel electrophoresis virtual labs is where to find the answers. Students often need guidance to interpret the results and understand the underlying concepts. The answers can be found in PDF format, which allows easy access and sharing. These PDF files provide detailed explanations, step-by-step procedures, and analysis of the virtual lab results.
A gel electrophoresis virtual lab answer PDF typically includes information on the experimental setup, such as the type of gel used (agarose or polyacrylamide) and the running buffer composition. It also covers the loading of the samples, including the DNA, RNA, or protein samples, as well as the ladder or molecular weight markers. The PDF guides the reader through the process of setting up the electrophoresis apparatus and running the gel for a specific time and voltage.
Furthermore, the PDF provides explanations on how to interpret the gel electrophoresis results. It covers topics such as the movement of charged molecules in an electric field, the separation of DNA fragments based on their size, and the visualizing of the bands using DNA-specific stains. Additionally, the PDF answers questions about analyzing the results, such as determining the relative sizes of DNA fragments, estimating the molecular weight of unknown samples, or identifying genetic mutations.
Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Answers PDF
In the realm of molecular biology, gel electrophoresis is a commonly used technique for separating and analyzing DNA, RNA, and proteins. This process involves applying an electric field to a gel matrix, which causes charged molecules to move through the gel at different rates based on their size and charge. Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental tool in genetic research, forensic analysis, and diagnostic testing.
Through the use of virtual lab simulations and interactive software, students and researchers can now explore gel electrophoresis experiments without the need for physical materials or equipment. These virtual labs provide a realistic and interactive experience, allowing users to manipulate variables, observe results, and analyze data. This technology has revolutionized the way that gel electrophoresis is taught and practiced, making it more accessible and cost-effective.
The Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Answers PDF is a valuable resource for those learning or teaching about gel electrophoresis. It provides step-by-step instructions, explanations, and answers to common questions that may arise during a virtual lab. The PDF format makes it easy to access and share this information, ensuring that students and educators have a comprehensive guide at their fingertips.
- The Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Answers PDF covers topics such as the theory behind gel electrophoresis, setting up virtual experiments, interpreting gel images, and analyzing data.
- It includes tips and tricks for troubleshooting common issues that may arise during virtual lab sessions.
- The PDF also provides sample answers and explanations for virtual lab questions, allowing users to compare their results and understanding with the expected outcomes.
Overall, the Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Answers PDF is an essential tool for anyone interested in learning or teaching about gel electrophoresis. It offers a comprehensive guide to virtual lab experiments, ensuring that users can fully understand and utilize this important technique in molecular biology research.
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a widely used molecular biology technique used to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, or protein samples based on their size and charge. It is an essential tool in various fields, including genetic research, forensics, and medical diagnostics. Gel electrophoresis can be performed using agarose gel for nucleic acids or polyacrylamide gel for proteins.
During gel electrophoresis, a mixture of DNA, RNA, or protein samples is loaded onto a gel, which is a porous matrix. An electric current is then applied to the gel, causing the samples to migrate through the gel matrix. The DNA, RNA, or protein molecules move towards the positive electrode (anode) if they are negatively charged, or towards the negative electrode (cathode) if they are positively charged.
The gel matrix acts as a sieving medium, slowing down the movement of larger molecules and allowing smaller molecules to move faster. As a result, the molecules become separated and form distinct bands along the gel. These bands can be visualized using various staining techniques, such as ethidium bromide for DNA or Coomassie blue for proteins.
The separated molecules can then be analyzed or further manipulated, depending on the research objectives. Gel electrophoresis is commonly used to determine the size of DNA fragments, identify gene mutations, analyze gene expression patterns, or detect specific proteins in a sample. It provides valuable information that can contribute to our understanding of genetic disorders, genetic relationships, and biomarkers for diseases.
How does Gel Electrophoresis work?

Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, or protein molecules by their size and charge. It is based on the principle that charged molecules will migrate through a gel matrix in response to an electric field. This technique is commonly used in molecular biology research and forensic analysis.
In gel electrophoresis, a gel matrix, usually made of agarose or polyacrylamide, is prepared and cast in a mold. The gel is then placed in an electrophoresis chamber filled with a buffer solution that provides the necessary ions for the movement of charged molecules. Two electrodes are placed at the ends of the gel chamber, creating a positive and negative terminal.
The DNA, RNA, or protein sample to be analyzed is mixed with a loading buffer that contains a tracking dye, which allows the progress of electrophoresis to be visualized. The sample is then loaded into wells made in the gel. When an electric current is applied, the negatively charged molecules will migrate towards the positive terminal while the positively charged molecules will migrate towards the negative terminal. The smaller molecules will move faster through the gel matrix, while the larger molecules will move slower.
Once the electrophoresis is complete, the gel is stained with a dye, such as ethidium bromide, which binds to the DNA or protein and becomes fluorescent under UV light. The bands formed by the separated molecules can then be visualized and interpreted. By comparing the positions of the bands with the known standards, scientists can determine the size, quantity, and purity of the molecules in the sample.
Gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool in molecular biology as it allows researchers to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and protein fragments to understand their composition, structure, and function. It has various applications such as DNA sequencing, paternity testing, disease diagnosis, and protein analysis.
The Importance of Gel Electrophoresis in Molecular Biology
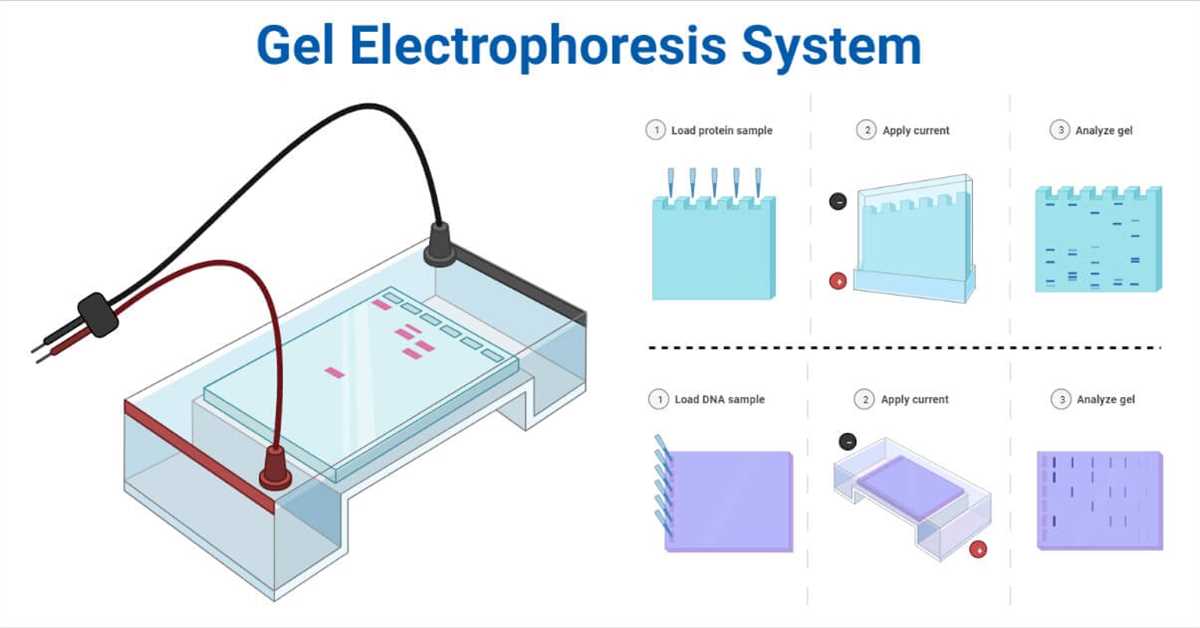
Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental technique used in molecular biology to separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. It plays a crucial role in various research areas, including genetics, genomics, and biotechnology.
One of the main reasons for the importance of gel electrophoresis is its ability to provide information about the size of DNA or RNA molecules. By running a sample through a gel matrix and subjecting it to an electric field, the molecules migrate at different speeds depending on their size. This allows scientists to determine the size range of DNA fragments, the presence of specific genes or mutations, and the purity of DNA or RNA samples.
Gel electrophoresis is also essential for analyzing genetic variation and studying gene expression. Researchers can use this technique to compare the DNA profiles of different individuals and identify genetic markers associated with diseases or traits. Additionally, gel electrophoresis can be used to measure the level of gene expression by separating and quantifying RNA molecules based on their abundance.
- Furthermore, gel electrophoresis is a vital tool in DNA sequencing, which is the process of determining the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. By fragmenting DNA into smaller pieces and sequencing them on a gel, scientists can decipher the genetic code and gain insights into the function and structure of genes.
- In the field of biotechnology, gel electrophoresis is used for the purification and analysis of proteins. It allows the separation of proteins based on their size and charge, enabling the identification and characterization of specific proteins in complex mixtures. This information is essential for understanding protein functions and developing new drugs or therapies.
- Lastly, gel electrophoresis is widely used in forensic science for DNA profiling and identifying suspects in criminal investigations. By comparing DNA samples using gel electrophoresis, scientists can determine the presence of specific genetic markers, providing valuable evidence in court cases.
In summary, gel electrophoresis is an indispensable technique in molecular biology due to its ability to separate, analyze, and quantify DNA, RNA, and proteins. It has revolutionized the field and continues to be a valuable tool for a wide range of research applications.
Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab: Procedure
In this virtual gel electrophoresis lab, you learned how to simulate gel electrophoresis using virtual tools. The procedure involved several steps:
- Preparing the gel: You prepared a gel using agarose and a buffer solution. You allowed the gel to solidify in a gel electrophoresis chamber.
- Preparing the DNA samples: You obtained DNA samples from different sources and prepared them by adding loading dye. The dye helps visualize the movement of the DNA during electrophoresis.
- Loading the gel: You carefully loaded each DNA sample into separate wells in the gel using a micropipette. You made sure to keep track of which sample was loaded in each well.
- Running the electrophoresis: You connected the gel electrophoresis chamber to a power source, which generated an electric field. This field caused the DNA samples to move through the gel based on their size and charge. You monitored the electrophoresis process to ensure that the DNA samples were separating properly.
- Visualizing the results: After the electrophoresis run, you stopped the electric current and removed the gel from the chamber. You stained the gel with a dye to make the DNA bands visible. Using a UV light or another appropriate imaging technique, you observed the DNA bands and recorded your observations.
Overall, this virtual gel electrophoresis lab allowed you to gain hands-on experience with the principles and techniques involved in gel electrophoresis. By simulating the procedure, you were able to understand the process of DNA separation based on size and charge. This virtual lab also provided an opportunity to analyze and interpret the results, further enhancing your understanding of gel electrophoresis in a practical and interactive way.
Q&A:
What is the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab?
The Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab is an online simulation tool that allows users to learn and practice the procedure of gel electrophoresis without the need for actual materials or equipment.
What is the procedure for the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab?
The procedure for the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab involves several steps. First, users select the DNA samples they want to analyze and load them into wells on the virtual gel. Then, they set the parameters for the electrophoresis, such as voltage and time. After running the electrophoresis, they analyze the results and interpret the DNA bands.
How can I access the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab?
The Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab can be accessed online through a web browser. It is typically available on educational websites or platforms that offer virtual science labs.
What are the benefits of using the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab?
The Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab allows users to practice the procedure of gel electrophoresis in a virtual environment, which eliminates the need for expensive equipment and materials. It also provides a safe and controlled environment for learning, where mistakes can be made without any consequences.
Can the results from the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab be trusted?
The results from the Virtual Gel Electrophoresis Lab can provide a good understanding of the procedure and principles of gel electrophoresis. However, since it is a simulation, there may be some limitations and discrepancies compared to real-life experiments. It is important to keep in mind that the virtual lab is meant for learning and practice purposes, and real-life experiments should be conducted for accurate results.
What is a virtual gel electrophoresis lab?
A virtual gel electrophoresis lab is a simulated laboratory activity that allows students to practice and learn the procedure of gel electrophoresis without the need for actual lab materials.