Geometry transformations are an essential part of understanding and analyzing shapes in mathematics. They allow us to manipulate and explore geometric figures, helping us uncover their hidden properties and connections. To assess students’ understanding and proficiency in these transformations, teachers often provide worksheets with various exercises and problems. Having an answer key is crucial not only for students to check their work but also for teachers to assess the accuracy of the solutions.
This comprehensive guide provides an answer key to a geometry transformations worksheet, allowing students to self-assess their progress and correct any mistakes made. Each exercise and problem in the worksheet is thoroughly explained, making it an excellent study tool for students to deepen their comprehension of different types of transformations. Moreover, the answer key serves as a valuable resource for teachers, enabling them to quickly grade the worksheets and identify areas where students may need additional support.
The answer key includes detailed step-by-step solutions for each problem, covering a wide range of concepts related to geometry transformations. Students will find answers to exercises involving translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. Furthermore, the key also highlights common errors to look out for and offers additional tips and insights to assist students in mastering each transformation technique.
By utilizing this geometry transformations worksheet answer key, both teachers and students can enhance their understanding and proficiency in geometry. Whether it is preparing for an exam, practicing problem-solving skills, or reviewing concepts, this resource proves to be an invaluable companion. With its comprehensive explanations and thorough solutions, it enables students to navigate and excel in the fascinating world of geometry transformations.
What is a geometry transformation?
A geometry transformation is a mathematical operation that changes the position, shape, or orientation of a geometric figure. It is a fundamental concept in geometry that allows us to study how figures can be manipulated and transformed in various ways.
The main types of geometry transformations include translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations. Each of these transformations has specific rules and properties that dictate how the figure is changed.
Translations involve shifting a figure from one location to another. This is done by moving every point of the figure in the same direction and by the same distance.
Reflecions involve flipping a figure across a line, called the line of reflection. Each point on the figure is transformed to a new location that is equidistant from the line of reflection.
Rotations involve rotating a figure around a fixed point, called the center of rotation. Each point on the figure is transformed to a new location based on the angle and direction of the rotation.
Dilations involve changing the size of a figure while maintaining its shape. Each point on the figure is transformed to a new location based on a scale factor, which determines how much the figure is enlarged or reduced.
Geometry transformations are used in various fields, including computer graphics, architecture, and engineering. They are essential for understanding spatial relationships and for solving problems involving geometric figures.
Types of Geometry Transformations
In geometry, there are several types of transformations that can be performed on geometric figures. These transformations are used to manipulate the shape, size, and position of the figures. Understanding these transformations is essential for solving problems and analyzing geometric patterns.
Translation: This transformation involves moving a figure from one position to another without changing its shape or size. It can be performed by sliding the figure along a straight line in any direction. Translations are commonly represented using vector notation, where the coordinates of each point are shifted by a fixed amount.
Rotation: Rotation involves turning a figure around a fixed point called the center of rotation. The figure is rotated by a certain angle in a specific direction. The center of rotation and the angle of rotation determine the final position of each point in the figure. Rotations can be clockwise or counterclockwise.
Reflection: Reflection is a transformation that produces a mirror image of a figure. It involves flipping the figure over a line of reflection, which acts as a mirror. Each point in the figure is reflected across the line to its corresponding point in the mirror image. Reflections can be performed horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
Dilation: Dilation is a transformation that changes the size of a figure while preserving its shape. It involves stretching or shrinking the figure by a certain scale factor. The scale factor determines how much the figure is dilated. If the scale factor is greater than 1, the figure is enlarged; if it is less than 1, the figure is reduced in size.
In summary, these are the main types of transformations in geometry: translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation. Each transformation has its own rules and properties, and they can be combined to create more complex transformations. Understanding and applying these transformations is fundamental in geometry and is essential for solving problems and analyzing geometric figures in various contexts.
How to Perform a Geometry Transformation

Geometry transformation involves changing the position, size, and shape of an object while preserving its properties. There are several types of transformations, including translation, rotation, reflection, and dilation. Each type of transformation has its own rules and procedures.
Translation: To perform a translation, you need to move the object horizontally or vertically by a certain distance. This can be done by adding or subtracting coordinates. For example, to translate a point (x, y) to (x+a, y+b), you need to add a to the x-coordinate and b to the y-coordinate.
Rotation: To perform a rotation, you need to rotate the object around a fixed point called the center of rotation. The angle of rotation determines the amount of rotation. To rotate a point (x, y) by an angle θ, you can use the following formulas:
- x’ = x*cos(θ) – y*sin(θ)
- y’ = x*sin(θ) + y*cos(θ)
Reflection: To perform a reflection, you need to mirror the object across a line called the line of reflection. The line of reflection acts as a mirror, reflecting the object on the opposite side. To reflect a point (x, y) across the line y = mx + b, you can use the following formulas:
- x’ = x – 2*m*(m*x – y + b) / (m^2 + 1)
- y’ = 2*m*x – y + 2*b / (m^2 + 1)
Dilation: To perform a dilation, you need to enlarge or shrink the object by a certain factor called the scale factor. The scale factor determines the change in size. To dilate a point (x, y) by a scale factor of k, you can use the following formulas:
- x’ = k*x
- y’ = k*y
By understanding and applying these transformation rules, you can manipulate geometric objects in various ways and solve problems involving transformations.
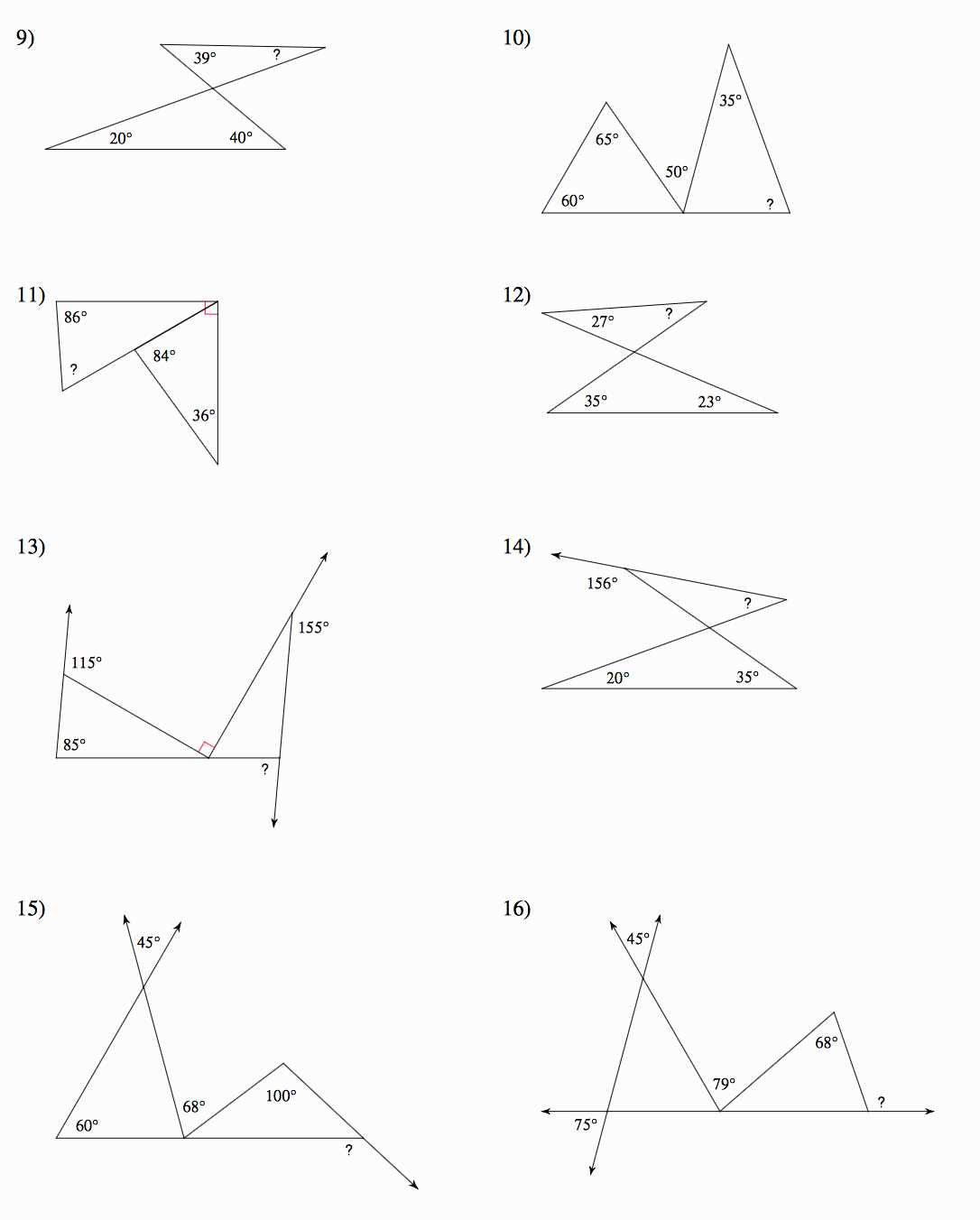
Common mistakes when solving geometry transformations
Geometry transformations can often be tricky to solve, and there are common mistakes that students make when working on these types of problems. Understanding these mistakes can help students avoid them and improve their problem-solving skills in geometry.
1. Neglecting to identify the correct transformation: One common mistake is failing to identify the correct transformation being used in the problem. Students may mistakenly assume that a figure has undergone a translation when it has actually undergone a rotation or reflection. It is important to carefully analyze the given information and the resulting figure to correctly identify the transformation involved.
2. Incorrectly applying the transformation rules: Another mistake is misunderstanding or misapplying the rules of the specific transformation being used. For example, when translating a figure, students may incorrectly determine the direction and distance of the translation. Likewise, when reflecting a figure, students may incorrectly identify the line of reflection. It is crucial to thoroughly understand the rules and properties of each transformation in order to apply them correctly.
3. Failing to consider the properties of the original figure: Sometimes, students forget to consider the properties of the original figure when solving a geometry transformations problem. For instance, if the original figure is a rectangle, the transformed figure should still have four right angles and opposite sides that are equal in length. Neglecting these properties can result in an incorrect solution.
4. Making errors in calculations: Calculation errors are another common mistake when solving geometry transformations. Students may make mistakes in measuring angles or distances, resulting in inaccurate transformations. It is important to carefully measure and calculate each step to ensure the accuracy of the solution.
In conclusion, understanding and avoiding common mistakes in geometry transformations can greatly improve students’ problem-solving skills in this area. By carefully analyzing the given information, correctly applying the transformation rules, considering the properties of the original figure, and minimizing calculation errors, students can successfully solve geometry transformations problems with confidence.
Using a Geometry Transformations Worksheet
Geometry transformations worksheets are a valuable tool for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of geometric concepts and transformations. These worksheets typically consist of a series of questions and problems that cover topics such as translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations. By completing these worksheets, students can enhance their geometric reasoning and problem-solving skills.
One of the key benefits of using a geometry transformations worksheet is that it provides students with a structured way to review and practice different types of transformations. The worksheets usually start with simple questions that introduce the basic concepts and gradually progress to more complex problems. This progression allows students to build their confidence and competence in applying geometric transformations.
Each problem in a geometry transformations worksheet usually includes a figure or shape that needs to be transformed. Students are then asked to perform a specific transformation on the figure, such as translating it along a certain vector, reflecting it across a line, rotating it around a point, or dilating it with respect to a given center of dilation. They may also be asked to describe the resulting figure or calculate certain properties, such as the coordinates of specific points.
The answer key for a geometry transformations worksheet is an essential component, as it allows students to check their work and verify their solutions. It provides step-by-step explanations and solutions for each problem, helping students understand the correct approach and reasoning behind the transformations. The answer key serves as a valuable tool for self-assessment, allowing students to identify any areas of weakness and seek additional practice or clarification.
In conclusion, a geometry transformations worksheet is a valuable resource for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of geometric concepts and transformations. By completing these worksheets and utilizing the accompanying answer key, students can enhance their geometric reasoning and problem-solving skills, ultimately improving their overall performance in geometry.
Answer Key for a Geometry Transformations Worksheet
A geometry transformations worksheet typically involves questions about different types of transformations, such as translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. These worksheets are designed to help students practice their understanding of geometric transformations and apply them to various shapes and figures.
Below is an answer key for a geometry transformations worksheet, which provides the correct answers to the questions or prompts on the worksheet. This answer key can be used by teachers to assess their students’ progress and understanding of the topic. It can also be provided to students as a reference to check their work and ensure accuracy.
Answer Key:
- 1. Translation: (-2, 4)
- 2. Reflection: x-axis
- 3. Rotation: 90 degrees counterclockwise
- 4. Dilation: scale factor of 2
- 5. Translation: (3, -5)
- 6. Reflection: y-axis
- 7. Rotation: 180 degrees clockwise
- 8. Dilation: scale factor of 0.5
It is important to note that the answers provided in this answer key may vary depending on the specific questions or prompts given in the worksheet. Teachers should ensure that the answers align with the given questions and provide appropriate guidance to their students.
Overall, a geometry transformations worksheet answer key serves as a helpful tool for both teachers and students. It allows teachers to assess their students’ understanding of geometric transformations, and it provides students with a reference to check their work and improve their skills in this topic.