In today’s rapidly changing job market, it’s important to understand the concepts related to employment, labor, and wages. Whether you are a job seeker, an employer, or simply interested in economic trends, having a solid grasp of these topics is essential. This guided reading activity will provide you with the answer key to help you navigate through the complex world of employment, labor, and wages.
First, let’s define some key terms. Employment refers to the act of being employed or having a job. Labor, on the other hand, refers to the physical or mental effort that is put into work. Lastly, wages are the financial compensation given to workers in exchange for their labor. Understanding these definitions will lay the foundation for comprehending the interconnectedness of these concepts.
This guided reading activity will explore various aspects of employment, labor, and wages. You will discover how employment rates are determined, the factors that influence labor supply and demand, and the different types of wages and compensation systems. By the end of this activity, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the key components that drive the job market and determine workers’ earning potential.
Guided Reading Activity Employment Labor and Wages Answer Key
In this guided reading activity, we will be reviewing the answer key for questions related to employment, labor, and wages. By utilizing this answer key, students will be able to assess their understanding of key concepts and assess the accuracy of their responses.
1. The three main types of business organization are: sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some advantages of a sole proprietorship include ease of starting up and full control over the business. Some disadvantages include unlimited liability and limited access to financial resources. A partnership is a business that is owned by two or more people. Some advantages of a partnership include shared decision-making and shared financial resources. Some disadvantages include unlimited liability and potential for conflicts between partners. A corporation is a legal entity that is separate from its owners. Some advantages of a corporation include limited liability for owners and easier access to financial resources. Some disadvantages include more extensive record-keeping requirements and double taxation.
- 2. Labor unions are organizations that represent workers and negotiate with employers on their behalf. They aim to secure better wages, benefits, and working conditions for their members. Some benefits of labor unions include collective bargaining power, job security, and access to healthcare and retirement benefits. Some disadvantages include the possibility of strikes and higher membership fees.
- 3. The minimum wage is the lowest hourly wage that employers are legally allowed to pay their workers. It is set by the government and varies by state. The purpose of the minimum wage is to ensure that workers receive a fair wage for their work and to prevent exploitation. However, critics argue that increasing the minimum wage can lead to job loss and higher prices.
- 4. Wage discrimination refers to the unequal treatment of workers in terms of their pay. This can occur based on factors such as gender, race, or ethnicity. The Equal Pay Act of 1963 aimed to address wage discrimination by prohibiting employers from paying different wages to men and women who perform substantially equal work. Despite this, wage gaps still exist, and efforts continue to eliminate wage discrimination.
Overall, this guided reading activity helped to reinforce key concepts related to employment, labor, and wages. By understanding the different types of business organizations, the role of labor unions, the minimum wage, and wage discrimination, students gained a deeper understanding of the complexities of the labor market and the importance of fair and equitable treatment for workers.
Different Types of Employment
There are various types of employment arrangements that individuals can enter into depending on their qualifications, preferences, and skills. These arrangements dictate the terms and conditions of the working relationship between employers and employees. Understanding the different types of employment can help individuals make informed decisions about their career paths and job opportunities.
1. Full-time employment
Full-time employment is the most common type of employment arrangement. In this arrangement, employees work a set number of hours per week, usually 35 to 40 hours. They are entitled to benefits such as paid leave, health insurance, and retirement plans. Full-time employees are usually considered permanent and have a stable income. They are expected to commit to the responsibilities and tasks assigned to them on a full-time basis.
2. Part-time employment
Part-time employment is suitable for individuals who want to work fewer hours per week compared to full-time employees. Part-time employees usually work less than 35 hours per week and may or may not be entitled to the same benefits as full-time employees. This type of employment arrangement offers flexibility and can be an option for those who have other commitments or prefer a more balanced work-life schedule.
3. Contract or freelance employment
Contract or freelance employment refers to individuals who work on a project or contractual basis. They are usually self-employed and provide their services to clients or companies on a short-term or temporary basis. Contractors or freelancers have more flexibility in terms of choosing their projects and determining their working hours. They may not be entitled to benefits like full-time employees but often have higher earning potentials.
4. Temporary or seasonal employment
Temporary or seasonal employment involves working for a fixed period of time or during specific seasons or events. Temporary employees are hired to cover staff shortages or to meet short-term demands. They may be employed by recruitment agencies or directly by employers. This type of employment can offer an income source for individuals who are looking for temporary work or additional income during busy periods.
5. Internship or apprenticeship
Internships or apprenticeships provide individuals with practical work experience in specific industries or professions. These programs are usually designed for students or graduates who aim to gain hands-on skills and knowledge in their field of study. Interns or apprentices may receive a stipend or be paid a lower wage compared to regular employees. The main goal of these programs is to provide valuable learning opportunities and bridge the gap between education and the workforce.
Understanding the different types of employment is essential for job seekers and individuals planning their career paths. Each type of employment has its own advantages and disadvantages, and individuals should consider their personal goals, preferences, and circumstances when deciding which employment arrangement is the most suitable for them.
Trends in Labor Market
The labor market is constantly evolving and changing due to various economic, social, and technological factors. Understanding the current trends in the labor market is essential for both job seekers and employers. Here, we will explore some of the key trends shaping the labor market today.
1. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have had a profound impact on the labor market, particularly in terms of job creation and automation. Many routine and repetitive tasks can now be automated, leading to a shift in the types of jobs available. As technology advances, the demand for skilled workers with expertise in areas such as data analysis, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity is on the rise. At the same time, certain roles may become obsolete, requiring workers to adapt and acquire new skills to remain competitive.
2. Gig Economy
The rise of the gig economy is another significant trend in the labor market. With the gig economy, individuals work on a project or task basis rather than having traditional full-time employment. This offers flexibility and independence for workers, but it also raises concerns regarding job security and benefits. The gig economy has expanded with the growth of online platforms and digital marketplaces, providing opportunities for freelancers, contractors, and independent workers.
3. Shift in Skills Requirements
Skills requirements have shifted in recent years, as employers increasingly prioritize soft skills and adaptability. While technical skills are still important, the ability to communicate effectively, work in teams, solve problems, and embrace change are becoming essential. As industries continue to evolve, workers who can demonstrate a combination of technical expertise and soft skills will be highly sought after.
4. Increasing Diversity and Inclusion
The labor market is becoming more diverse and inclusive, reflecting changing societal attitudes and demographics. Companies are recognizing the value of diversity and actively seeking to create inclusive workplaces. This has led to increased efforts to recruit and retain individuals from diverse backgrounds, including women, minorities, and individuals with disabilities. Furthermore, diversity and inclusion initiatives are proven to enhance creativity, innovation, and overall business performance.
5. Remote and Flexible Work
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards remote and flexible work arrangements. Many employers have realized the benefits of allowing employees to work remotely, and this trend is likely to continue even after the pandemic subsides. Remote work offers greater work-life balance, reduces commuting time, and allows access to global talent pools. However, it also presents challenges such as maintaining team cohesion and ensuring productivity.
Overall, the labor market is experiencing significant changes driven by technology, shifts in skills requirements, diversity and inclusion efforts, and the growth of the gig economy. Staying informed about these trends can help individuals navigate their careers and enable employers to adapt their hiring strategies to attract and retain top talent.
Factors Affecting Employment Rates
Employment rates are influenced by various factors that impact the labor market. These factors play a crucial role in determining the availability of jobs and the ability of individuals to secure employment. Here are some key factors that affect employment rates:
Economic Growth:
Economic growth is a significant determinant of employment rates. When the economy is thriving and experiencing positive growth, businesses tend to expand, leading to an increase in job opportunities. Conversely, during periods of economic downturn or recession, businesses may cut back on hiring or even lay off employees, resulting in higher unemployment rates.
Demographic Changes:
Demographic changes can also influence employment rates. The size and composition of the workforce, including factors such as population growth, aging population, and migration patterns, can affect the demand and supply of labor. For example, an aging population may result in a decrease in the labor force participation rate, while a growing working-age population may lead to increased employment opportunities.
Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements have had a profound impact on the labor market. Automation and advancements in artificial intelligence have led to increased productivity and efficiency in many industries. While this can create new job opportunities, it can also result in job displacement and the need for individuals to acquire new skills to remain employable.
Government Policies:
Government policies, such as labor regulations, tax incentives, and minimum wage laws, can directly impact employment rates. These policies can either encourage or discourage businesses from hiring and investing in the workforce. For instance, lower taxes and relaxed regulations may incentivize businesses to expand and hire more employees, while higher minimum wages may lead to reduced hiring.
Educational Attainment:
The level of educational attainment within a population can affect employment rates. Higher levels of education typically correlate with higher employment rates and greater earning potential. Individuals with advanced degrees or specific skill sets are often in higher demand and more likely to secure employment.
Overall, employment rates are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, demographic, technological, government, and educational factors. Understanding and addressing these factors is essential for policymakers, businesses, and individuals seeking to improve employment opportunities and labor market outcomes.
Understanding Labor and Wages
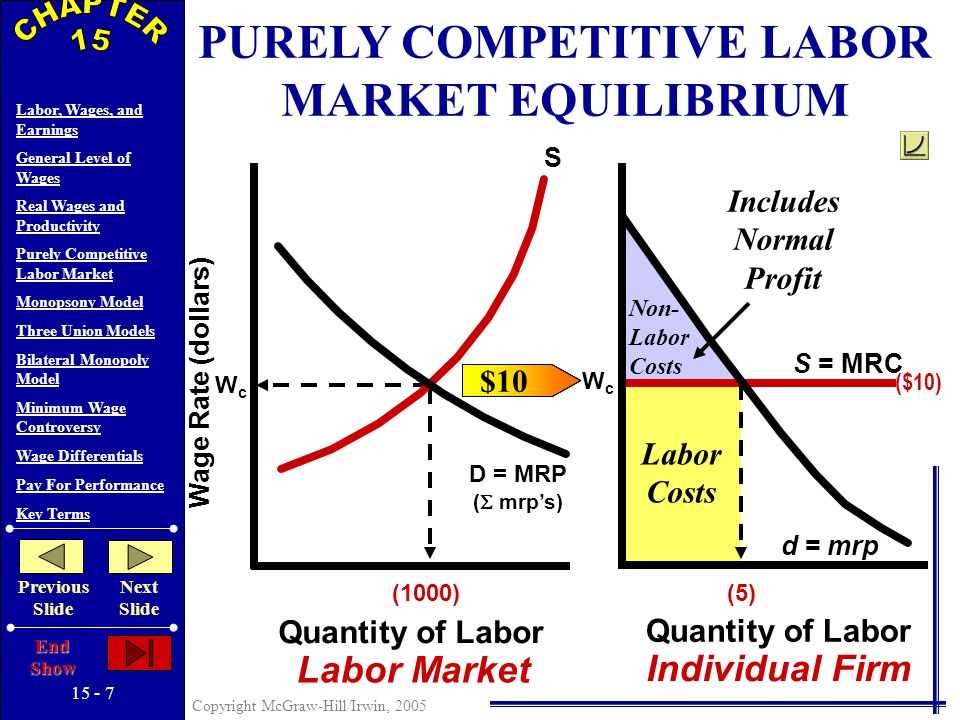
When discussing employment, labor, and wages, it is important to have a clear understanding of the concepts and their relationship. Labor refers to the physical and mental effort expended in the production of goods and services. It includes both skilled and unskilled work. Wages, on the other hand, are the monetary compensation paid to employees for their labor. Wages can be influenced by various factors, such as the demand for certain skills, the availability of labor, and the bargaining power of workers.
The labor market operates based on the principles of supply and demand. The supply of labor is determined by the number of people available and willing to work, while the demand for labor is influenced by the needs of businesses and the overall state of the economy. When the demand for labor exceeds the supply, wages tend to rise. Conversely, when there is an oversupply of labor, wages may decrease. This dynamic is often observed in industries with high levels of competition and in regions with high unemployment rates.
Factors that affect wages and labor market dynamics include education and skill levels, technological advancements, government policies, and labor unions. Higher levels of education and specialized skills generally lead to higher-paying jobs. Technological advancements can both create and eliminate jobs, impacting the overall demand for labor. Government policies, such as minimum wage laws and taxation, also play a role in determining wages. Additionally, labor unions negotiate on behalf of workers to secure better wages and working conditions.
Understanding the relationship between labor and wages is crucial for both employers and employees. Employers need to ensure that their wage offers are competitive in order to attract and retain skilled workers. Employees, on the other hand, need to understand the factors that influence wages in order to make informed decisions about their careers and negotiate fair compensation for their labor.
Challenges in Wage Determination
Wage determination is a complex process that involves various factors and challenges. One key challenge is the influence of supply and demand in the labor market. When the demand for certain skills or occupations is high and the supply is low, employers may be willing to pay higher wages to attract and retain qualified workers. On the other hand, when there is an oversupply of workers in a particular field, employers may have more bargaining power and can potentially keep wages low.
Another challenge in wage determination is the impact of government policies and regulations. Minimum wage laws, for example, set a minimum wage that employers must pay their workers. While these laws aim to protect workers and ensure fair pay, they can also create challenges for businesses, especially small ones, that may struggle to afford higher wages. Additionally, tax policies, labor laws, and other regulations can affect wage levels and employment conditions.
The influence of productivity is another important factor in wage determination. More productive workers tend to earn higher wages as their contributions to the company’s output are valued and rewarded. However, measuring and assessing productivity objectively can be challenging, especially in jobs that involve a high level of subjectivity or where output is difficult to quantify.
Furthermore, the presence and influence of labor unions can also impact wage determination. Unions negotiate on behalf of workers and aim to secure higher wages and better working conditions. Collective bargaining agreements, strikes, and other union actions can affect wage levels and create tensions between workers and employers.
In conclusion, wage determination is a multi-faceted process with various challenges. Supply and demand dynamics, government policies, productivity considerations, and labor union influence all play a role in determining wages. Understanding these challenges is important for employers, workers, and policymakers in creating a fair and balanced labor market.
Importance of Labor Laws and Regulations
Labor laws and regulations play a crucial role in ensuring fair and equitable treatment of workers in the employment sector. These laws and regulations are designed to protect the rights of employees and establish standards for working conditions, wages, and benefits. They also serve to prevent exploitation and discrimination in the workplace.
1. Protection of workers: Labor laws and regulations provide legal safeguards for workers, ensuring that they are treated fairly and have access to certain rights. These include the right to a safe and healthy work environment, the right to fair compensation, the right to rest and breaks, and protection against unfair labor practices. These laws also establish guidelines for hiring and firing practices, preventing discrimination and ensuring equal opportunities for all employees.
2. Empowering workers: Labor laws and regulations empower workers by giving them a voice and a platform to express their concerns and grievances. These laws often establish mechanisms for collective bargaining and the formation of labor unions, allowing workers to negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. This empowers workers to have a say in their employment terms and contributes to a more balanced employer-employee relationship.
- 3. Ensuring economic stability: Labor laws and regulations contribute to economic stability by establishing minimum wage standards, regulating maximum working hours, and providing protections against unfair labor practices. These measures help to prevent the exploitation of workers and ensure that they receive fair compensation for their work. By establishing standards and regulations, labor laws also create a level playing field for businesses, promoting fair competition and economic growth.
- 4. Promoting social justice: Labor laws and regulations serve as a tool for promoting social justice and reducing inequality in society. By ensuring fair treatment and equal opportunities for all workers, regardless of their background or circumstances, these laws contribute to a more just and equitable society. They help reduce discrimination, promote diversity and inclusion, and create a more harmonious and cohesive workforce.
In conclusion, labor laws and regulations are of utmost importance in the employment sector as they protect and empower workers, ensure economic stability, and promote social justice. These laws and regulations establish standards and guidelines for fair treatment and help create a balanced and equitable workplace for all. It is essential for countries and organizations to enforce and abide by these laws in order to create a society that values and respects the rights and well-being of its workers.