Welcome to the first lesson of guided reading on Colonial America! In this lesson, we will explore the key events, people, and ideas that shaped early American history. By the end of this lesson, you will have a solid understanding of the foundations of colonial America and how it evolved into the nation it is today.
Throughout this lesson, you will be presented with a series of questions and prompts that will help guide your reading and comprehension of the material. These questions will cover topics such as the reasons for European colonization, the establishment of the 13 colonies, the impact of Native Americans, and the development of the economy and government in colonial America.
By utilizing the answer key provided, you will be able to check your understanding and gauge your progress as you work through the reading. The answer key will provide detailed explanations and analysis for each question, allowing you to deepen your knowledge and make connections between different aspects of colonial America.
So, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of colonial America! This lesson and the accompanying answer key will serve as valuable tools to help you navigate and comprehend the complexities of this pivotal period in American history.
Guided Reading Colonial America Lesson 1 Answer Key
In this lesson, students were introduced to the key concepts and vocabulary related to Colonial America. The answer key for this lesson provides a comprehensive overview of the main ideas and allows students to check their understanding.
Key Vocabulary:
- Colonial America: Refers to the period of American history between the 17th and 18th centuries when the thirteen British colonies in North America declared their independence and formed the United States of America.
- Colonization: The act of establishing a colony or settlement in a new territory.
- Pilgrims: A group of English separatists who settled in Plymouth, Massachusetts in 1620 seeking religious freedom.
- Puritans: A group of English Protestants who wanted to reform the Church of England and established the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1630.
- Mayflower Compact: An agreement signed by the Pilgrims aboard the Mayflower ship in 1620, establishing a basis for self-government and the rule of law in the Plymouth Colony.
Guided Reading Questions:
- What was Colonial America and when did it occur?
- Who were the Pilgrims and why did they settle in Plymouth?
- What were the main goals of the Puritans in establishing the Massachusetts Bay Colony?
- What was the significance of the Mayflower Compact?
The answer key for these questions can be found in the provided answer sheet. It is important for students to review the answers and understand the key concepts discussed in the lesson. By completing this guided reading activity, students will have a solid foundation of knowledge about Colonial America.
Overview

In this lesson, we will be exploring the colonial era in America during the 17th and 18th centuries. We will examine the various reasons why Europeans decided to colonize America, the challenges they faced, and the impact of colonization on the indigenous peoples.
The lesson will begin with an introduction to the three main European powers involved in colonization: England, France, and Spain. We will discuss their motivations for establishing colonies in America, such as the desire for wealth, religious freedom, and territorial expansion.
The next section of the lesson will focus on the experiences of the colonists themselves. We will learn about the different types of colonies that were established, including the Chesapeake Bay colonies, the New England colonies, and the Southern colonies. We will examine how these colonies were governed and the social and economic structures that developed as a result of colonization.
Finally, we will explore the impact of colonization on the indigenous peoples of America. We will discuss the interactions between Europeans and Native Americans, including conflicts, trade relationships, and cultural exchange. We will also consider the lasting effects of colonization on Native American communities and their efforts to resist or adapt to the changes brought by European settlers.
Throughout the lesson, there will be opportunities for interactive activities and discussions to deepen understanding and engage students in the topic. By the end of the lesson, students should have a comprehensive understanding of the colonial era in America and its significance in shaping the history of the United States.
Historical Background
The colonization of America by Europeans started in the late 16th century and continued throughout the 17th century. The first permanent English settlement in America was established in 1607 at Jamestown, Virginia. This marked the beginning of a significant period in American history known as colonial America.
Colonial America was a time of exploration, expansion, and the establishment of new societies in the New World. The English, as well as the Spanish, French, and Dutch, sought to establish colonies in America for various reasons, including economic opportunities, religious freedom, and geopolitical dominance. The colonization of America led to encounters and conflicts between Europeans and Native Americans, as well as the transatlantic slave trade, which played a significant role in shaping the economic and social dynamics of colonial America.
The thirteen British colonies in colonial America eventually declared their independence from Great Britain in 1776, leading to the American Revolution and the establishment of the United States of America. However, the impact of the colonial period can still be seen in the social, economic, and political structures of modern-day America. Understanding the historical background of colonial America is essential for understanding the foundations of the United States and the development of American society as we know it today.
Main Themes
The guided reading on colonial America covers several main themes that help to provide a comprehensive understanding of this period in history. These themes include the motivations for colonization, the impact on Native American populations, the development of colonial governments, and the emergence of a distinct colonial identity.
Motivations for Colonization
One of the key themes explored in this lesson is the various motivations for colonization in America. Students learn that European countries such as Spain, England, and France had different reasons for establishing colonies in the New World. Some were driven by economic opportunities, such as the search for new trade routes and resources, while others were influenced by religious or political motives. This theme helps students understand the diverse factors that contributed to the rapid expansion of European colonies in America.
Impact on Native American Populations
Another important theme discussed in the guided reading is the significant impact of colonization on Native American populations. Students explore the complex interactions between European settlers and Native American tribes, including the effects of disease, warfare, and displacement. They also learn about the diversity of Native American cultures and the ways in which they adapted to the arrival of Europeans. This theme helps students understand the lasting consequences of colonization on indigenous peoples.
Development of Colonial Governments
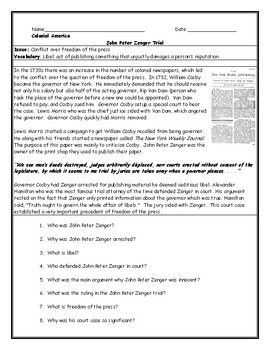
Students also examine the development of colonial governments as a key theme in the guided reading. They learn about the different forms of colonial government, including royal, proprietary, and charter colonies, and the roles of governors, legislatures, and town meetings. Additionally, students explore the concept of self-government in the colonies and its influence on the later development of American democracy. This theme allows students to understand the evolution of political systems in colonial America.
Emergence of a Distinct Colonial Identity
The final theme explored in the guided reading is the emergence of a distinct colonial identity. Students learn about the cultural, economic, and social factors that contributed to the formation of a unique colonial identity. They explore the importance of religious beliefs, the growth of trade and commerce, and the development of social institutions in shaping colonial society. This theme helps students understand the roots of American culture and identity.
Key Events
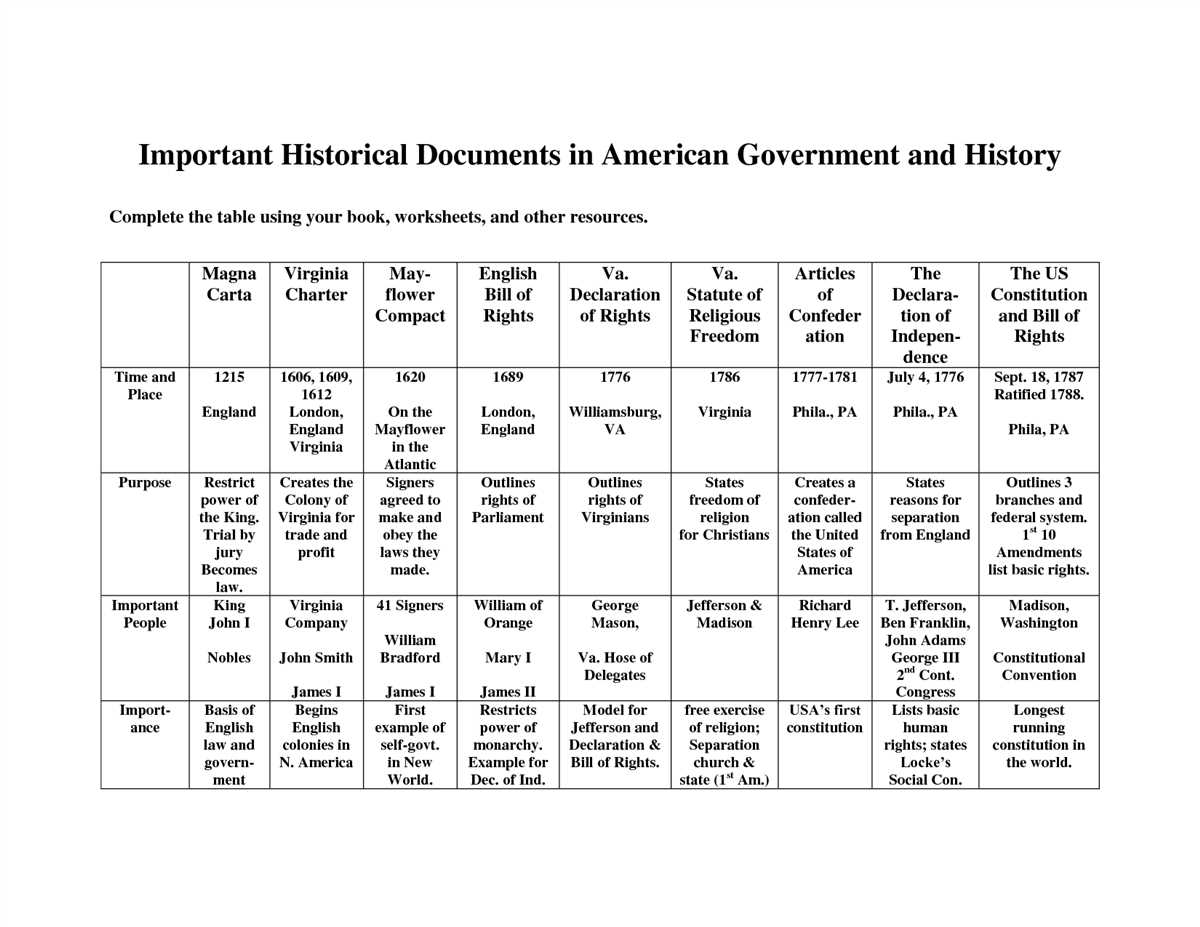
In this lesson, we will explore the key events that shaped colonial America. These events include the arrival of the Pilgrims on the Mayflower, the establishment of Jamestown, the Salem Witch Trials, and the Boston Tea Party.
The arrival of the Pilgrims on the Mayflower in 1620 marked the beginning of European settlement in America. The Pilgrims, seeking religious freedom, established the Plymouth Colony in present-day Massachusetts. Their arrival set the stage for future colonization and the growth of English settlements in America.
- The establishment of Jamestown: In 1607, the English established Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in America. Although the early years were challenging, with struggles against disease and conflicts with Native Americans, Jamestown eventually grew and became the capital of the Virginia Colony.
- The Salem Witch Trials: In 1692, the small village of Salem, Massachusetts, was gripped by a wave of hysteria over witchcraft. Over 200 people were accused of witchcraft, and 20 were executed. The Salem Witch Trials highlighted the dangers of mass hysteria and the importance of due process in legal proceedings.
- The Boston Tea Party: In 1773, a group of colonists in Boston protested against British taxation by dumping tea into the harbor. This act of defiance, known as the Boston Tea Party, was a catalyst for the American Revolution. It symbolized the colonists’ resistance to British control and their desire for independence.
These key events illustrate the challenges and triumphs of colonial America, shaping its history and ultimately leading to the formation of the United States of America.
Lessons Learned
Guided Reading Colonial America Lesson 1: Answer Key
In this lesson, we explored the colonial period of American history, focusing on the reasons for colonization, the early settlements, and the challenges faced by the colonists. We have covered a lot of information, and there are several key takeaways from this lesson:
- The main reasons for colonization were economic opportunities, religious freedom, and political goals.
- The early settlements in colonial America faced numerous challenges, such as harsh climates, unfamiliar landscapes, and conflicts with Native American tribes.
- The colonists developed various methods of self-governance, including town meetings, colonial assemblies, and the establishment of the Mayflower Compact.
- The colonial economies were diverse, with industries ranging from agriculture and trade to shipbuilding and fishing.
- The colonization of America led to the displacement and mistreatment of Native American tribes, leading to a long history of conflict and tension.
By studying the colonial period, we can gain a better understanding of the origins of American society and the foundations of our nation. It is important to recognize the complexities and challenges faced by the early settlers, as well as the impact of colonization on Native American populations. By learning from these lessons, we can strive to create a more inclusive and equitable society today.
Overall, this guided reading lesson on colonial America provides insight into the early years of American history and the lessons learned from this period.