
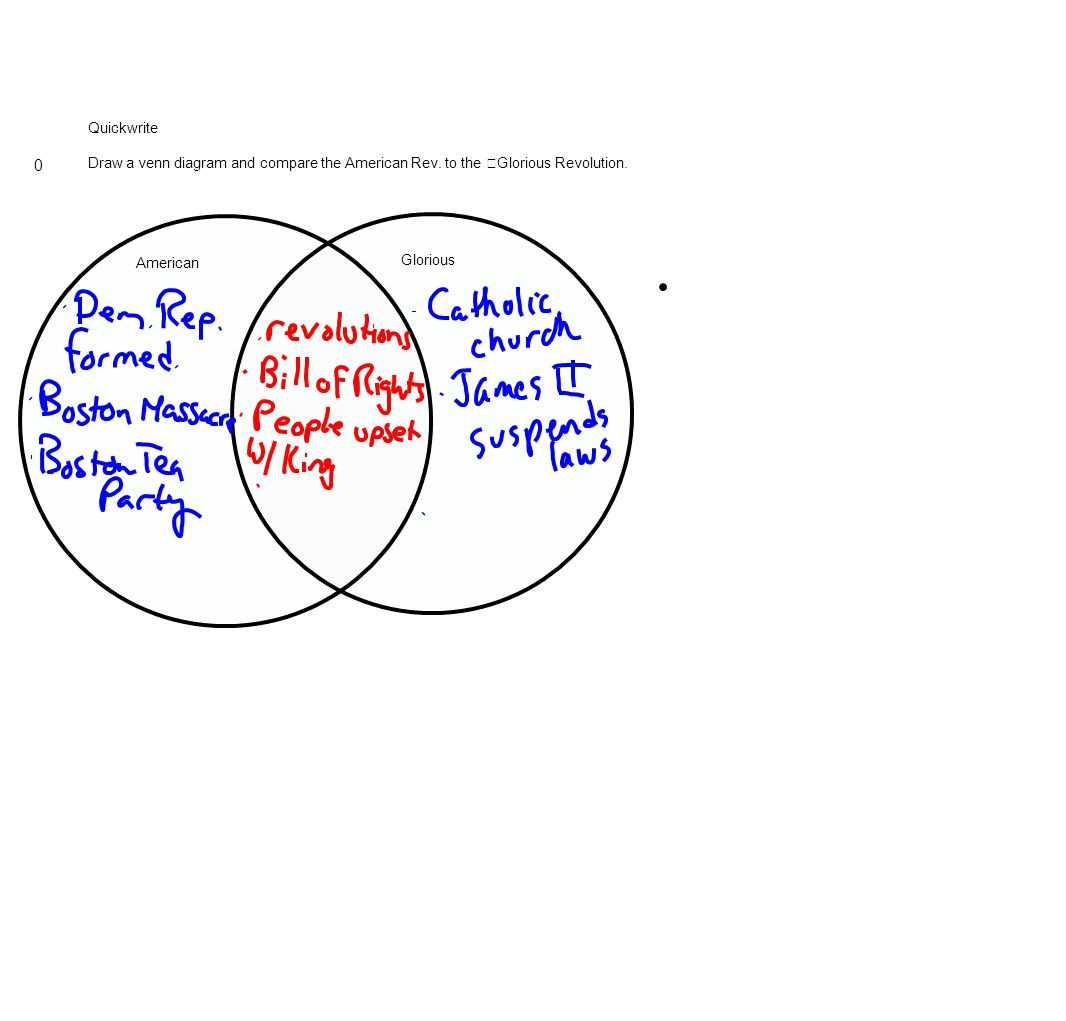
Welcome to this guided reading on the American Revolution! In this article, we will explore the answer key to help you better understand this pivotal point in American history. The American Revolution, which took place between 1765 and 1783, marked the beginning of the United States as an independent nation.
To fully comprehend this period, it is important to examine the causes and consequences of the American Revolution. One key cause was the growing tension between the American colonies and Great Britain. Issues such as high taxes, lack of representation, and increased British control over the colonies led to a desire for greater autonomy among the colonists.
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the future of the United States. The war itself was marked by several key events, including the writing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776, the Battle of Saratoga in 1777, and the final victory at Yorktown in 1781. These events shaped the course of the war and ultimately led to the establishment of the United States as a free and independent nation.
In this guided reading, you will find the answer key to questions related to the American Revolution. This will include topics such as the major battles, important figures, and the impact of the war on both the American colonies and Great Britain. By studying this answer key, you will gain a deeper understanding of this crucial period in American history.
Guided Reading: The American Revolution Answer Key
In this guided reading, you will find the answer key to questions related to the American Revolution. The American Revolution was a pivotal event in American history, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent nation. It was a conflict between Great Britain and the 13 American colonies, which sought to break away from British rule.
Question 1: What were the main causes of the American Revolution?
- The main causes of the American Revolution were taxation without representation, British attempts to exert control over the colonies, and the desire for greater freedom and self-governance.
Question 2: How did the American Revolution impact the colonists?
- The American Revolution had a profound impact on the colonists. It led to the drafting of the Declaration of Independence, the formation of a new nation, and the establishment of a democratic government based on the principles of liberty and equality.
Question 3: What role did key figures play in the American Revolution?
- Key figures, such as George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Benjamin Franklin, played a crucial role in the American Revolution. They provided leadership, drafted important documents, and fought for the cause of independence.
Question 4: How did the American Revolution impact the world?
- The American Revolution had a significant impact on the world. It inspired other countries to seek independence and influenced the development of democratic ideals and principles around the globe.
Question 5: What were some of the major battles of the American Revolution?
- Some of the major battles of the American Revolution include the Battle of Lexington and Concord, the Battle of Bunker Hill, the Battle of Saratoga, and the Battle of Yorktown.
In conclusion, the American Revolution was a transformative event in history. It led to the birth of a new nation and set the stage for the development of democratic ideals worldwide. By understanding the key events and figures of the American Revolution, we can gain insight into the struggles and triumphs of those who fought for independence.
Overview of the American Revolution

The American Revolution was a landmark event in the history of the United States. It marked the turning point where the Thirteen Colonies transitioned from being a part of the British Empire to becoming an independent nation. The revolution took place between the years 1775 and 1783, and it was fueled by a range of political, economic, and ideological factors.
One of the key causes of the American Revolution was the issue of taxation without representation. The British government imposed various taxes on the colonists, such as the Sugar Act and the Stamp Act, without giving them a voice in the decision-making process. This sparked widespread discontent and resistance among the colonists, who believed that they should not be subject to taxes without having representatives in the British Parliament.
- 1775-1776: The War Begins
- 1776-1777: The War Intensifies
- 1778-1781: International Involvement and Yorktown
- 1783: Treaty of Paris
The American Revolution officially started in 1775 with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. These battles were fought between British soldiers and colonial militia, and they marked the beginning of armed conflict between the colonists and the British forces. In 1776, the Second Continental Congress declared the independence of the United States with the signing of the Declaration of Independence.
The war continued to escalate in the following years, with major battles such as the Battle of Saratoga in 1777. This battle was a significant turning point in the war, as it resulted in a decisive victory for the American forces and led to France formally joining the war on the side of the colonists.
During this period, the American Revolution gained international recognition and support. The colonists formed alliances with countries such as France and Spain, who provided military aid and assistance. The turning point of the war came in 1781 with the Siege of Yorktown, where the American and French forces successfully trapped and defeated the British army under General Cornwallis.
In 1783, the American Revolution came to an end with the signing of the Treaty of Paris. This treaty officially recognized the independence of the United States and established the boundaries of the new nation. The American Revolution had far-reaching implications, not only for the United States but also for the development of democratic ideals and the spread of revolutionary ideas around the world.
Key Events Leading to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was a significant turning point in history that led to the birth of the United States of America. Several key events occurred in the years leading up to the revolution, fueling tensions between the American colonists and the British government.
1. The French and Indian War (1754-1763)
The French and Indian War was a conflict between the British and French over control of North America. The British victory in this war increased their colonial holdings but also left them heavily in debt. To help pay off this debt, the British government began imposing various taxes on the American colonies, sparking resentment and protests from the colonists.
2. The Stamp Act of 1765
The Stamp Act was one of the first direct taxes imposed on the American colonies by the British government. It required all legal documents, newspapers, pamphlets, and even playing cards to be printed on specially stamped paper. This act outraged the colonists, who saw it as a violation of their rights as British citizens. The protests and resistance to the Stamp Act played a crucial role in uniting the colonies against British rule.
3. The Boston Massacre (1770)
The Boston Massacre occurred when British soldiers fired on a group of American colonists, killing five people. This event escalated tensions between the colonists and the British troops stationed in Boston. It became a symbol of British tyranny and further fueled the growing desire for independence among the American colonists.
4. The Boston Tea Party (1773)
In response to the Tea Act of 1773, which granted the British East India Company a monopoly on the tea trade, a group of American colonists disguised as Mohawk Indians boarded British ships in Boston Harbor and dumped 342 chests of tea into the water. This act of protest against taxation without representation became known as the Boston Tea Party and led to harsh reprisals by the British government.
5. The Battle of Lexington and Concord (1775)
The Battle of Lexington and Concord marked the beginning of the American Revolution. British troops were sent to seize colonial weapons in Concord, Massachusetts. American minutemen confronted them, leading to a skirmish in Lexington and a larger battle in Concord. This armed conflict solidified the colonists’ resolve to fight for their freedom and ultimately led to the Declaration of Independence and the Revolutionary War.
The Role of Major Figures in the American Revolution
In the American Revolution, there were several key figures who played significant roles in the fight for independence from Britain. These individuals exhibited leadership, determination, and courage, and their actions had a profound impact on the outcome of the revolution.
George Washington: George Washington is widely regarded as the leader of the American Revolution. As Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army, Washington led his troops in numerous battles and displayed exceptional tactical skills. His persistence and strategic thinking were instrumental in securing several crucial victories, including the battles of Trenton and Princeton.
Thomas Jefferson: Thomas Jefferson is best known for drafting the Declaration of Independence, which laid out the principles and grievances that fueled the revolution. As a delegate to the Continental Congress, Jefferson’s eloquence and clarity of thought were instrumental in shaping the ideals and goals of the new nation.
- Benjamin Franklin: Benjamin Franklin was a key figure in both the political and diplomatic aspects of the revolution. As an influential member of the Continental Congress, Franklin helped draft the Declaration of Independence and later negotiated the Treaty of Paris, which formally ended the war. His diplomatic skills and persuasive demeanor played a crucial role in securing support from foreign nations, such as France.
- Abigail Adams: Abigail Adams, the wife of John Adams, played a significant role in supporting the revolution. She was an advocate for women’s rights and urged her husband and other leaders to include women’s voices in the fight for independence. Adams also corresponded with her husband, offering advice and insights on political matters.
These major figures, along with countless others, including Patrick Henry, John Adams, and Alexander Hamilton, played vital roles in the American Revolution. Their leadership, intellect, and dedication to the cause of freedom shaped the course of history and paved the way for the birth of the United States of America.
Causes and Effects of the American Revolution

The American Revolution, which took place from 1765 to 1783, was a significant event in American history that brought about major changes in the political, social, and economic landscape of the country. It was driven by a number of causes and had far-reaching effects that shaped the future of the United States.
One of the key causes of the American Revolution was the imposition of taxes on the American colonies by the British government. The Sugar Act of 1764 and the Stamp Act of 1765 were seen as unjust by the colonists, as they had no representation in the British Parliament. This led to widespread protests and boycotts, which in turn fueled the desire for independence among the colonial population.
- Taxation without representation: The imposition of taxes without proper representation was a major grievance of the colonists, as it violated their rights as British subjects.
- Protests and boycotts: The colonists protested against the unfair taxation measures through various means, including boycotts of British goods.
- Formation of the Continental Congress: In response to the growing dissatisfaction with British rule, the First and Second Continental Congresses were convened, leading to the establishment of a unified colonial voice.
- The Declaration of Independence: The American Revolution culminated in the signing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776, in which the colonists declared their independence from British rule.
The American Revolution had profound effects on the development of the United States. It not only resulted in the establishment of an independent nation, but also laid the foundation for democratic principles and individual liberties that would shape the country’s future.
- Creation of a new nation: The American Revolution led to the formation of the United States of America, with its own government and institutions.
- Development of democratic principles: The ideals of freedom and equality that inspired the revolution laid the groundwork for the development of democratic principles and the establishment of a representative government.
- Expansion of individual liberties: The American Revolution emphasized the importance of individual rights, leading to the inclusion of the Bill of Rights in the US Constitution, which protected citizens’ freedoms and limited the power of the government.
- Influence on other revolutions: The success of the American Revolution inspired other countries and colonies to fight for their independence, having a significant impact on the global struggle for self-determination.
In conclusion, the American Revolution was a transformative event in American history, sparked by the colonists’ grievances against British rule and culminating in the establishment of an independent nation. Its causes and effects continue to shape the United States to this day.
The American Revolution: Battles and Strategies

The American Revolution was a pivotal event in American history. It was a war fought between Great Britain and the thirteen American colonies, which ultimately led to the creation of an independent nation. The revolution was marked by a series of battles and military strategies that shaped the course of the war.
One of the most significant battles of the American Revolution was the Battle of Bunker Hill. This battle took place on June 17, 1775, in Charlestown, Massachusetts. The American colonists, under the command of Colonel William Prescott, fortified Breed’s Hill and Bunker Hill to protect against British forces. Despite being outnumbered and low on ammunition, the colonists were able to inflict heavy casualties on the British army before being forced to retreat. Although the British technically won the battle, the high casualties they suffered made it a Pyrrhic victory.
The American colonists employed various military strategies throughout the revolution. One such strategy was guerrilla warfare, which involved hit-and-run tactics and ambushes. This strategy was especially effective against the highly trained British army, as it allowed the colonists to strike quickly and disappear before the British could react. Additionally, the colonists relied heavily on aid from foreign powers, such as France, which provided military support in the form of troops, supplies, and naval assistance. These strategies, along with the determination and resilience of the American people, played a crucial role in securing victory in the American Revolution.
Key Events and Strategies of the American Revolution:
- The Battles of Lexington and Concord (1775)
- The Battle of Saratoga (1777)
- The Battle of Yorktown (1781)
- The Declaration of Independence (1776)
- The Treaty of Paris (1783)
- The Siege of Boston (1775-1776)
The Legacy of the American Revolution
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the development of the United States and set the stage for the nation’s future. The ideas and principles that shaped the revolution continue to influence American society and government to this day. In this final section, we will explore the lasting legacy of the American Revolution.
The Spread of Democratic Ideals
The American Revolution ignited a spark of democratic ideals that spread far beyond the 13 colonies. The revolution challenged the notion of monarchy and inspired people around the world to strive for self-government. The principles of liberty, equality, and individual rights that were espoused during the revolution became the cornerstone of democratic movements throughout history. The success of the American Revolution proved that a group of dedicated individuals could overthrow an oppressive government and establish a new system that prioritized the rights of the people.
The Creation of a New Nation
The American Revolution led to the formation of the United States as an independent nation. The signing of the Declaration of Independence and the subsequent victory in the Revolution allowed the American colonies to break free from British rule and establish their own government. This marked the birth of a new nation, founded on the principles of freedom and self-determination. The American Revolution served as a catalyst for the formation of a constitutional republic, with a system of checks and balances that would become a model for democratic governments worldwide.
The Abolition of Slavery
While the institution of slavery still persisted in the newly formed United States after the Revolution, the ideals and principles of the revolution created a platform for the eventual abolition of slavery. The contradiction between the fight for freedom and individual rights and the practice of slavery became increasingly apparent, leading to a growing abolitionist movement. The American Revolution planted the seeds of change that would eventually lead to the emancipation of slaves and the abolition of slavery in the United States.
Influence on Other Revolutions

The American Revolution inspired and influenced other revolutions around the world. The French Revolution, for example, drew inspiration from the American Revolution and the ideals it represented. The French Revolution sought to overthrow the monarchy and establish a democratic government based on the principles of liberty and equality. The American Revolution also served as a model for Latin American revolutions against Spanish colonial rule in the early 19th century. The American Revolution’s legacy resonated across continents and continued to shape the course of history.
In conclusion, the American Revolution was a watershed moment in history that had a lasting impact on the world. The spread of democratic ideals, the creation of a new nation, the eventual abolition of slavery, and its influence on other revolutions are just a few examples of the revolution’s legacy. The ideas and principles that emerged during this time continue to guide and inspire people around the world in their struggle for justice, freedom, and self-determination.
Q&A:
What was the American Revolution?
The American Revolution was a war fought between Great Britain and thirteen of its North American colonies, which had declared themselves the independent United States of America.
When did the American Revolution take place?
The American Revolution took place from 1775 to 1783.
What were the causes of the American Revolution?
The causes of the American Revolution included taxation without representation, restrictions on trade, and a desire for self-governance.
What were the major consequences of the American Revolution?
The major consequences of the American Revolution include the formation of the United States as an independent nation, the expansion of democratic ideals, and the inspiration for other revolutions around the world.
How did the American Revolution impact the world?
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the world by inspiring other countries to fight for their own independence and by promoting the ideals of liberty, equality, and self-determination.