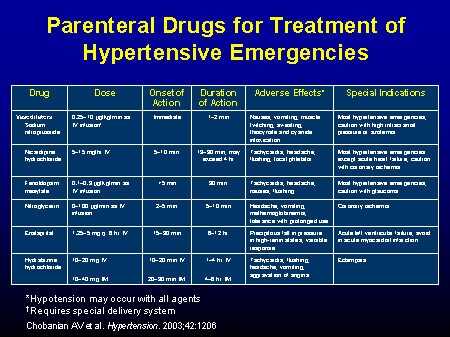
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. Hypertension can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease and stroke, if left untreated.
In this case study, we will explore the scenario of a patient with hypertension and provide answers to common questions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and management of the condition. Through this case study, we hope to shed light on the importance of early detection and proper management of hypertension to reduce the risk of complications.
The patient in this case study is a 45-year-old male who presents with consistently high blood pressure readings over the past few months. He has a family history of hypertension and is overweight. The first step in diagnosing hypertension is measuring blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer. The patient’s blood pressure readings consistently show levels of 140/90 mmHg or higher, confirming the diagnosis of hypertension.
Hypertension Case Study with Answers
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistently high blood pressure levels, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this case study, we will explore a hypothetical scenario of a patient with hypertension and discuss possible answers and solutions.
Case Study: Mr. Smith is a 55-year-old male who presents with elevated blood pressure readings during his routine check-up. His blood pressure consistently reads 160/100 mmHg, and he has a family history of hypertension. Mr. Smith leads a sedentary lifestyle, smokes cigarettes, and has a diet high in sodium and saturated fats.
Possible answers and solutions for Mr. Smith’s hypertension:
- Lifestyle modifications: Mr. Smith should be advised to make certain lifestyle changes to help control his blood pressure. This includes quitting smoking, reducing sodium intake, following a healthy and balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress levels.
- Medication: Based on Mr. Smith’s consistently elevated blood pressure readings, it may be necessary to prescribe antihypertensive medication to help lower his blood pressure. The choice of medication will depend on various factors, such as his overall health, any existing medical conditions, and potential drug interactions.
- Regular monitoring: Mr. Smith should be advised to monitor his blood pressure regularly at home using an appropriate blood pressure monitor. This will help to track his progress and ensure that his blood pressure levels are within a healthy range.
- Follow-up visits: Regular follow-up visits with Mr. Smith’s healthcare provider are essential to assess his progress, adjust medication if needed, and provide ongoing support and guidance. These visits will also allow for the monitoring of any potential side effects or complications related to hypertension or its treatment.
- Education and support: Mr. Smith should receive education and support regarding hypertension management. This can include providing information on the importance of medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and the potential risks of uncontrolled hypertension. Additionally, he may benefit from participation in support groups or counseling to address any emotional or psychological challenges related to his condition.
In conclusion, hypertension is a serious health condition that requires proper management and treatment. By implementing lifestyle modifications, considering medication, regular monitoring, follow-up visits, and providing education and support, patients like Mr. Smith can effectively control their blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications associated with hypertension.
What is Hypertension?
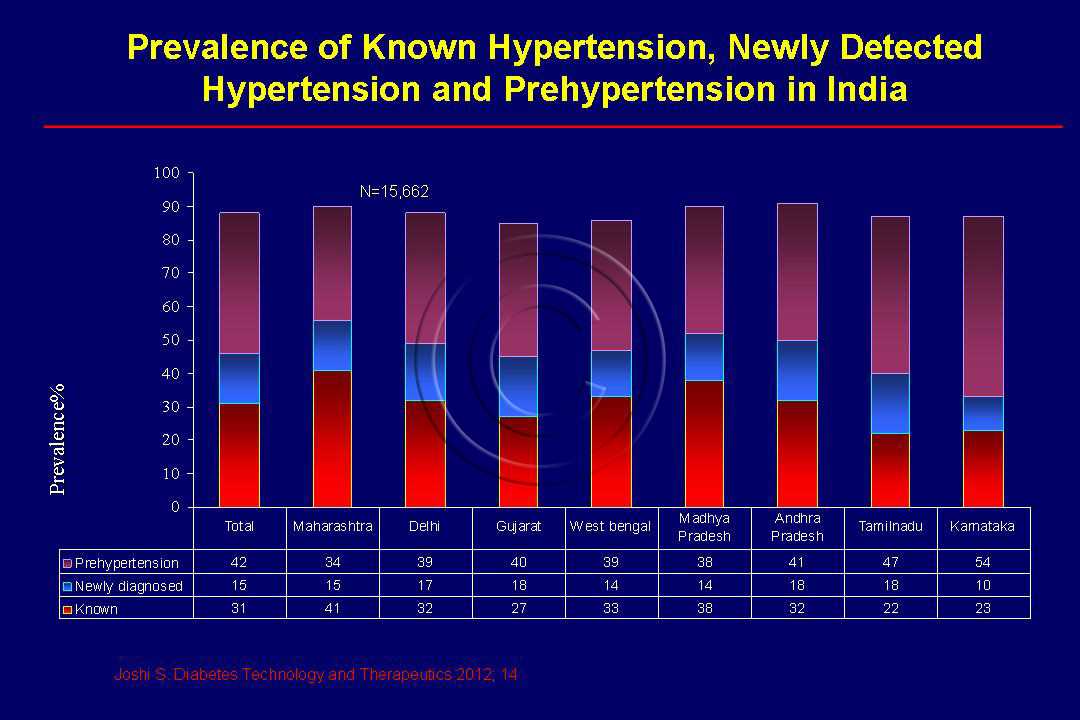
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition characterized by the elevation of blood pressure in the arteries. It is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and if left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
When a person has hypertension, the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is too high, causing strain on the heart and blood vessels. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is typically recorded as two numbers, systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure represents the force exerted by the blood when the heart contracts, while diastolic pressure represents the force when the heart is at rest between beats.
- Primary hypertension: This is the most common form of hypertension and has no identifiable cause. It is often the result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as family history, age, obesity, and lifestyle choices.
- Secondary hypertension: This type of hypertension is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or the use of certain medications. Treating the underlying condition can help control blood pressure.
Hypertension is often called the “silent killer” because it usually has no symptoms. However, it can be diagnosed through regular blood pressure measurements. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, reducing salt intake, and limiting alcohol consumption, can help manage hypertension. In some cases, medication may be required to control blood pressure and prevent complications.
Hypertension Case Study: Patient Background
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this case study, we will explore the background of a patient with hypertension and analyze their symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options.The patient, Mrs. Smith, is a 60-year-old female who presented to her primary care physician with complaints of persistent headaches, occasional dizziness, and fatigue. Upon further examination, it was found that she had a blood pressure reading of 160/100 mmHg, which indicated stage 2 hypertension. Mrs. Smith has a family history of hypertension, with both her parents being diagnosed with the condition in their 50s. She also has a sedentary lifestyle and a body mass index (BMI) of 30, classified as obese.
Based on Mrs. Smith’s symptoms, family history, and lifestyle factors, it is evident that she is at a high risk of developing complications related to hypertension. These can include cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke, as well as kidney damage and vision problems. Therefore, it is crucial to implement a comprehensive treatment plan to manage her blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications.
The treatment plan for Mrs. Smith will include lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and weight loss, as well as dietary changes to lower sodium intake and increase consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Additionally, her healthcare provider may prescribe antihypertensive medications, such as ACE inhibitors or diuretics, to help control her blood pressure.
In conclusion, Mrs. Smith’s case highlights the importance of timely diagnosis and management of hypertension. With proper treatment, including lifestyle modifications and medication, she can improve her blood pressure control and reduce the risk of complications associated with hypertension.
Hypertension Diagnosis and Treatment
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. It is an important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. In many cases, hypertension is asymptomatic and can go undiagnosed for a long time. However, it is crucial to diagnose and treat hypertension early to prevent complications.
The diagnosis of hypertension is made by measuring blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer. The measurement consists of two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). A blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg or lower is considered normal, while a reading of 130/80 mmHg or higher indicates hypertension. Multiple readings taken on different occasions are required to confirm the diagnosis.
Once hypertension is diagnosed, treatment aims to reduce blood pressure levels and manage the condition. Lifestyle modifications are often the first step, including regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables. Limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are also important lifestyle changes.
If lifestyle modifications alone are not sufficient to control blood pressure, medication may be prescribed. Antihypertensive medications include diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and calcium channel blockers. The choice of medication depends on factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, and any other underlying medical conditions.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make necessary adjustments. It is important for individuals with hypertension to adhere to their prescribed treatment regimen and make necessary lifestyle changes to manage their condition effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
Hypertension Case Study: Patient Progress and Challenges
In this hypertension case study, the patient has shown some progress in managing their blood pressure, but has also faced some challenges along the way. The patient initially presented with high blood pressure readings and was diagnosed with hypertension. They were educated about the importance of lifestyle modifications and prescribed antihypertensive medication to help control their blood pressure.
Over the course of several visits, the patient has shown improvement in their blood pressure readings, with more readings falling within the target range. They have been adhering to their medication regimen and have made some positive changes to their diet, including reducing their sodium intake and increasing their consumption of fruits and vegetables. The patient has also started engaging in regular physical activity, which has further contributed to the improvement in their blood pressure.
However, there have been challenges that the patient has faced in managing their hypertension. One challenge is maintaining consistency in their medication regimen. The patient has occasionally missed doses or forgotten to take their medication, which resulted in temporary spikes in their blood pressure. This highlights the importance of medication adherence and the need for the patient to find strategies to remember to take their medication consistently.
Another challenge the patient has encountered is managing stress. They have been experiencing high levels of stress due to work and personal life challenges, which have had an impact on their blood pressure. The patient has been advised to engage in stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and engaging in hobbies or activities they enjoy to help manage their stress levels.
Overall, the patient has shown progress in managing their hypertension by making lifestyle changes and adhering to their medication regimen. However, challenges such as medication adherence and managing stress continue to be areas where additional support and strategies are needed to further improve the patient’s blood pressure control.
Hypertension Case Study: Healthcare Provider’s Approach
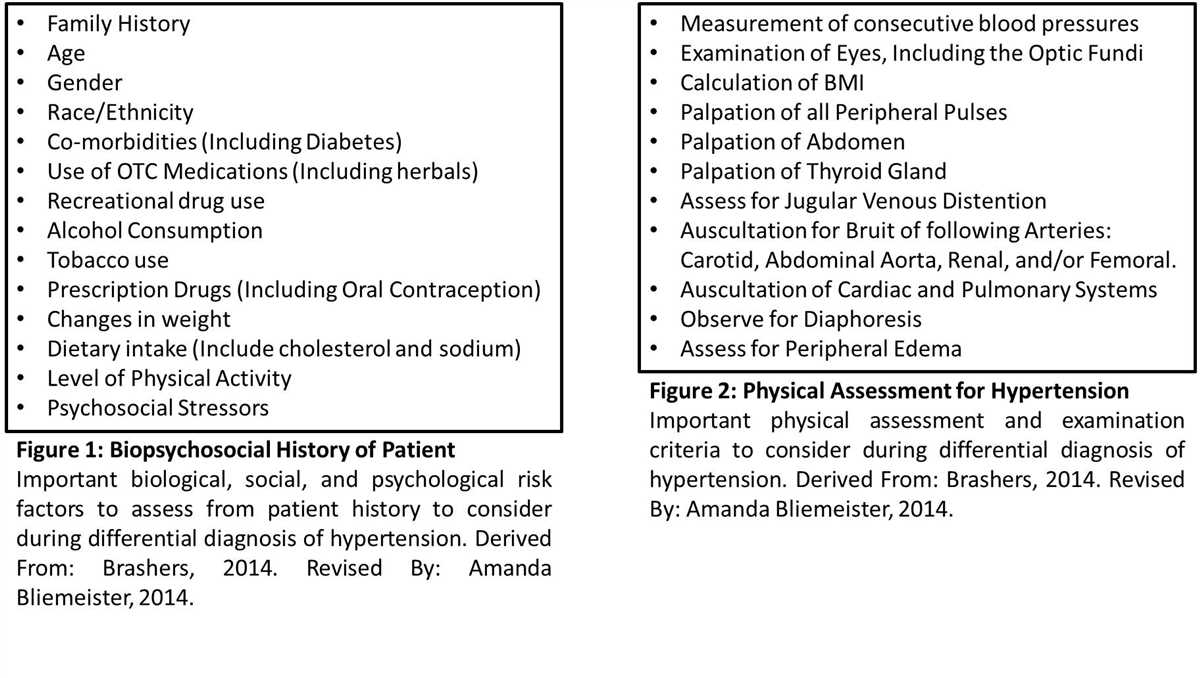
In this hypertension case study, the healthcare provider took a comprehensive approach to managing the patient’s condition. The initial assessment included a thorough medical history and physical examination to gather information about the patient’s lifestyle, family history, and any potential underlying causes of hypertension.
1. Lifestyle Modifications: The healthcare provider emphasized the importance of lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a healthy diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables, weight management, smoking cessation, and stress reduction techniques.
2. Medication Management: The healthcare provider prescribed antihypertensive medications to help control the patient’s blood pressure. The choice of medication was based on the patient’s individual needs and any comorbidities. The healthcare provider also monitored the patient’s response to medication, making adjustments as necessary.
3. Regular Check-ups: The healthcare provider scheduled regular check-ups to monitor the patient’s blood pressure, assess for any side effects of medication, and provide ongoing support and education. These visits also allowed for any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
4. Patient Education: The healthcare provider ensured that the patient was educated about hypertension, its risks, and the importance of medication adherence. The patient was also provided with resources and information to support their lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise recommendations.
5. Referrals: The healthcare provider referred the patient to other healthcare professionals as needed, such as a registered dietitian for dietary counseling or a mental health professional for stress management support.
Overall, this case study demonstrates the healthcare provider’s comprehensive approach to managing hypertension. By addressing lifestyle modifications, medication management, regular check-ups, patient education, and referrals, the healthcare provider aimed to achieve optimal blood pressure control and improve the patient’s overall health.