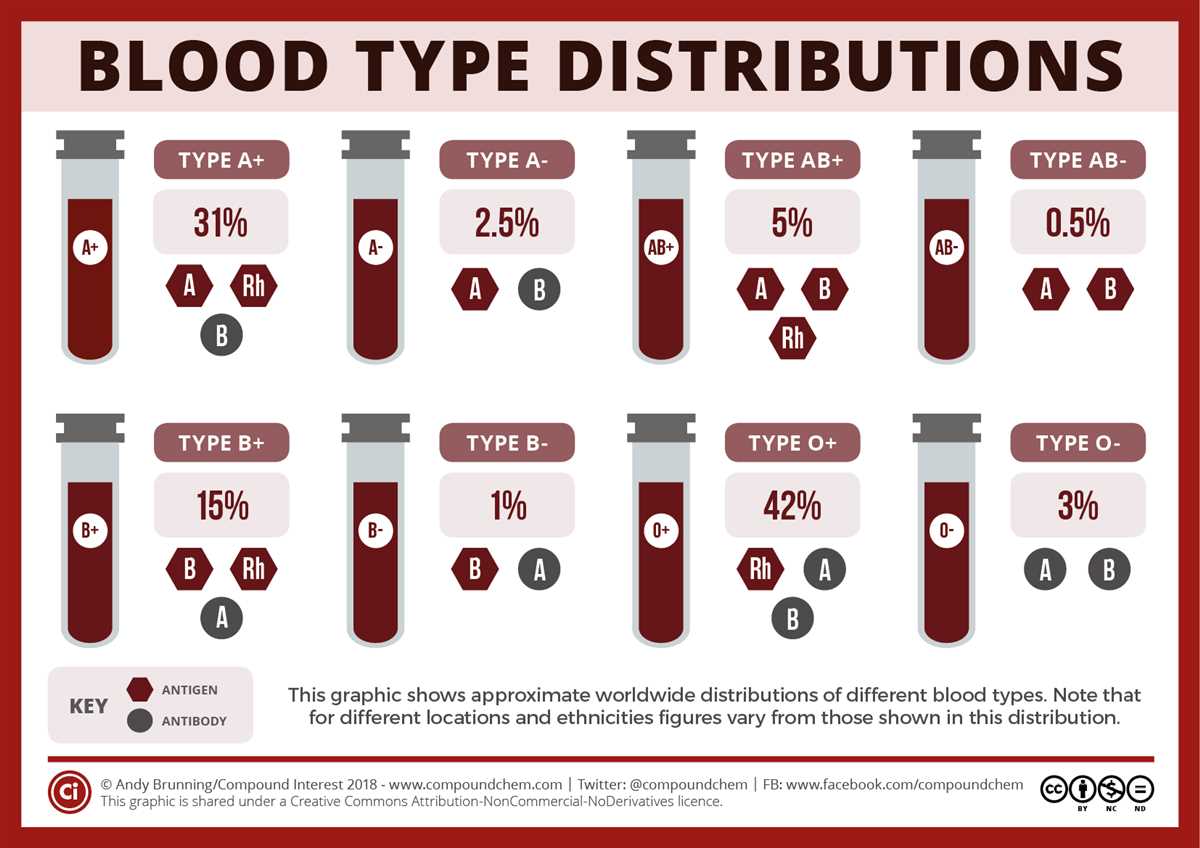
Regular blood tests are an essential part of modern healthcare. They provide valuable information about a person’s overall health and can help diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. The chart below is designed to record the results of blood tests, which typically include measurements of several key indicators, such as blood cell counts, cholesterol levels, and liver function.
The first section of the chart focuses on complete blood counts (CBC). This includes information on red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. RBCs are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body, while WBCs help fight off infections. Platelets, on the other hand, play a crucial role in blood clotting. By recording these numbers, healthcare professionals can assess a person’s overall blood health.
The second section of the chart is dedicated to measuring cholesterol levels. Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the blood and plays a vital role in the body’s functioning. However, high levels of cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. The chart allows for recording both LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides, which are another type of fat in the blood.
Understanding Blood Tests: An Essential Guide
When it comes to monitoring our health, blood tests play a crucial role. They provide valuable insights into our overall well-being, allowing healthcare professionals to detect and diagnose a wide range of medical conditions. Understanding blood tests can be complex, but with the right knowledge, you can make sense of the information they provide.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC is one of the most common blood tests performed. It provides essential information about the different types of blood cells present in our body, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. By analyzing these cell counts, doctors can assess your overall health and detect conditions such as anemia or infections.
Blood Chemistry: Blood chemistry tests measure the levels of different substances in your blood, such as electrolytes, proteins, glucose, and cholesterol. These tests help evaluate your organ function, detect imbalances, and identify potential health risks. For example, elevated cholesterol levels could indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
- Glucose: Glucose levels are crucial for monitoring and diagnosing diabetes. High blood sugar levels may indicate diabetes, whereas low levels could be a sign of hypoglycemia.
- Liver Function: Liver function tests assess how well your liver is working and can detect liver damage or disease.
- Kidney Function: Kidney function tests measure the levels of waste products and electrolytes in your blood, providing insights into your kidney health.
Cholesterol Profile: This blood test measures the levels of different types of cholesterol in your blood, including LDL (bad cholesterol), HDL (good cholesterol), and triglycerides. Abnormal cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Coagulation Panel: Coagulation tests assess how well your blood clots. They help diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications.
Overall, understanding the meaning and significance of blood test results requires consultation with a healthcare professional. They can interpret the data in the context of your medical history and symptoms, providing accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a common blood test that provides important information about the overall health and functioning of a person’s blood. The CBC measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It is a valuable tool that can help diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions.
The CBC includes several key parameters that are analyzed:
- Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count: This measures the number of red blood cells in a specified volume of blood. It helps assess oxygen-carrying capacity and can provide insight into various conditions such as anemia or polycythemia.
- Hemoglobin (Hb) Level: Hemoglobin is a protein within red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Low hemoglobin levels can indicate anemia or other issues related to oxygen transportation.
- Hematocrit (Hct) Level: This measures the proportion of red blood cells in relation to the total volume of blood. It is another parameter used to evaluate blood oxygen-carrying capacity and can be helpful in diagnosing anemia or polycythemia.
- White Blood Cell (WBC) Count: The WBC count measures the number of white blood cells present in a specified volume of blood. It provides an indication of the body’s immune system and can help identify infections or inflammation.
- Platelet Count: Platelets are important for blood clotting. Low platelet counts can lead to an increased risk of bleeding, while high platelet counts may indicate an increased risk of clotting disorders.
The information obtained from a CBC can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor a variety of conditions, including infections, anemia, blood disorders, and immune system abnormalities. It is an essential tool in assessing overall blood health and can provide valuable insights into a person’s overall well-being.
Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
The Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) is a blood test that provides valuable information about the body’s overall metabolic status. It consists of a series of tests that measure various chemicals and substances in the blood, including glucose, electrolytes, and kidney function markers. The results of the BMP can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and certain hormonal imbalances.
Glucose: The BMP includes a measurement of blood glucose levels, which indicates the amount of sugar present in the blood. Abnormal glucose levels can be an indication of diabetes or other metabolic disorders. High glucose levels may indicate poor blood sugar control, while low levels may suggest hypoglycemia or insulin overdose.
Electrolytes: The BMP also assesses the levels of electrolytes in the blood, including sodium, potassium, and chloride. These minerals play a crucial role in maintaining proper cell function and fluid balance in the body. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can lead to symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, and irregular heart rhythms.
Kidney function markers: The BMP includes tests that assess the functioning of the kidneys, including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels. These markers give insights into how well the kidneys are filtering waste products from the blood. Abnormal kidney function test results could indicate kidney disease or impairment.
By analyzing the results of the BMP, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into a patient’s metabolic health and detect any abnormalities or imbalances that may require further investigation or treatment. It is important to note that the interpretation of these test results should always be done in conjunction with other clinical information to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan.
Lipid Panel
The lipid panel is a blood test that measures the levels of different types of fats (lipids) in the blood. It is a useful tool in assessing a person’s risk for developing cardiovascular disease. The test usually includes measurements of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Total cholesterol is the sum of all cholesterol in the blood, including both LDL and HDL cholesterol. LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Triglycerides are a type of fat that can also contribute to heart disease if their levels are too high.
The lipid panel is an important tool for healthcare providers because it can help them determine if a person has high cholesterol or other lipid abnormalities. High total cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, and high triglycerides are all risk factors for cardiovascular disease. By identifying these risk factors, healthcare providers can recommend lifestyle changes and/or medications to help reduce a person’s risk.
The results of the lipid panel are typically reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood. Optimal levels vary depending on a person’s individual risk factors, but in general, a total cholesterol level below 200 mg/dL, an LDL cholesterol level below 100 mg/dL, an HDL cholesterol level above 40 mg/dL (for men) or 50 mg/dL (for women), and triglyceride levels below 150 mg/dL are considered desirable.
Interpretation of Lipid Panel Results:
- Total cholesterol: XYZ mg/dL (Desirable: less than 200 mg/dL)
- LDL cholesterol: XYZ mg/dL (Desirable: less than 100 mg/dL)
- HDL cholesterol: XYZ mg/dL (Desirable: above 40 mg/dL for men, above 50 mg/dL for women)
- Triglycerides: XYZ mg/dL (Desirable: less than 150 mg/dL)
Based on the above lipid panel results, it can be concluded that XYZ has a total cholesterol level of XYZ mg/dL, which is within the desirable range. Their LDL cholesterol level is XYZ mg/dL, also within the desirable range. Their HDL cholesterol level is XYZ mg/dL, which is above the minimum desirable level for women. Lastly, their triglyceride level is XYZ mg/dL, which is below the desirable level.
Liver Function Tests (LFTs)

Liver Function Tests (LFTs) are a group of blood tests that provide information about the functioning of the liver. They help in the diagnosis and monitoring of liver diseases and conditions. LFTs measure various enzymes, proteins, and substances in the blood that are produced or affected by the liver.
One of the most commonly measured enzymes in LFTs is alanine transaminase (ALT). Elevated levels of ALT may indicate liver damage or injury, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. Aspartate transaminase (AST) is another enzyme that is measured in LFTs. Elevated levels of AST may also indicate liver damage, but it can also be elevated in other conditions like muscle injury or heart disease.
LFTs also measure bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. Elevated levels of bilirubin can indicate liver disease or blocked bile ducts. Total protein and albumin levels are also measured in LFTs. Low levels of these proteins can indicate liver dysfunction.
Globulins, which are a group of proteins involved in the immune response, are also measured in LFTs. High levels of globulins can indicate liver inflammation or certain types of liver diseases. LFTs may also measure alkaline phosphatase (ALP), another enzyme produced by the liver. Elevated levels of ALP can indicate liver or bone disease.
In summary, Liver Function Tests (LFTs) provide valuable information about the functioning of the liver. They measure various enzymes, proteins, and substances in the blood that are produced or affected by the liver. Abnormal results in LFTs can indicate liver damage, disease, or dysfunction, and further evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Kidney Function Tests
Kidney function tests are a group of laboratory tests that provide valuable information about how well your kidneys are functioning. These tests are commonly performed to diagnose and monitor kidney diseases and assess the overall health of your kidneys.
1. Creatinine levels: One of the most commonly measured kidney function tests is the creatinine blood test. Creatinine is a waste product that is produced by your muscles and filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. High levels of creatinine in the blood may indicate impaired kidney function.
2. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels: BUN is another waste product that the kidneys remove from the bloodstream. An elevated BUN level may be a sign of kidney dysfunction or other conditions, such as dehydration or high protein intake.
3. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): GFR is a measure of how well your kidneys are able to filter waste products from the blood. It is considered the best indicator of kidney function. A GFR below normal range may indicate kidney disease.
4. Urine tests: Urine tests can provide valuable information about kidney function, including the presence of protein or blood in the urine. Proteinuria (presence of protein in the urine) is a common sign of kidney damage.
- Albuminuria: Albumin is a type of protein that should not be present in the urine. Its presence may indicate kidney damage.
- Hematuria: The presence of blood in the urine may be a sign of kidney disease, infection, or other urinary tract problems.
Regular kidney function tests are important for patients with known kidney disease, as well as for individuals at risk of developing kidney problems, such as those with diabetes or high blood pressure. These tests help healthcare providers monitor kidney function, detect the progression of kidney disease, and make appropriate treatment decisions.
Thyroid Function Tests

The thyroid is a small gland located in the front of the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Thyroid function tests are blood tests that measure the levels of these hormones and other markers to assess the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid function tests can help diagnose thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of thyroid treatment or to investigate the cause of symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, and changes in heart rate.
In the chart below, you can record the information from the blood tests:
| Test | Normal Range | Results |
|---|---|---|
| TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) | 0.4 – 4.0 mIU/L | — |
| T4 (Thyroxine) | 4.5 – 12.5 mcg/dL | — |
| T3 (Triiodothyronine) | 80 – 200 ng/dL | — |
| Thyroid Antibodies | Negative | — |
Remember that the normal ranges may vary slightly depending on the laboratory, so it’s important to refer to the reference range provided by your healthcare provider.
Thyroid function tests are an essential tool in diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders. By recording and monitoring the results over time, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding treatment and adjustments to medication dosage.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns or symptoms related to thyroid function. They can evaluate your test results in combination with your medical history and physical examination to provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.