
Understanding the interactions among living things is crucial in comprehending the intricate web of life on Earth. This worksheet provides an answer key to help students navigate through various questions and scenarios surrounding these interactions. By delving into topics such as competition, predation, symbiosis, and ecological succession, students can develop a deeper understanding of how organisms depend on and interact with one another in their environments.
One key aspect covered in this worksheet is competition, where organisms compete for limited resources such as food, water, and shelter. Students will learn about the different types of competition, including intraspecific (between individuals of the same species) and interspecific (between individuals of different species). By understanding the mechanisms and consequences of competition, students can gain insights into the dynamics of populations and their ability to adapt and survive.
Predation is another significant interaction explored in this worksheet. Students will explore the predator-prey relationship and the impact it has on population dynamics. They will learn about the different strategies predators employ to capture their prey and the adaptations prey develop to evade predators. By examining various examples of predation, students can grasp how the balance between predators and prey influences the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
The concept of symbiosis is also introduced in this worksheet. Symbiosis is a close and prolonged interaction between two or more different species. Students will explore examples of different types of symbiotic relationships, such as mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Through these examples, students will gain an understanding of the benefits and costs associated with these interactions and how they contribute to the overall diversity and functioning of ecosystems.
Lastly, the worksheet covers the topic of ecological succession. Ecological succession is the gradual process of change and development in the structure of an ecological community over time. Students will learn about primary and secondary succession, as well as the factors that contribute to these processes. By studying the stages of succession and the role of pioneer species, students can grasp the importance of these processes in shaping and renewing ecosystems.
Understanding the Concept of Interactions Among Living Things
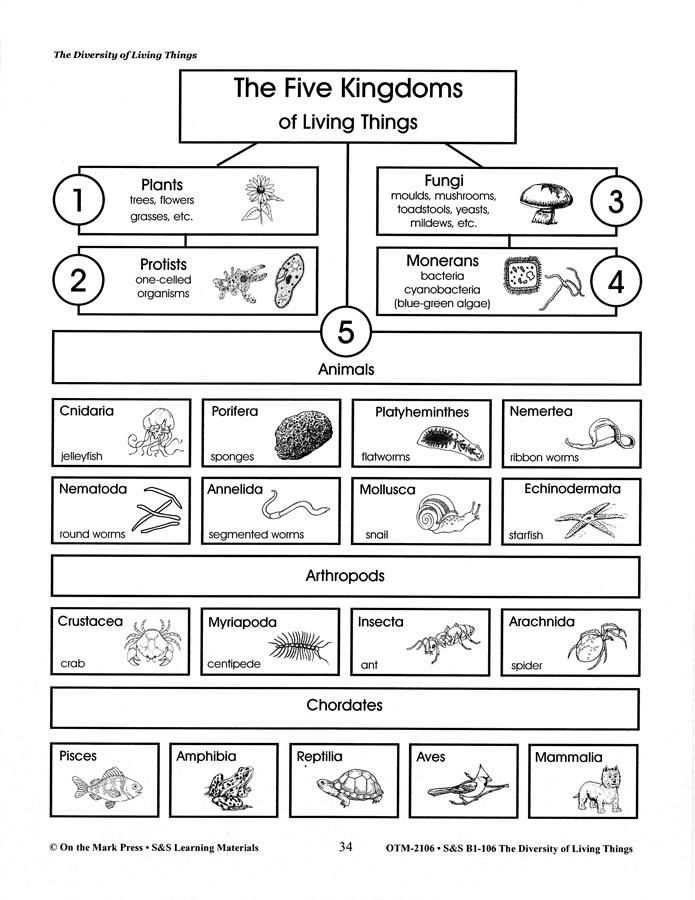
Interactions among living things, also known as ecological interactions, are the dynamic relationships that exist between different organisms within an ecosystem. These interactions play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems, as they influence the population size, distribution, and behavior of species. By understanding these interactions, scientists are able to gain insights into the complex web of life and how different organisms depend on and interact with each other.
One key concept in understanding interactions among living things is the idea of symbiosis. Symbiosis refers to a close and long-term interaction between two different species, where both organisms benefit from the relationship. There are three main types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, where both species benefit; commensalism, where one species benefits while the other is unaffected; and parasitism, where one species benefits at the expense of the other. These symbiotic relationships illustrate the interconnectedness and interdependence of organisms within an ecosystem.
In addition to symbiosis, interactions among living things also include:
- Predation: The act of one organism capturing and feeding on another organism, resulting in a predator-prey relationship.
- Competition: The struggle between organisms for limited resources, such as food, water, or mates.
- Cooperation: The collaboration between organisms to achieve a common goal, such as when a group of animals cooperatively hunts for food.
- Amensalism: A relationship where one organism is negatively affected while the other is unaffected.
- Neutralism: A relationship where two species coexist without affecting each other.
Overall, understanding the concept of interactions among living things is fundamental to understanding the intricate dynamics of ecosystems. By studying these interactions, scientists can gain insights into how changes in one species or aspect of an ecosystem can have far-reaching consequences for other organisms. This knowledge is crucial for conservation efforts and the preservation of biodiversity.
Exploring the different types of interactions in ecosystems

An ecosystem is a complex network of interactions among living organisms and their environment. These interactions can be categorized into different types, each playing a unique role in the functioning of the ecosystem. Understanding these types of interactions can help us understand how the different organisms in an ecosystem depend on and influence each other.
1. Predation: In predation, one organism (predator) hunts, captures, and feeds on another organism (prey). This interaction is essential for controlling populations and maintaining balance in ecosystems. For example, predators like lions hunting and feeding on herbivores such as zebras help regulate the herbivore population and prevent overgrazing in grasslands.
2. Competition: Competition occurs when multiple organisms in an ecosystem compete for limited resources such as food, water, or territory. This interaction can lead to adaptations and evolutionary changes as organisms try to outcompete each other. For instance, trees in a forest may compete for sunlight, leading to taller trees with longer branches as they try to capture more light.
3. Mutualism: Mutualism is a type of interaction where both organisms involved benefit from their association. This interaction is often seen between species that rely on each other for survival. A classic example is the relationship between bees and flowers. Bees collect nectar from flowers for food, while inadvertently pollinating the flowers and aiding in their reproduction.
4. Commensalism: Commensalism is an interaction where one organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited. For example, some birds build their nests in trees, gaining protection and shelter, while the tree is unaffected by their presence.
5. Parasitism: In parasitism, one organism (parasite) benefits at the expense of another organism (host). The parasite relies on the host for resources and shelter, often causing harm to the host. An example is a tick feeding on the blood of a mammal, causing irritation and potential diseases.
These are just a few of the many types of interactions that occur in ecosystems. Each interaction plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature and ensuring the survival of different species within an ecosystem.
The Role of Competition in Interactions Among Living Things
In the natural world, competition plays a crucial role in shaping interactions among different living organisms. This competition can occur between individuals of the same species (intraspecific competition) or between individuals of different species (interspecific competition). The competition for resources such as food, water, and habitat can greatly influence the distribution and abundance of organisms in an ecosystem.
Intraspecific competition occurs when individuals of the same species compete with one another for limited resources. This type of competition can be seen in many animal species, where individuals may fight for territory or mates. For example, male lions compete for dominance over a pride and access to females, while plants compete for sunlight and nutrients in a dense forest. In these scenarios, the individuals that are most successful in obtaining the necessary resources have a greater chance of survival and reproductive success, leading to the gradual evolution of traits that enhance their competitiveness.
Interspecific competition occurs when individuals of different species compete for the same resources. This type of competition is common in nature, as different species often occupy similar ecological niches and depend on the same resources for survival. For example, different bird species may compete for nesting sites or insects as a food source. In such cases, competition can lead to the exclusion of one species from a particular area or the evolution of different feeding strategies or adaptations that reduce direct competition.
Overall, competition plays a significant role in shaping the structure and dynamics of ecosystems. It influences the distribution and abundance of organisms, drives natural selection and evolutionary processes, and can lead to the development of specialized adaptations. Understanding the role of competition in interactions among living things is essential for comprehending the complexity of ecosystems and the delicate balance of nature.
The importance of predation and symbiosis in ecosystems
Predation and symbiosis are two critical interactions that play a vital role in maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems. Predation, which involves the consumption of one organism by another, is an essential mechanism for regulating population sizes and controlling species diversity. Predators exert selective pressure on their prey, favoring the survival of individuals with traits that make them less vulnerable to predation. This process, known as natural selection, contributes to the evolution of species and helps maintain the overall health of an ecosystem.
Symbiosis, on the other hand, is a mutually beneficial relationship between two or more different species. There are different types of symbiosis, including mutualism, where both species benefit; commensalism, where one species benefits while the other is unaffected; and parasitism, where one species benefits at the expense of the other. Symbiotic relationships are integral to the functioning of ecosystems as they promote resource utilization, increase nutrient cycling, and enhance overall productivity.
In a predator-prey relationship, predators help regulate the population size of their prey, preventing overpopulation and maintaining the ecological balance. Without predation, prey populations can grow rapidly, leading to resource depletion, increased competition, and ultimately, the collapse of the ecosystem. Predation also acts as a mechanism for weeding out weaker individuals and keeping populations healthy and strong.
Symbiotic relationships, on the other hand, contribute greatly to the diversity and stability of ecosystems. Mutualistic relationships, such as the one between pollinators and flowering plants, ensure the successful reproduction of both species. Commensalistic relationships, like the relationship between barnacles and whales, provide benefits to one species without harming the other. Parasitic relationships, while seemingly negative, also serve an important ecological role by regulating populations and controlling the spread of diseases.
In conclusion, the interactions of predation and symbiosis are crucial for the functioning and longevity of ecosystems. Predation helps regulate population sizes and maintain biodiversity, while symbiotic relationships promote resource utilization and enhance overall productivity. Both of these interactions are indispensable for the survival and well-being of species within an ecosystem and should thus be carefully considered and protected.
Examining the Impact of Human Activities on Interactions among Living Things
Human activities have a profound impact on interactions among living things in various ecosystems around the world. These activities often disrupt the delicate balance of natural systems and can lead to significant consequences for both the environment and the species that inhabit it.
Deforestation: One of the most prevalent human activities that affect interactions among living things is deforestation. The clearing of vast areas of forests for agriculture, urban development, or logging disrupts the habitats and food chains of numerous plant and animal species. This habitat loss can lead to the extinction or migration of certain species, affecting the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem.
Pollution: Another major human activity that impacts interactions among living things is pollution. Whether it is air, water, or soil pollution, the release of harmful substances into the environment can have devastating effects on flora and fauna. Polluted water bodies, for example, can lead to the death of aquatic organisms, disrupt their reproduction and growth, and ultimately impact the entire aquatic food web.
Table: The Impact of Human Activities on Interactions among Living Things:
| Human Activities | Impact |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Loss of habitat, disruption of food chains, potential extinction |
| Pollution | Death of organisms, disruption of reproduction and growth, impact on food webs |
Climate change: Human-induced climate change is yet another significant factor that affects interactions among living things. The rise in global temperatures and changes in weather patterns can alter ecosystems and disrupt the phenology and behavior of species. This, in turn, affects predator-prey relationships, pollination patterns, and the availability of resources, leading to cascading effects throughout the food chain.
Overfishing: Overfishing, especially in marine ecosystems, can also have a detrimental impact on interactions among living things. Removal of certain fish species in large quantities disrupts the natural balance within a food web and can lead to population declines in other species dependent on those fish as a food source. The loss of keystone species due to overfishing can cause widespread ecological imbalance.
In conclusion, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, climate change, and overfishing have far-reaching effects on interactions among living things. It is crucial for us to recognize these impacts, adopt sustainable practices, and work towards preserving the delicate balance of our ecosystems for the benefit of all species.
Steps to Promote Positive Interactions Among Living Things

Positive interactions among living things are essential for the health and stability of ecosystems. By promoting these interactions, we can help create a harmonious environment where different species can thrive. Here are some steps that can be taken to promote positive interactions:
- Create habitat diversity: Providing a variety of habitats with different resources and conditions can attract a greater diversity of species. This can be achieved by planting different types of vegetation, creating ponds or wetlands, and maintaining a mixture of habitats.
- Promote native species: Native species are better adapted to the local environment and are more likely to interact positively with other species. By planting native plants and creating habitats that support native wildlife, we can help foster interactions that have evolved over time.
- Provide food and water sources: Making sure that there are ample food and water sources available can encourage positive interactions among different species. This can include providing bird feeders, bird baths, and water features that attract a variety of wildlife.
- Reduce pesticide use: Pesticides can have detrimental effects on the environment and disrupt natural interactions among living things. By reducing the use of pesticides, we can create a healthier environment for all species and promote more positive interactions.
- Education and awareness: Increasing awareness about the importance of positive interactions among living things can help promote understanding and action. By educating ourselves and others about the benefits of biodiversity, we can inspire people to take steps to protect and enhance interactions in their own surroundings.
By implementing these steps, we can create an environment that supports the coexistence and positive interactions among different living things. This will not only benefit the individual species but also contribute to the overall health and balance of the ecosystems we depend on.
Q&A:
What are the steps to promote positive interactions among living things?
The steps to promote positive interactions among living things include creating habitats and environments that support diverse species, conserving and protecting natural resources, educating and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity, practicing sustainable agriculture and forestry, and promoting cooperation and collaboration among different organizations and communities.
Why is creating habitats important for positive interactions among living things?
Creating habitats that are suitable for different species allows them to thrive and coexist. It provides them with food, shelter, and a place to reproduce, leading to positive interactions among different organisms.
How does conserving and protecting natural resources contribute to positive interactions among living things?
Conserving and protecting natural resources ensures that ecosystems are preserved and habitats are not destroyed. This allows different species to have access to the resources they need, promoting positive interactions such as mutualism and symbiosis.
How does education and awareness about biodiversity help promote positive interactions among living things?
By educating people and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity, individuals are more likely to take actions that protect and conserve the environment. This leads to the preservation of habitats and ecosystems, fostering positive interactions among living things.
What role does sustainable agriculture and forestry play in promoting positive interactions among living things?
Sustainable agriculture and forestry practices minimize the impact on the environment and prioritize the conservation of natural resources. This helps maintain biodiversity and allows different species to coexist, promoting positive interactions among living things.