
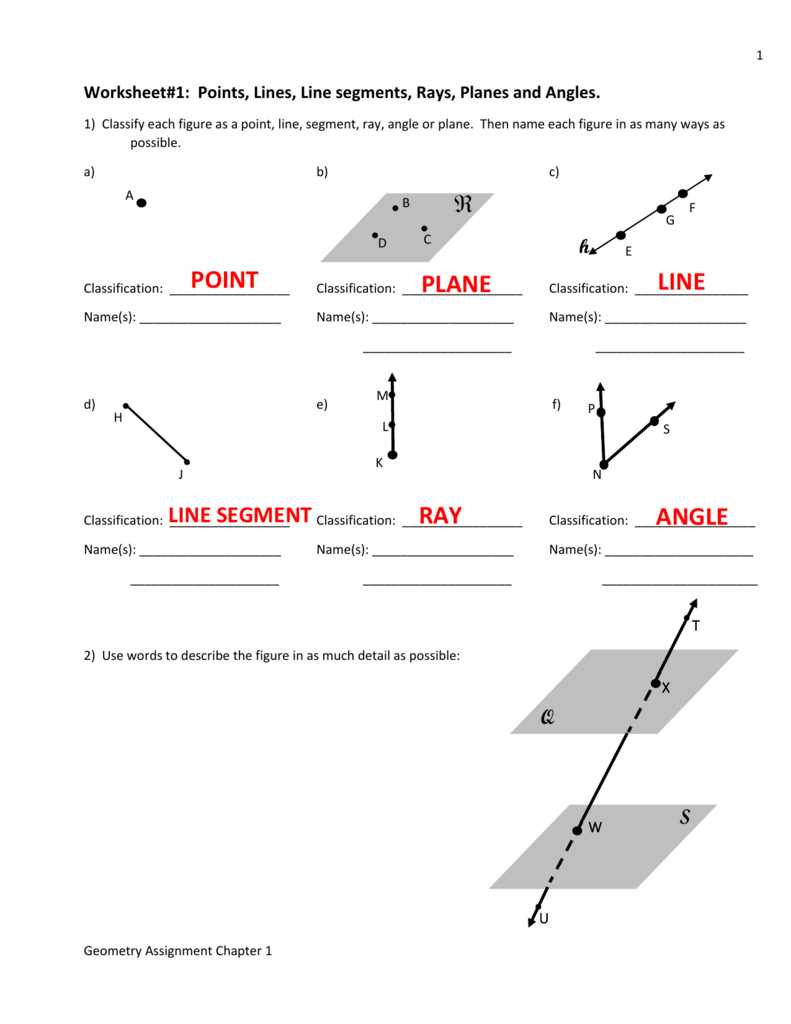
Line segments and distance are fundamental concepts in geometry and are necessary for understanding the relationship between points and shapes. A line segment is a part of a line that has two distinct endpoints, while distance represents the length of this segment. To practice and reinforce these concepts, teachers often provide students with line segments and distance worksheets.
Line segment and distance worksheets typically consist of various exercises that require students to find the length of a given line segment or determine the endpoints of a segment with a given length. These worksheets help students develop their skills in measuring distance and understanding the properties of line segments.
When completing line segment and distance worksheets, students can follow a step-by-step approach to find the answers. They must identify the coordinates or endpoints of the line segment and then use the distance formula or properties of similar triangles to calculate the length. It is essential to remember that the distance between two points in a coordinate plane is the hypotenuse of a right triangle formed by the horizontal and vertical distances between the points.
Line Segments and Distance Worksheet Answers

In order to find the length of a line segment, you need to know the coordinates of the two points that define the segment. Once you have the coordinates, you can substitute them into the distance formula and solve for the length. For example, if the coordinates of the two points are (3, 4) and (6, 8), you would substitute these values into the distance formula and calculate the square root of ((6 – 3)^2 + (8 – 4)^2) to find the length of the line segment.
When completing a line segments and distance worksheet, you may also encounter questions that involve finding the midpoint of a line segment. The midpoint of a line segment is the point that is equidistant from the two endpoints. To find the midpoint, you can average the x-coordinates of the two endpoints and the y-coordinates of the two endpoints. For example, if the coordinates of the endpoints are (2, 3) and (8, 12), you would find the midpoint by averaging the x-coordinates (2 + 8) / 2 = 5 and the y-coordinates (3 + 12) / 2 = 7. Therefore, the midpoint of the line segment is (5, 7).
Worksheet Answers:
- Question 1: The length of the line segment between the points (2, 3) and (8, 12) is approximately 10.63 units.
- Question 2: The midpoint of the line segment with endpoints (-5, 6) and (9, -3) is (2, 1.5).
- Question 3: The length of the line segment between the points (0, 0) and (5, 12) is approximately 13 units.
- Question 4: The midpoint of the line segment with endpoints (-3, 2) and (6, -9) is (1.5, -3.5).
These are just a few examples of the types of questions you may encounter on a line segments and distance worksheet. By understanding the distance formula and how to find the midpoint, you can confidently solve these types of problems.
Understanding Line Segments and Distance
A line segment is a part of a line that consists of two endpoints and all the points in between. It can be measured by finding the distance between its two endpoints. Distance refers to the space between two points and can be calculated using various methods, such as the Pythagorean theorem or the distance formula.
In geometry, line segments are commonly used to represent and measure different lengths. They are often denoted by placing a line over the letters representing the endpoints, such as AB. The length of a line segment can be determined by measuring the straight distance between its endpoints, either using a ruler or by applying mathematical formulas.
When working with line segments and distance, it is important to understand the concept of magnitude. Magnitude refers to the size or extent of a quantity or measurement. In the context of line segments, magnitude relates to the length of the segment. By calculating the distance between the endpoints, we can determine the magnitude or length of a line segment.
Understanding line segments and distance is crucial in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and construction. These concepts are used to measure and represent physical dimensions accurately. Whether it’s determining the length of a beam or ensuring precise measurements in a blueprint, line segments and distance play a vital role in these industries.
In conclusion, line segments are parts of lines that consist of two endpoints and all the points in between. They can be measured by finding the distance between their endpoints, which refers to the space between two points. Understanding line segments and distance is essential in accurately measuring and representing physical dimensions in various fields.
Calculating Distance between Two Points
Calculating the distance between two points is an essential skill in geometry and spatial reasoning. Whether you are working with coordinates on a grid or real-life measurements, finding the distance between two points helps determine the length of line segments and distances in a given space.
To calculate the distance between two points, you will need their coordinates or measurements. In a two-dimensional coordinate system, the x-coordinate and y-coordinate represent the position of a point. By using the formula derived from the Pythagorean theorem, you can find the distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) as follows:
d = √((x₂ – x₁)² + (y₂ – y₁)²)
This formula calculates the square root of the sum of the squares of the differences in the x-coordinates and y-coordinates. It provides the distance as a positive value.
For example, let’s say we have two points A(1, 3) and B(4, 7). By plugging these coordinates into the formula, we can find the distance between them:
- Step 1: Calculate the difference in x-coordinates: (4 – 1) = 3
- Step 2: Calculate the difference in y-coordinates: (7 – 3) = 4
- Step 3: Square the differences: 3² = 9, 4² = 16
- Step 4: Sum the squares: 9 + 16 = 25
- Step 5: Take the square root of the sum: √(25) = 5
Therefore, the distance between points A(1, 3) and B(4, 7) is 5 units.
Calculating the distance between two points is fundamental in various fields, including geometry, physics, and navigation. It allows us to determine the length of line segments, the perimeter of polygons, and the distance traveled between two locations. Practicing this skill helps build spatial awareness and problem-solving abilities.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem to Find Distance
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental mathematical concept that allows us to find the distance between two points in a coordinate plane. It is based on the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. By using this theorem, we can calculate the distance between any two points in a coordinate plane.
To understand how the Pythagorean Theorem works, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine we have two points, point A with coordinates (x1, y1) and point B with coordinates (x2, y2). We can draw a right triangle using these points, with the line segment connecting them as the hypotenuse of the triangle.
According to the Pythagorean Theorem, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. In this case, the hypotenuse is the line segment connecting points A and B, and the other two sides are the horizontal and vertical line segments connecting the points to the x and y-axes.
Using the formula derived from the Pythagorean Theorem, we can calculate the distance between points A and B as follows:
Distance = √((x2 – x1)^2 + (y2 – y1)^2)
This formula can be used to find the distance between any two points in a coordinate plane, as long as we know their coordinates. It is a powerful tool in geometry and can be applied in various real-world scenarios, such as measuring the distance between two cities on a map or calculating the length of a diagonal in a rectangle.
In conclusion, the Pythagorean Theorem allows us to find the distance between two points in a coordinate plane by calculating the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle formed by these points. By using the formula derived from this theorem, we can apply it to various real-world situations and solve geometry problems involving distance.
Applying the Distance Formula
The distance formula is a mathematical tool that allows us to find the distance between two points in a coordinate plane. It is derived from the Pythagorean theorem and can be used to calculate the length of a line segment between any two points. The formula is as follows:
d = √((x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²)
Where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the two points.
When applying the distance formula, it is important to first identify the coordinates of the two points you want to find the distance between. Once you have the coordinates, you can plug them into the formula and simplify the expression to find the length of the line segment. Remember to square the differences of the x and y coordinates, sum them up, and take the square root of the result.
For example, let’s say we want to find the distance between point A (2, 3) and point B (5, 7). We can plug these coordinates into the formula:
- x1 = 2, y1 = 3, x2 = 5, y2 = 7
- d = √((5 – 2)² + (7 – 3)²)
- d = √(3² + 4²)
- d = √(9 + 16)
- d = √25
- d = 5
Therefore, the distance between point A and point B is 5 units. The distance formula can be applied to any two points in a coordinate plane, allowing us to accurately measure the length of line segments and solve various problems related to distances.
Solving Problems with Line Segment Relationships
Line segments and their relationships play a crucial role in geometry, and being able to solve problems involving these relationships is an essential skill. By understanding the properties of line segments and using mathematical techniques, such as the Pythagorean theorem and basic algebra, we can solve a wide variety of problems.
One common problem involves finding the length of a line segment given certain information. For example, if we know the coordinates of two points on a line segment, we can use the distance formula to find the length of the segment. This formula, √((x2 – x1)^2 + (y2 – y1)^2), calculates the distance between two points in a coordinate plane. By plugging in the coordinates of the given points, we can find the length of the line segment.
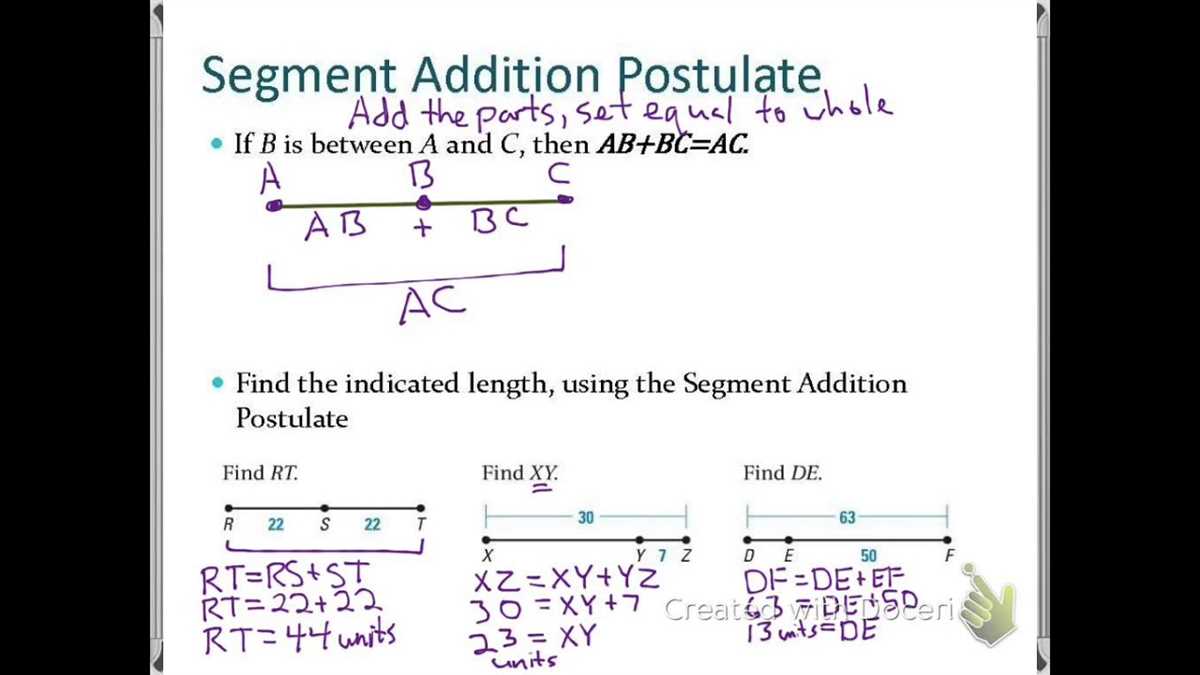
In addition to finding the length of a line segment, we can also solve problems involving the relationships between multiple line segments. For example, if we have two line segments that intersect at a point, we can use the segment addition postulate to find the length of the entire segment formed by the two segments. This postulate states that if three points A, B, and C are collinear and point B is between A and C, then the length of AB plus the length of BC equals the length of AC. By applying this postulate, we can find the length of the segment formed by the two intersecting line segments.
Overall, solving problems with line segment relationships requires a good understanding of the properties of line segments and the ability to apply mathematical techniques. By using formulas and postulates, we can accurately calculate the lengths of line segments and solve a variety of problems related to line segments. With practice and familiarity, these skills become second nature, allowing us to confidently approach and solve problems involving line segments.
Checking Your Answers with the Answer Key
After completing the line segments and distance worksheet, it’s important to check your answers to ensure accuracy. You can use the provided answer key to compare your answers and identify any mistakes or areas that need improvement.
Using the Answer Key
To use the answer key effectively, follow these steps:
- Refer to the corresponding question number on the worksheet.
- Locate the answer for that question in the answer key.
- Compare your answer with the one given in the answer key.
- If your answer matches the one in the answer key, mark it as correct.
- If your answer is different, recheck your work and try to identify any errors or misconceptions.
- If you are still unable to find the correct answer, seek guidance from your teacher or a classmate.
It’s important to approach checking your answers with an open and critical mindset. Use the answer key as a tool to learn from your mistakes and gain a better understanding of the concepts. Pay attention to the steps and calculations involved in the correct answers to improve your problem-solving skills.
Reviewing Your Performance
Once you have checked all your answers using the answer key, take some time to review your overall performance. Consider the following questions:
- Did you answer most of the questions correctly?
- Did you identify any specific areas where you struggled?
- Did you make any common mistakes that can be avoided in the future?
Reflecting on your performance will help you identify areas that need further practice or clarification. Make note of any concepts or problem types that you found challenging, and seek additional resources or assistance to improve your understanding.
Remember, the goal of completing the line segments and distance worksheet is not just to find the correct answers but also to develop a deeper understanding of the topic. Use the answer key as a tool for learning and growth, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed.