In the field of mathematics and operations research, linear programming is a powerful tool for solving optimization problems. It involves the process of finding the best possible solution to a given problem, subject to certain constraints. This technique has various applications in diverse fields such as economics, logistics, engineering, and management.
The linear programming project answer key serves as a guide or reference for students or professionals who are working on linear programming problems. It provides the correct solutions to the given problem and helps users understand the steps and methodology involved in solving such problems. The answer key usually includes the objective function, constraints, decision variables, and the optimal solution.
By referring to the linear programming project answer key, students can compare their solutions and learn from any mistakes they may have made. Additionally, the answer key allows users to verify the accuracy of their answers and gain confidence in their problem-solving skills. It also serves as a valuable learning resource, enabling students to understand the logic behind the optimal solution and apply the techniques to similar problems in the future.
Furthermore, the linear programming project answer key can be a useful tool for teachers and instructors. It helps them assess their students’ understanding of the subject matter and identify areas where additional instruction or clarification may be necessary. Additionally, instructors can use the answer key to explain the steps involved in solving the problem, emphasizing the key concepts and techniques involved in linear programming.
Linear Programming Project Answer Key: Guideline for Success
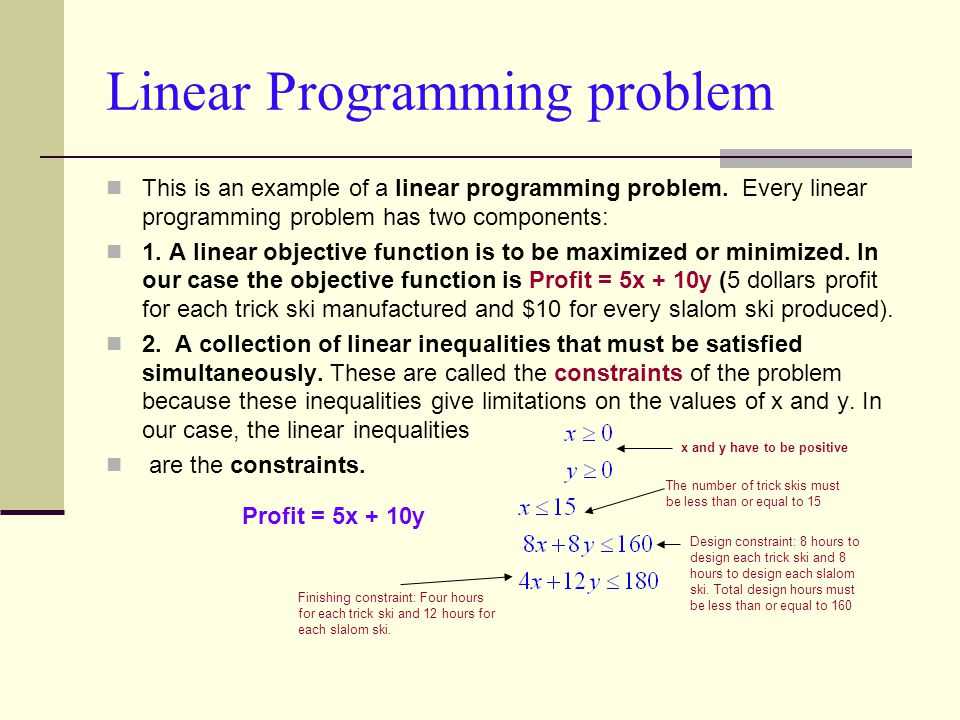
Linear programming is a powerful tool for optimization problems, allowing us to find the best solution among a set of possible choices. However, solving linear programming problems can be challenging without proper guidance. This answer key provides a guideline for success in tackling linear programming projects, helping you approach and solve these problems effectively.
1. Define the objective function and constraints: Before diving into the problem, it is essential to clearly define the objective function you want to maximize or minimize, as well as any constraints you need to consider. This will provide clarity and structure to your problem-solving approach.
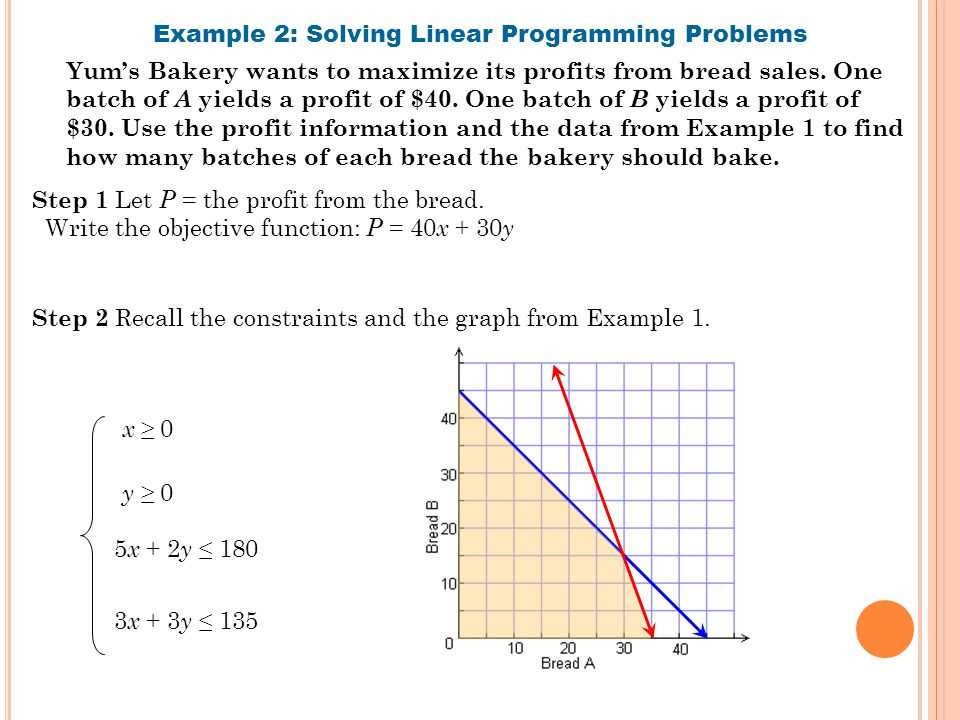
2. Graphical representation: Utilize graphical representation to visualize the feasible region, which is the combination of values that satisfy all the constraints. This will help you identify the optimal solution visually and gain a better understanding of the problem.
3. Identify the corner points: The corner points of the feasible region are the potential optimal solutions for the linear programming problem. Identify these points and evaluate the objective function at each point to determine the best solution.
4. Check for alternate optimal solutions: Sometimes, there can be multiple corner points that yield the same optimal value for the objective function. Ensure to check for alternate optimal solutions by evaluating the objective function at each corner point.
5. Sensitivity analysis: Sensitivity analysis is crucial to understand how changes in the coefficients of the objective function or constraints affect the optimal solution. Perform sensitivity analysis to assess the stability and reliability of the solution.
6. Interpret the results: Once you have obtained the optimal solution, it is essential to interpret the results in the context of the problem. Make sure to provide a clear explanation of the solution and any limitations or assumptions made during the analysis.
In conclusion, tackling linear programming projects successfully involves defining the objective function and constraints, utilizing graphical representation, identifying corner points, checking for alternate optimal solutions, performing sensitivity analysis, and interpreting the results. By following these guidelines, you can approach linear programming problems with confidence and achieve optimal solutions.
Understanding the Basics of Linear Programming

Linear programming is a mathematical technique used to optimize the allocation of resources in order to achieve a specific objective. It involves analyzing a set of linear equations and inequalities to find the best possible solution given a set of constraints. This technique has applications in various fields such as economics, business management, transportation planning, and manufacturing.
Objective Function: In linear programming, an objective function is a mathematical expression that represents the goal or objective of the problem. It is usually in the form of a linear equation to be maximized or minimized. The objective function can include multiple variables that need to be optimized.
Constraints: Constraints are limitations or restrictions that must be considered when solving a linear programming problem. These can include resource availability, capacity limits, budget constraints, and other factors that affect decision-making. Constraints are typically represented as linear inequalities or equations.
Feasible Region: The feasible region is the set of all feasible solutions that satisfy all the constraints in a linear programming problem. It represents the region of the graph where the objective function can be optimized. The feasible region is determined by plotting the constraints on a graph and finding the overlapping region.
Optimal Solution: An optimal solution in linear programming is the best feasible solution that maximizes or minimizes the objective function. It is the point within the feasible region that provides the highest or lowest value for the objective function. The optimal solution is determined by evaluating the objective function at each vertex or corner point of the feasible region.
Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis is a technique used to evaluate how changes in the parameters of a linear programming problem affect the optimal solution. It helps in understanding the sensitivity of the solution to variations in the constraints or objective function coefficients. Sensitivity analysis provides valuable insights into the robustness and stability of the solution.
Applications: Linear programming has numerous applications in various industries. It can be used to optimize production schedules, minimize costs, maximize profits, allocate resources efficiently, solve transportation and assignment problems, and make informed decisions in business operations. The ability to model complex problems and find optimal solutions makes linear programming a powerful tool for decision-making and planning.
Step-by-Step Approach for Solving Linear Programming Problems
A linear programming problem involves optimizing an objective function, subject to a set of constraints, within given bounds and conditions. To solve such problems, a step-by-step approach can be followed:
- Identify the Objective Function: Determine the objective of the problem, whether it is to maximize or minimize a certain quantity. This function is typically represented as a mathematical expression, such as maximizing profits or minimizing costs.
- Establish the Decision Variables: Define the variables that are within control and can be adjusted to achieve the objective. These variables could represent quantities, such as the number of units produced or the amount of resources allocated.
- Formulate the Constraints: Identify the constraints or limitations that exist in the problem. These restrictions could be based on resource availability, capacity constraints, or other limitations. Constraints are generally represented as equations or inequalities.
- Construct the Feasible Region: Plot the constraints on a graph to visualize the feasible region, which represents the set of all possible combinations of decision variables that satisfy the constraints. This region is bounded by the feasible boundaries defined by the constraints.
- Determine the Corner Points: Identify the corner points of the feasible region, which are the vertices or extreme points. These points represent the possible solutions that can be considered.
- Calculate the Objective Function: Evaluate the objective function at each corner point to determine the optimal solution. This involves substituting the values of the decision variables into the objective function and calculating the resulting value.
- Compare and Select Optimal Solution: Compare the objective function values at each corner point and select the solution that optimizes the objective, whether it is maximizing or minimizing. The optimal solution may be a single corner point or a combination of multiple adjacent corner points.
By following this step-by-step approach, linear programming problems can be systematically analyzed and solved to find the optimal solution that meets the given objectives and constraints.
Key Components of a Linear Programming Project
When undertaking a linear programming project, there are several key components that need to be considered in order to successfully solve the problem and interpret the results. These components include the objective function, constraints, decision variables, and the feasible region.
The objective function is the mathematical representation of the goal or objective of the project. It defines what is being optimized, whether it be maximizing profit, minimizing cost, or something else. The objective function is typically a linear equation that is either maximized or minimized.
Constraints are the limitations or restrictions that must be taken into account when finding the optimal solution. These constraints are represented by a system of linear inequalities or equations. They can include factors such as resource limitations, production constraints, or demand requirements. Each constraint narrows down the feasible region and limits the possible solutions.
Decision variables are the unknowns or variables that need to be determined in order to optimize the objective function. They represent the quantities or decisions that the project seeks to find. Decision variables have certain bounds or restrictions based on the problem context. For example, if the decision variable represents the number of units produced, it cannot be negative.
The feasible region is the set of all possible solutions that satisfy the constraints. It is typically represented graphically as a shaded area in two-dimensional space or as a polytope in higher dimensions. The feasible region is bounded by the constraints and can be visualized as the area where all constraints intersect.
Summary:
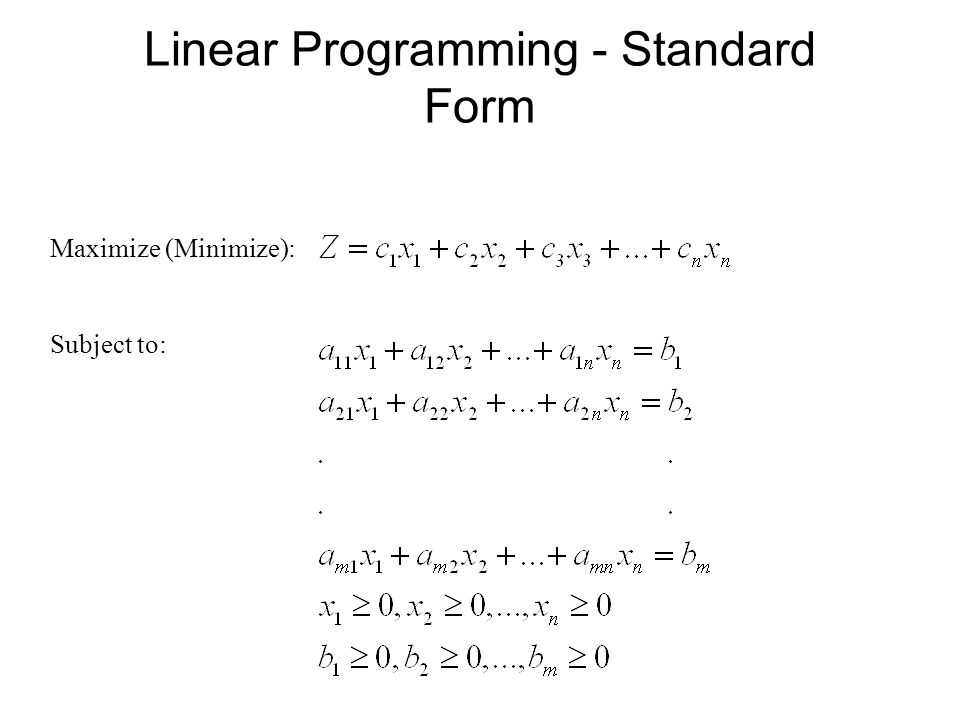
- The objective function defines the goal of the project and is typically a linear equation.
- Constraints are limitations or restrictions that must be satisfied.
- Decision variables are the unknowns or variables being determined.
- The feasible region is the set of all possible solutions that satisfy the constraints.
Analyzing Real-World Scenarios with Linear Programming
Linear programming is a powerful mathematical tool that can be used to solve complex real-world problems. By analyzing these scenarios using linear programming techniques, we can optimize decision-making and find the best possible solution to a given problem. Linear programming helps businesses, governments, and individuals tackle a wide range of challenges, from resource allocation to production planning and scheduling.
One example of using linear programming in real-world scenarios is in the transportation industry. Companies that transport goods face the challenge of optimizing their routes to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. By inputting various constraints such as distance, fuel consumption, and time constraints, linear programming models can determine the most optimal routes for delivery trucks, reducing fuel expenses and improving overall productivity.
Another area where linear programming is widely applied is in financial portfolio management.
Investors strive to maximize their returns while minimizing their risks through diversification. Linear programming techniques can be used to create portfolios with optimal asset allocations based on various constraints, such as risk tolerance and expected returns. By using linear programming models, investors can make informed decisions about which assets to include in their portfolios, optimizing their investments to achieve their financial goals.
Linear programming is also useful in the field of production planning and scheduling.
Manufacturing companies often face the challenge of allocating resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to meet production demands while minimizing costs. Linear programming models can help determine the optimal production schedule, taking into account constraints such as available resources, order deadlines, and production capacities. By using linear programming techniques, companies can streamline their production processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Overall, linear programming is an essential tool for analyzing real-world scenarios and optimizing decision-making in various industries. Whether it’s in transportation, finance, or manufacturing, linear programming can help companies and individuals make informed choices and achieve their goals more efficiently. By carefully considering the constraints and objectives of a problem, linear programming provides valuable insights and solutions that can drive success and innovation.
Interpreting and Evaluating Results in Linear Programming
Linear programming is a mathematical technique used to optimize the allocation of resources and find the best possible solution to a problem. Once the linear programming model has been formulated and solved, it is crucial to interpret and evaluate the results to make informed decisions and assess the effectiveness of the solution.
One important aspect of interpreting the results is understanding the values of the decision variables. Decision variables represent the quantities to be determined or optimized, and their values provide insights into the optimal solution. By examining the values of decision variables and comparing them to their constraints, it is possible to determine if the solution is feasible and satisfies all the requirements.
Another crucial aspect of evaluating the results is assessing the objective function value. The objective function represents the goal or objective of the problem, such as maximizing profit or minimizing costs. The optimal solution should yield the highest or lowest objective function value possible. By comparing the objective function value obtained from the linear programming model to a predetermined benchmark or target value, it is possible to determine the degree of success in achieving the desired outcome.
In addition to interpreting the decision variable values and evaluating the objective function value, it is also important to consider the sensitivity analysis results. Sensitivity analysis provides information about the impact of changes in the constraints or objective function coefficients on the optimal solution. It allows decision-makers to assess the robustness of the solution and identify potential vulnerabilities or opportunities. By analyzing the sensitivity analysis results, it is possible to make informed decisions regarding adjustments to the model or to address any potential risks or uncertainties.
In conclusion, interpreting and evaluating the results in linear programming is essential for understanding the optimal solution and making informed decisions. It involves assessing the feasibility of the solution, evaluating the objective function value, and considering the sensitivity analysis results. By thoroughly analyzing these aspects, decision-makers can make informed choices, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Tips and Strategies for Optimizing Linear Programming Solutions
Optimizing linear programming solutions can be a challenging task, but with the right tips and strategies, you can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your models. Here are some key recommendations to consider:
- Review and refine your objective function: The objective function represents the goal or objective you are trying to optimize. Reviewing and refining this function can help you better align it with your business or project goals, leading to more meaningful and accurate results.
- Validate your constraints: Constraints are the limitations or restrictions that must be considered in the linear programming model. It is essential to validate these constraints to ensure they accurately reflect the real-world conditions. Make sure to test different scenarios and assumptions to account for any potential variations.
- Perform sensitivity analysis: Sensitivity analysis involves evaluating how changes in the input variables affect the optimal solution. By conducting sensitivity analysis, you can identify critical variables and address any potential risks or uncertainties. This analysis can help you make informed decisions and assess the robustness of your model.
- Consider alternative solutions: Linear programming models often have multiple feasible solutions. Exploring alternative solutions can provide valuable insights and help uncover better or more efficient options. Evaluate different scenarios and compare the outcomes to choose the most appropriate solution for your specific needs.
Overall, optimizing linear programming solutions requires a thorough understanding of the problem, careful consideration of variables and constraints, and a systematic approach to model refinement. By following these tips and strategies, you can enhance the quality and impact of your linear programming projects.