Welcome to this article on the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key. In this lab, students are tasked with graphing data on the menstrual cycles of different individuals, and analyzing the patterns and trends that emerge from the data. This lab is designed to deepen students’ understanding of the menstrual cycle and its variations.
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that occurs in the female reproductive system. It is governed by the interaction of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, and it involves the preparation of the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg. The cycle is typically divided into four phases: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
In the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12, students collect data on the length of menstrual cycles for a sample of individuals. They then graph this data on a line graph, with the x-axis representing the cycle number and the y-axis representing the length of the cycle. By analyzing the graph, students can identify patterns such as cycle length variability, irregularity, and the presence of any trends over time.
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key
The Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key is a tool that helps students analyze and interpret the data collected during the lab. By graphing the hormone levels and various other parameters related to the menstrual cycle, students can gain a deeper understanding of the physiological changes that occur throughout the cycle.
The answer key provides a detailed explanation of how to graph the data and how to interpret the results. It includes information about the different hormones involved in the menstrual cycle, such as estrogen and progesterone, and their respective levels during different phases of the cycle. This information allows students to identify patterns and correlations between hormone levels and specific events in the menstrual cycle, such as ovulation and menstruation.
One of the key features of the answer key is the inclusion of sample graphs. These graphs serve as visual aids for students, helping them understand how to represent the data accurately and how to draw valid conclusions from it. The sample graphs also show the expected changes in hormone levels and other parameters throughout the menstrual cycle, providing a reference for students to compare their own data to.
The answer key also provides explanations for any anomalies or unexpected findings that students may encounter during the lab. This helps students understand that not all menstrual cycles are the same and that individual variations can occur. It also encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students are encouraged to analyze and interpret their data in light of the information provided in the answer key.
In conclusion, the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key is a valuable resource for students studying the menstrual cycle. It helps them analyze their data, interpret their findings, and gain a deeper understanding of the complex physiological processes that occur during the menstrual cycle.
Key Components of the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12
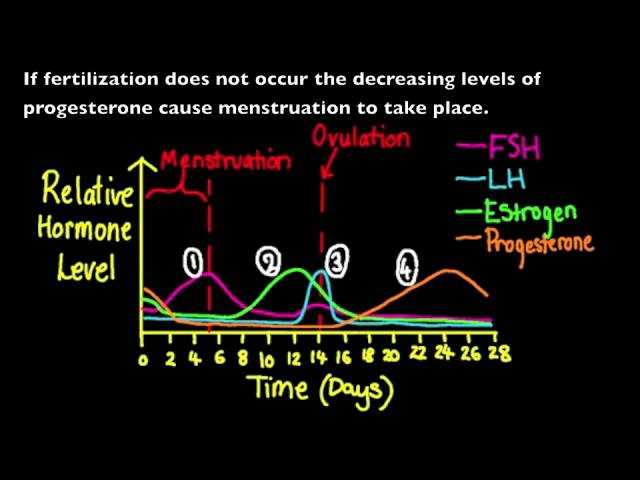
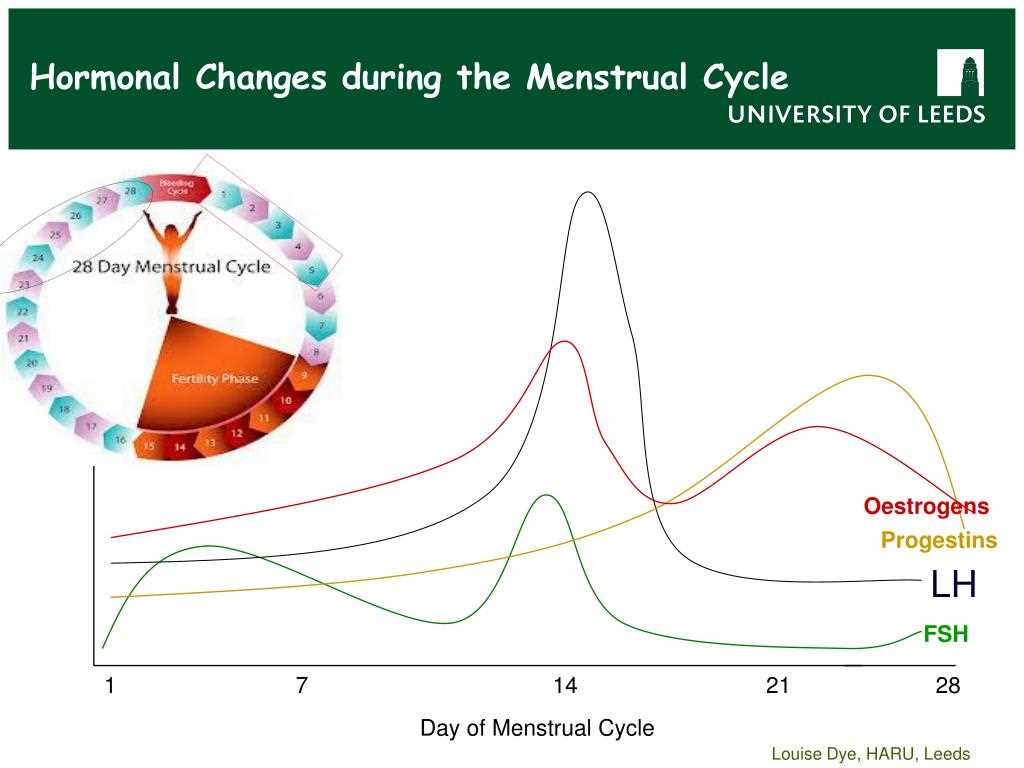
The Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 is an essential tool for studying and understanding the various phases and hormones involved in the female menstrual cycle. The lab allows students to graphically represent and analyze data related to hormone levels and the changes that occur during different stages of the cycle.
One of the key components of the lab is the collection and analysis of hormonal data. Students are required to collect daily measurements of the hormones estrogen and progesterone throughout a full menstrual cycle. These measurements are then plotted on a graph to visually represent the fluctuations in hormone levels over time.
Another important aspect of the lab is the identification of the different phases of the menstrual cycle. By analyzing the data and observing patterns on the graph, students can identify and label the follicular, ovulatory, and luteal phases, as well as the menstrual phase. This allows them to better understand the timing and duration of each phase and the hormonal changes that occur during each stage.
The lab also involves the calculation of average hormone levels for each phase of the menstrual cycle. By calculating the mean hormone concentrations during specific phases, students can determine the average levels of estrogen and progesterone during different stages of the cycle. This helps in understanding the relative levels of these hormones and their role in regulating the menstrual cycle.
Overall, the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 provides students with a hands-on experience in analyzing and interpreting hormonal data and graphically representing the menstrual cycle. By actively engaging in the lab, students gain a deeper understanding of the key components and phases of the menstrual cycle and the role of hormones in regulating this physiological process.
Interpreting the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key
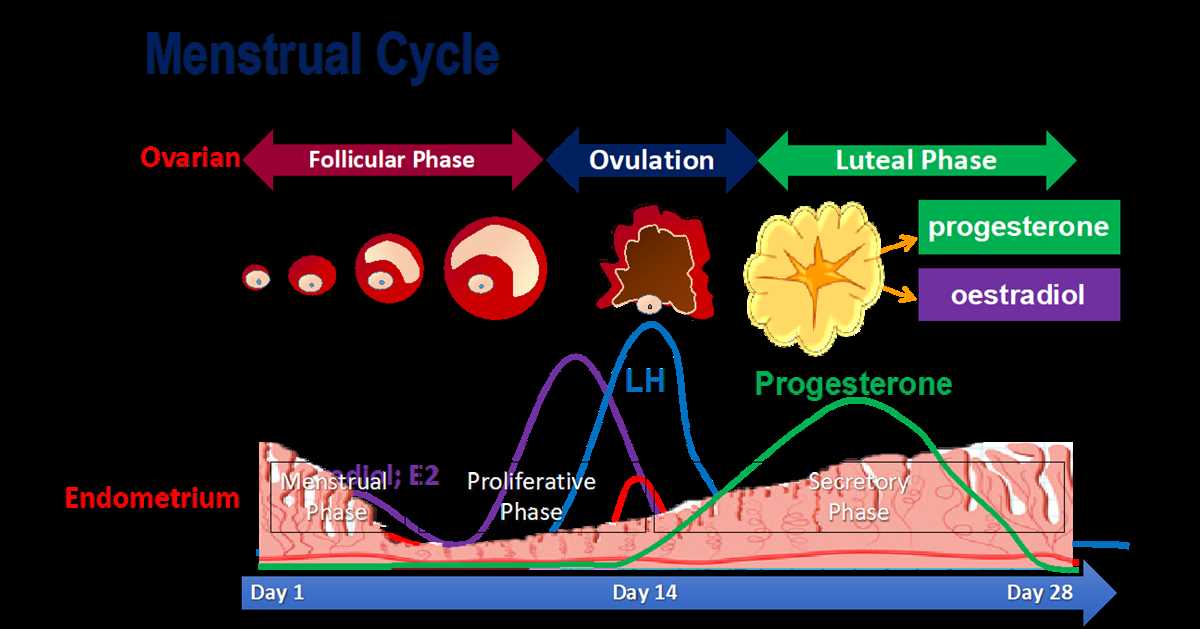
When interpreting the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 Answer Key, it is important to understand the patterns and trends that can be observed in the graph. The graph typically consists of a horizontal axis representing the days of the menstrual cycle and a vertical axis representing the levels of certain hormones or physical symptoms. By analyzing these levels over time, we can gain insights into the menstrual cycle and various aspects of reproductive health.
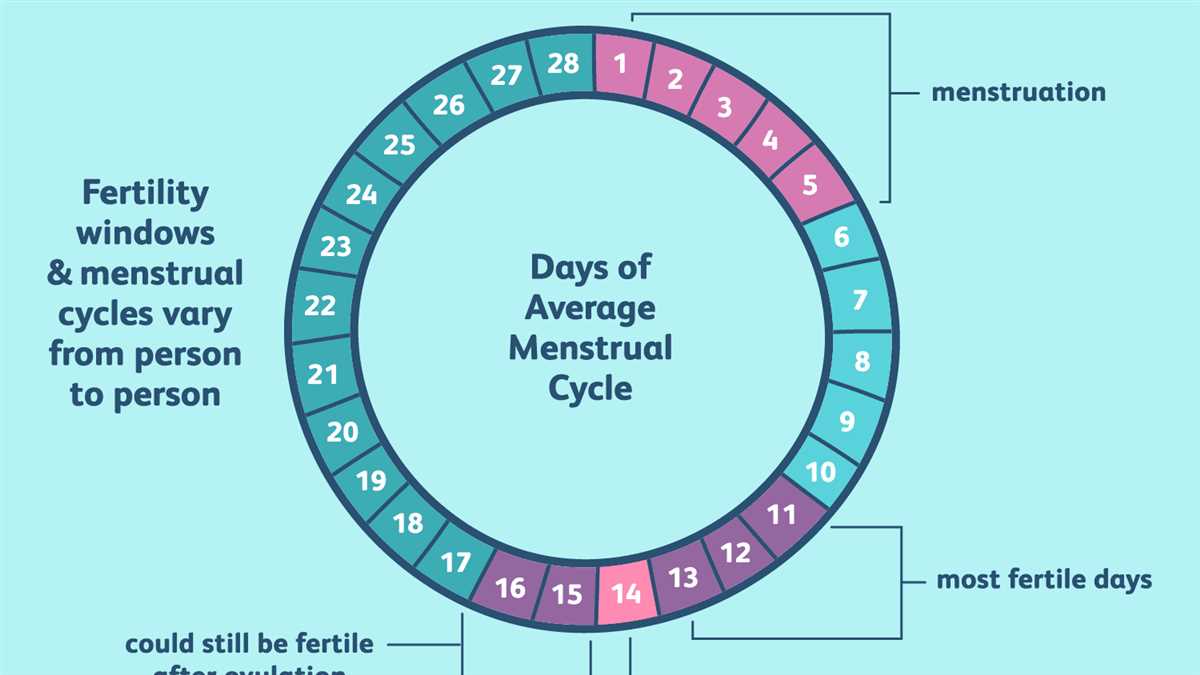
One key aspect to look for in the answer key is the presence of a regular menstrual cycle. A regular cycle typically lasts between 21 and 35 days, with around 28 days being the average. By examining the graph, we can assess whether the menstrual cycle falls within this range. If the cycle is consistently shorter or longer than the average, it may indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or other reproductive health issue that should be further investigated.
Another important aspect to consider is the presence and levels of certain hormones throughout the menstrual cycle. The key may include data on hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). By analyzing the fluctuations in these hormone levels, we can determine if ovulation has occurred and if the menstrual cycle is functioning properly. For example, a sharp increase in LH usually indicates that ovulation is imminent, while a consistent elevation in progesterone levels suggests that the individual has entered the luteal phase of the cycle.
Furthermore, the answer key may provide information on other physical symptoms associated with the menstrual cycle. This could include data on basal body temperature, cervical mucus consistency, or the presence of menstrual bleeding. By examining these symptoms alongside the hormone levels, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the individual’s reproductive health and the overall functioning of their menstrual cycle.
Key Takeaways:
- The answer key allows for the interpretation of patterns and trends in the menstrual cycle graph.
- Regular menstrual cycles typically last 21-35 days, with an average of 28 days.
- Examining hormone levels can indicate ovulation and overall menstrual cycle function.
- Other physical symptoms like basal body temperature and cervical mucus consistency may provide further insights.
Tips for Completing the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12
Completing the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can successfully complete the lab and achieve accurate results. Here are some tips to help you:
1. Gather all the necessary materials
Before starting the lab, make sure you have all the required materials. This may include a menstrual calendar, graph paper, pencils, rulers, and colored pens or markers. Having everything prepared beforehand will make the process smoother and more organized.
2. Understand the objectives and instructions
Read the lab instructions and objectives carefully to ensure that you understand what is expected of you. Make note of any specific guidelines or criteria that need to be followed while graphing the menstrual cycle.
3. Collect data consistently
Accurate data collection is crucial for graphing the menstrual cycle. Record the start and end dates of each menstrual cycle, noting any irregularities or variations. Make sure to collect data consistently and without any gaps to ensure an accurate representation of the cycle.
4. Use appropriate graphing techniques
When graphing the menstrual cycle, choose a suitable graphing technique that effectively represents the data. This could be a line graph, bar graph, or any other method that best displays the information. Ensure that your graph is clear, organized, and easy to interpret.
5. Analyze and interpret the data
Once you have completed graphing the menstrual cycle, take the time to analyze and interpret the data. Look for patterns, trends, and any significant variations in the cycle. Use this analysis to draw conclusions and answer any questions or objectives stated in the lab.
By following these tips and approaching the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12 with attention to detail and accuracy, you can successfully complete the lab and gain a better understanding of the menstrual cycle.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12
While conducting the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12, it is important to be aware of common mistakes that students often make. By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your data.
1. Not collecting data consistently: One common mistake is failing to collect data consistently throughout the entire menstrual cycle. It is crucial to record data for each day of the cycle to accurately identify patterns and trends. Missing data points can lead to incomplete or inaccurate conclusions.
2. Inconsistent measurement techniques: Another mistake is using different measurement techniques for each data point. It is important to use consistent and standardized methods for measuring variables such as body temperature and cervical mucus. Deviating from a consistent technique can introduce errors and make it difficult to compare data points.
3. Unreliable data recording: Incorrectly recording data is a common mistake in any lab. Make sure to double-check your data recording to avoid entry errors. It is also crucial to label data points clearly and include necessary annotations to ensure proper interpretation later on.
4. Neglecting to account for external factors: The menstrual cycle can be influenced by various external factors, such as stress, illness, or medications. Failing to account for these factors can confound the results and make it difficult to observe clear patterns. Make sure to document any external factors that may have an impact on the menstrual cycle.
5. Lack of data analysis: Some students may make the mistake of simply graphing the data without conducting any meaningful analysis. It is important to analyze the data and look for patterns, trends, and correlations. This can help you draw conclusions and make accurate interpretations.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following proper data collection and analysis techniques, you can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your findings in the Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab 12.