
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the “cradle of civilization,” was one of the earliest civilizations in the world. Located in the region now known as the Middle East, Mesopotamia was a land between two rivers: the Tigris and the Euphrates. This fertile land was an ideal location for early human settlements, as it provided the necessary resources for agriculture and animal husbandry.
In this map activity, students were challenged to identify and label various cities and landmarks of ancient Mesopotamia, such as Ur, Babylon, and the Persian Gulf. By completing this activity, students gain a better understanding of the geography and importance of these ancient cities and how they contributed to the development of the Mesopotamian civilization.
The answer key for this map activity provides the correct labels for each city and landmark, ensuring that students can compare their own answers and learn from any mistakes. The key also includes additional information about each location, such as its significance in ancient times and any notable achievements or events associated with it.
Overall, this map activity and its answer key serve as valuable educational tools for students learning about ancient Mesopotamia. It allows them to engage with the material in a hands-on way, while also providing the opportunity for self-assessment and further exploration of the important landmarks and cities of this fascinating civilization.
Mesopotamia Map Activity Answer Key
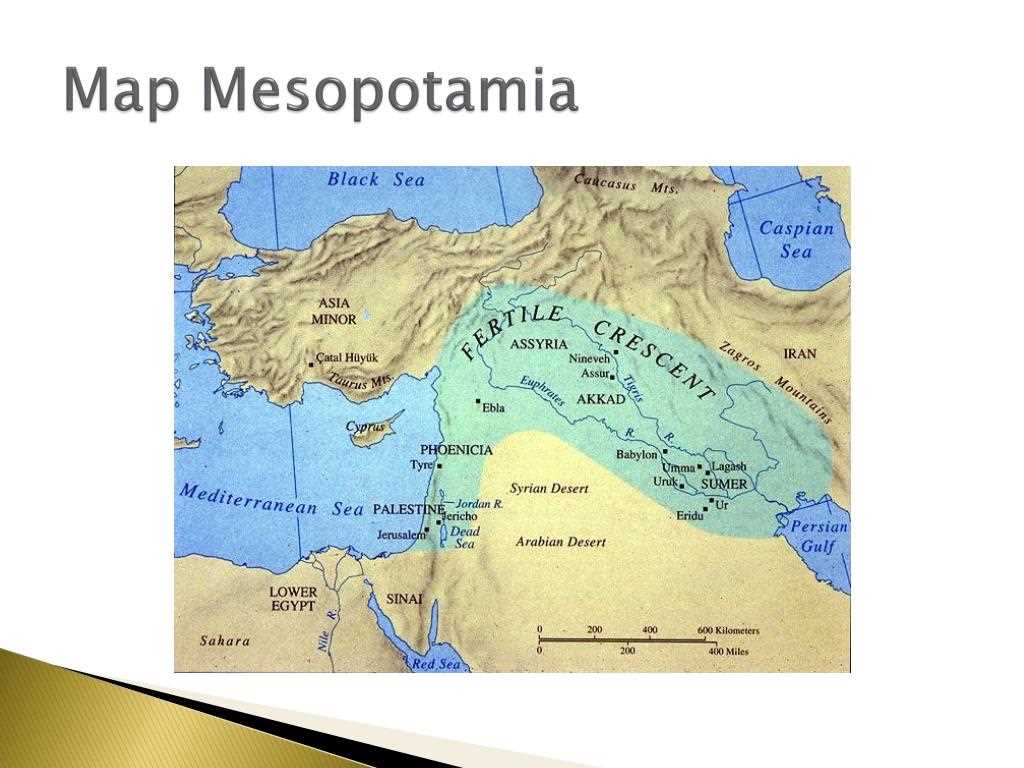
In the Mesopotamia map activity, students were tasked with labeling and identifying key features of the ancient civilization of Mesopotamia. The answer key provides the correct labels and information for each feature on the map.
Key Features:
- Euphrates River: The Euphrates River runs through the middle of Mesopotamia, providing a vital water source for irrigation and transportation.
- Tigris River: The Tigris River is another important water source in Mesopotamia, running parallel to the Euphrates River.
- Sumer: Sumer was the earliest civilization in Mesopotamia, known for its advanced city-states and development of writing.
- Babylon: Babylon was a major city in Mesopotamia and the capital of the Babylonian Empire, known for its impressive architecture and famous Hanging Gardens.
- Assyria: Assyria was a powerful empire in Mesopotamia, known for its military prowess and conquests.
- Ur: Ur was an ancient city in Sumer, known for its well-preserved ziggurat and status as a center of trade.
- Nineveh: Nineveh was the capital of the Assyrian Empire and one of the largest cities in the world at its peak.
By correctly labeling and understanding these key features on the map, students gain a better understanding of the geography and importance of Mesopotamia in ancient history.
Understanding the Map Activity
The Mesopotamia map activity is an educational exercise that helps students develop a deeper understanding of the geography of ancient Mesopotamia. By analyzing and studying the map, students can gain insights into the physical features of the region, as well as the cities and civilizations that thrived in this area thousands of years ago.
One key objective of the map activity is to familiarize students with the major rivers that played a significant role in the development of Mesopotamia. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers were essential sources of water for agriculture, transportation, and trade. By identifying and labeling these rivers on the map, students can grasp the importance of water resources in ancient civilizations and how they shaped the way people lived.
To successfully complete the map activity, students need to locate and identify important cities and civilizations that existed in Mesopotamia during various periods. This exercise helps them understand the significance of urban centers like Ur, Babylon, and Nineveh in the development of Mesopotamian society. By identifying these cities on the map, students can visualize how they were strategically located along the rivers and served as hubs of political, economic, and cultural activities.
In addition to cities, students also need to locate and label other important features on the map, such as mountains, deserts, and bodies of water. This exercise allows students to recognize the geographical challenges and opportunities that influenced the development of ancient Mesopotamia. For example, the presence of mountains and deserts acted as natural barriers, shaping the interactions and trade routes between different regions.
Overall, the Mesopotamia map activity provides students with a hands-on learning experience that enhances their understanding of the geography, history, and civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia. By analyzing and interpreting the map, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the complexities and interconnections of this fascinating region.
Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
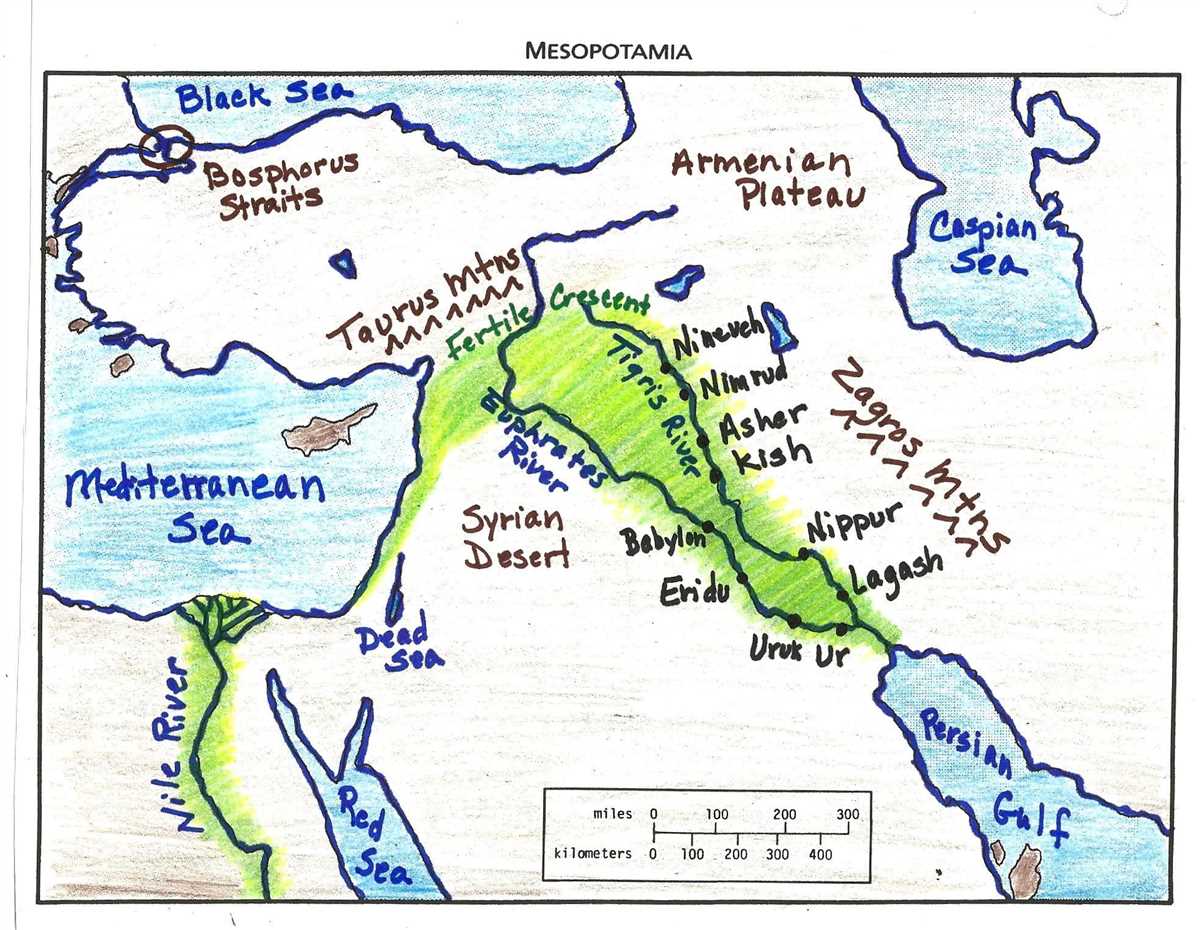
Mesopotamia, which means “land between rivers” in Greek, was a historical region located in the eastern Mediterranean. It is often referred to as the cradle of civilization because it is considered one of the birthplaces of human civilization. The region was home to some of the earliest known human settlements and saw the emergence of advanced agricultural practices, complex societies, and written language.
One of the key features of Mesopotamia was its geography. It was situated between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which created fertile land for agriculture. The abundance of water and fertile soil allowed the early inhabitants of Mesopotamia to develop intensive farming techniques and establish permanent settlements. The success of their agricultural endeavors led to surplus food production and the rise of complex societies.
As civilization flourished in Mesopotamia, several city-states emerged, including Sumer, Akkad, Babylon, and Assyria. These city-states were ruled by kings and developed unique political, religious, and legal systems. They built impressive architectural structures, such as ziggurats and palaces, and engaged in trade with neighboring regions.
One of the most significant contributions of Mesopotamia to human history is the invention of writing. The Sumerians, an ancient Mesopotamian civilization, developed the world’s first known writing system called cuneiform. This system involved pressing wedge-shaped marks onto clay tablets, and it was used for recording administrative documents, literature, religious texts, and other forms of written communication.
In addition to writing, Mesopotamia also made advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and technology. The Babylonians, for example, developed a sophisticated system of mathematics based on the number 60, which formed the basis of modern timekeeping. They also created one of the earliest known astronomical observations and were able to predict eclipses and track celestial movements.
In conclusion, Mesopotamia holds a significant place in history as the cradle of civilization. Its fertile land, early agricultural practices, city-states, and contributions to writing and other areas of knowledge laid the foundation for future civilizations and shaped the course of human history.
Key Locations on the Map
Mesopotamia, known as the “land between rivers,” was located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in present-day Iraq. This region was home to several key locations that played an important role in the development of ancient civilization.
One notable location on the map is Ur, which was a significant Sumerian city-state. Ur was an important center for trade and agriculture, known for its ziggurat, a massive stepped tower that served as a temple. The city was also the birthplace of Abraham, a central figure in the religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
The city of Babylon, located along the Euphrates River, was another key location on the map. As the capital of the ancient Babylonian empire, it was a major political and cultural center. The city was famously known for its hanging gardens, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Babylon was also home to the Code of Hammurabi, one of the earliest known legal codes.
Another important location on the map is Nineveh, an ancient Assyrian city situated on the eastern bank of the Tigris River. Nineveh served as the capital of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and was a significant cultural and military center. The city was known for its impressive fortified walls, royal palaces, and extensive library collection.
The city of Uruk, one of the earliest cities in Mesopotamia, was also prominently featured on the map. Uruk was a major center for trade and worship, with its temple dedicated to the goddess Inanna. The city is famous for its monumental architecture, including the White Temple and the Eanna District.
These key locations on the map provide insights into the rich history and cultural achievements of Mesopotamia. From the bustling trading hub of Ur to the majestic city of Babylon, each place played a vital role in shaping the civilization that emerged in this region thousands of years ago.
Answering the Map Activity Questions
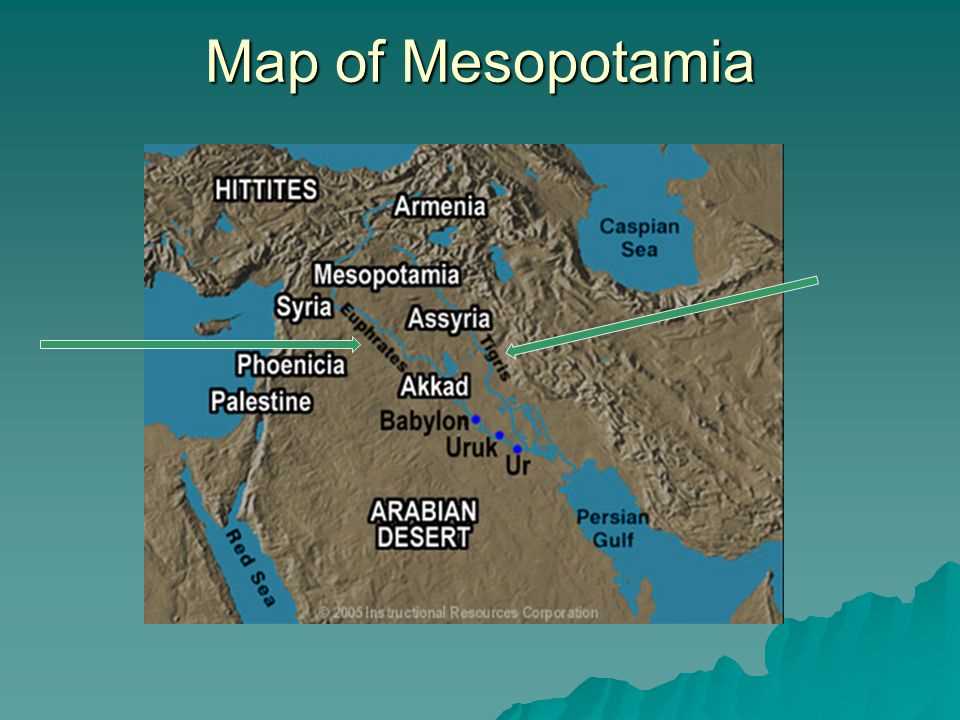
After completing the Mesopotamia map activity, you might have some questions about the different locations and features on the map. Here are the answers to some common questions that students often have:
- 1. What are the major rivers in Mesopotamia?
- 2. What are the important cities in Mesopotamia?
- 3. What is the significance of the Fertile Crescent?
- 4. What does the map tell us about the geography of Mesopotamia?
- 5. How does the map help us understand the historical significance of Mesopotamia?
In Mesopotamia, the major rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates. These rivers played a crucial role in the development of early civilizations in the region.
Some important cities in Mesopotamia include Ur, Babylon, Nineveh, and Uruk. These cities were centers of trade, culture, and governance in ancient times.
The Fertile Crescent is an important region in Mesopotamia known for its fertile soil and favorable climate. It supported the growth of agriculture and settlement, leading to the development of some of the world’s first civilizations.
The map of Mesopotamia shows us that the region is characterized by rivers, mountains, and deserts. These geographic features influenced the development of civilizations by providing resources, natural barriers, and trade routes.
The map helps us understand the historical significance of Mesopotamia by showing the locations of major cities, rivers, and other important features. It allows us to visualize the physical geography of the region and understand how it influenced the development of civilization.
Overall, the map activity provides valuable information about the geography and historical significance of Mesopotamia. By answering the questions and analyzing the map, we can gain a deeper understanding of this ancient civilization and its importance in human history.