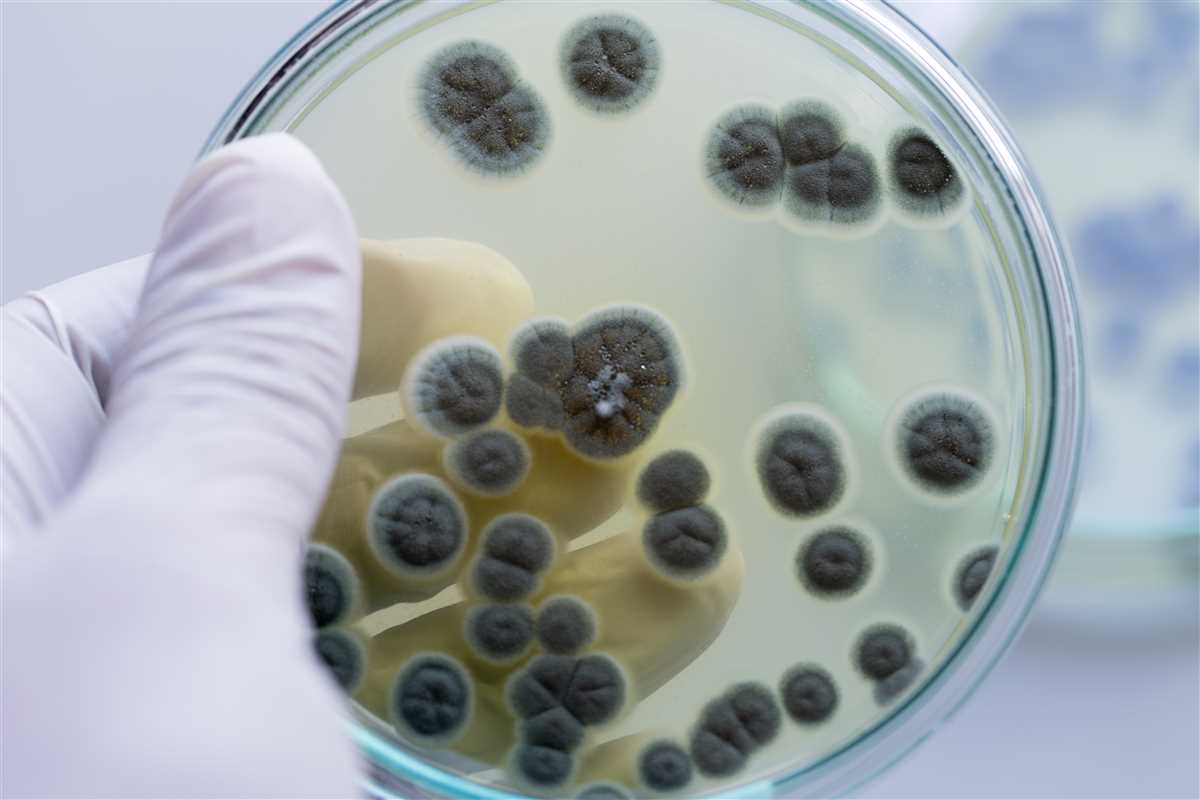
A microbial challenge test is a scientific procedure used to evaluate the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents or materials in preventing the growth of microorganisms. It is an essential step in the development and testing of disinfectants, antiseptics, and other products used to control the spread of infectious diseases.
The purpose of a microbial challenge test is to determine the minimum concentration or exposure time needed to inhibit or kill microorganisms. This is achieved by exposing the test material or product to a known quantity of microorganisms and measuring their growth or survival rates. The test results allow researchers to assess the efficacy of different formulations and make informed decisions regarding their use.
In a typical microbial challenge test, a sample of the test material is inoculated with a high concentration of microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi. The sample is then incubated under controlled conditions for a specified period of time. After incubation, the number of viable microorganisms in the sample is determined using various techniques, such as colony counting or turbidity measurements. The results are compared to those of a control sample that was not treated with the test material, allowing researchers to determine the extent of microbial inhibition or killing.
Microbial challenge tests are important in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of antimicrobial products. They provide valuable data on the ability of these products to prevent the transmission of pathogens and promote public health. By evaluating their performance under controlled laboratory conditions, researchers can make informed decisions about the use and regulation of antimicrobial agents, contributing to the development of effective strategies for infection control.
Microbial Challenge Test: A Comprehensive Guide
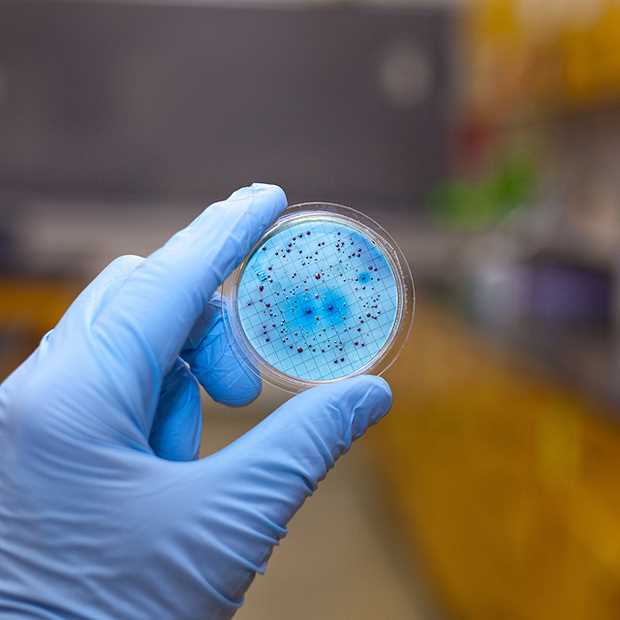
Microbial challenge tests are a critical part of ensuring the safety and efficacy of various products, especially in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. These tests help determine the ability of a product to withstand exposure to microbial contamination, providing important information about its overall quality and effectiveness. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key aspects of microbial challenge testing, including its purpose, methodology, and key considerations.
Purpose: The primary purpose of a microbial challenge test is to assess the ability of a product to resist or inhibit microbial growth. Microorganisms can pose a significant risk to the safety and efficacy of products, as they can cause spoilage, produce toxins, or lead to infections in consumers. By subjecting a product to a controlled microbial challenge, manufacturers can evaluate its ability to withstand these potential threats and make informed decisions regarding formulation and preservation.
Methodology: The methodology of a microbial challenge test typically involves the inoculation of a product with a known quantity of specific microorganisms. These microorganisms are carefully selected based on their relevance to the intended use of the product and their ability to survive or proliferate under certain conditions. The product is then stored under specific environmental conditions, and samples are regularly evaluated for microbial growth. This allows manufacturers to determine the effectiveness of preservatives and antimicrobial agents present in the product.
Key Considerations: When conducting a microbial challenge test, several key considerations must be taken into account. These include selecting appropriate microorganisms and challenge conditions, ensuring the test is representative of real-world usage conditions, and interpreting the results accurately. Additionally, it is essential to adhere to regulatory guidelines and industry standards to ensure the validity and reliability of the test results.
Conclusion: Microbial challenge testing is a crucial step in the development and manufacturing of various products. By subjecting products to controlled microbial challenges, manufacturers can assess their ability to resist or inhibit microbial growth, thereby ensuring their safety and efficacy. By following the principles outlined in this comprehensive guide, manufacturers can conduct reliable and informative microbial challenge tests that contribute to the overall quality and integrity of their products.
The Significance of Microbial Challenge Test in Product Safety
The microbial challenge test is a crucial step in ensuring the safety and quality of various products, particularly those that are intended for human consumption or use. This test is designed to evaluate the ability of a product to resist or inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and molds. By subjecting the product to a controlled contamination with known strains of microorganisms, the test provides valuable information about its effectiveness in preventing microbial contamination during storage and use. This information is vital in safeguarding consumer health and preventing potential outbreaks of foodborne illnesses or infections.
One of the primary objectives of the microbial challenge test is to assess the antimicrobial properties of a product. This includes determining its ability to inhibit the growth of common pathogens, as well as any specific microorganisms that may be of concern in the given product’s intended application. Through this evaluation, manufacturers can identify any weaknesses or limitations in their product’s formulation or production process, allowing them to make necessary adjustments to ensure its effectiveness in preventing microbial contamination. This proactive approach is essential in maintaining product safety and minimizing the risk of adverse health effects for consumers.
The microbial challenge test also plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Health authorities, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), often require manufacturers to conduct this test as part of their product approval process. By demonstrating that their product meets the required standards for microbial resistance, manufacturers can ensure compliance with regulatory guidelines and gain market approval. Additionally, the results of the microbial challenge test can be used to establish appropriate storage and handling instructions for the product, further ensuring its safety throughout its shelf life.
In conclusion, the microbial challenge test is a critical component of ensuring the safety of various products. Its evaluation of a product’s ability to resist microbial contamination provides valuable information for manufacturers to enhance their formulations and production processes. Moreover, it is integral to regulatory compliance and market approval. By undergoing this test, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to product safety and consumer well-being.
Understanding Microbial Challenge Test Methodology
A microbial challenge test is a procedure used to assess the efficacy of antimicrobial products or treatments against specific microorganisms. It involves exposing the microorganisms to the product or treatment and measuring their ability to survive or grow. This test methodology is crucial in evaluating the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents and ensuring their safety for the intended use.
One of the key aspects of understanding microbial challenge test methodology is choosing the appropriate microorganisms for testing. The selected microorganisms should represent the target pathogens that the product or treatment is designed to eliminate or control. This ensures that the results obtained from the test accurately reflect the real-world effectiveness of the antimicrobial agent.
The microbial challenge test methodology typically involves the following steps:
- Inoculation: The chosen microorganisms are introduced onto the surface or into the substance being tested. Care must be taken to ensure an even distribution of the microorganisms.
- Exposure: The inoculated surface or substance is then exposed to the antimicrobial product or treatment. This can be done through direct application, immersion, or other appropriate methods.
- Incubation: The treated surface or substance is incubated under controlled conditions for a specified period of time to allow the microorganisms to grow or survive.
- Sampling: Samples are collected from the treated surface or substance to determine the presence and viability of the microorganisms. This can be done using swabbing, rinsing, or other appropriate sampling methods.
- Analysis: The collected samples are then analyzed, usually through microbiological techniques, to quantify and characterize the surviving or growing microorganisms.
The results obtained from microbial challenge tests provide valuable information on the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents and their ability to control the growth of specific microorganisms. This information is critical in determining the suitability of the product or treatment for use in various applications, such as healthcare settings, food processing facilities, and consumer products.
Common Microorganisms Used in Microbial Challenge Test
In microbial challenge testing, various microorganisms are used to evaluate the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents or the resistance of materials against microbial growth. These microorganisms are carefully selected based on their relevance to the intended application and their ability to survive and thrive under certain conditions.
Bacterial Strains:
Staphylococcus aureus: This gram-positive bacterium is commonly used in microbial challenge testing due to its ability to form biofilms and its association with various infections. It is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections and has been used to evaluate the efficacy of antimicrobial coatings and medical devices.
Escherichia coli: This gram-negative bacterium is often used as a representative of enteric bacteria in microbial challenge testing. It is commonly found in the gut and can cause urinary tract infections and gastrointestinal illnesses. It is used to assess the effectiveness of disinfectants and to evaluate the resistance of materials to bacterial contamination.
Fungal Strains:

Aspergillus niger: This fungus is widely used in microbial challenge testing due to its ability to grow on a variety of substrates and its association with food spoilage. It is commonly used to evaluate the antifungal properties of materials and the efficacy of preservatives.
Candida albicans: This yeast-like fungus is commonly found in the human body and can cause opportunistic infections. It is often used in microbial challenge testing to assess the effectiveness of antifungal agents and the resistance of materials to fungal growth.
Viral Strains:
Enterovirus: This group of viruses includes various strains that cause illnesses such as gastrointestinal infections and respiratory diseases. Enteroviruses are commonly used in microbial challenge testing to evaluate the efficacy of disinfectants and antiviral agents.
Influenza virus: This highly contagious virus is known for causing seasonal flu outbreaks. It is often used in microbial challenge testing to assess the effectiveness of antiviral agents and the resistance of materials to viral contamination.
The choice of microorganisms for microbial challenge testing should be based on their relevance to the intended application and their ability to represent real-world microbial challenges. By carefully selecting and testing these microorganisms, researchers can assess the efficacy and safety of antimicrobial agents, disinfectants, and materials in various settings.
Interpreting Microbial Challenge Test Results: What They Mean for Product Safety
Microbial challenge tests are an important tool used in the evaluation of product safety. These tests are designed to simulate real-world conditions and determine how well a product can resist or eliminate microorganisms. The results of these tests provide valuable information about the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents and the potential risks associated with a product.
When interpreting microbial challenge test results, it is important to consider the specific microorganisms used in the test, as well as the conditions in which the product was tested. Different microorganisms have different levels of resistance, and products may perform differently under different environmental conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the relevance of the specific test organisms and conditions to the intended use of the product.
Key factors to consider when interpreting microbial challenge test results include:
- The type and concentration of microorganisms used in the test
- The specific antimicrobial agents or strategies employed by the product
- The temperature, pH, and moisture levels during the test
- The duration of the test
- The intended use and expected exposure of the product to microorganisms
Based on the results of a microbial challenge test, product safety can be assessed. If a product demonstrates effective antimicrobial activity against the test microorganisms and conditions, it suggests that the product is likely to be safe and effective in real-world scenarios. On the other hand, if a product fails to eliminate or inhibit the growth of the test microorganisms, it may indicate a potential risk of microbial contamination or infection when used in real-life situations.
In conclusion, interpreting microbial challenge test results requires careful consideration of the specific test conditions and organisms used. By understanding the relevance of the results to the intended use of the product, manufacturers and regulatory authorities can make informed decisions regarding product safety.
The Importance of Microbial Challenge Test in Different Industries
The microbial challenge test plays a crucial role in various industries, ensuring the safety and quality of products. It involves exposing the product to a specific level of microorganisms to evaluate its ability to resist microbial growth. This test is especially important in industries that produce perishable goods, such as food and pharmaceuticals, where microbial contamination can have severe consequences.
In the food industry, microbial challenge testing is vital to prevent foodborne illnesses. By subjecting the product to different types of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeast, and mold, companies can assess its resistance and shelf life. This helps in determining the appropriate storage conditions and packaging materials to minimize microbial growth. Moreover, accurate microbial challenge testing ensures compliance with regulatory standards and enhances consumer trust in the product.
The pharmaceutical industry also heavily relies on microbial challenge testing to ensure the safety and efficacy of drugs and medical devices. Products intended for internal or external use need to be free from harmful bacteria and other microorganisms. Microbial challenge tests help in evaluating the effectiveness of preservatives and antimicrobial agents present in these products. Additionally, this testing is crucial in detecting microbial contamination during manufacturing processes, preventing potential outbreaks or health risks.
In cosmetic and personal care industries, microbial challenge testing is essential to ensure the safety and stability of products. Cosmetics and personal care products come into direct contact with the skin, making them susceptible to microbial contamination. This testing helps in assessing the effectiveness of preservatives and antimicrobial agents to combat microbial growth. It also aids in identifying potential sources of contamination, such as inadequate manufacturing processes or improper storage conditions.
In conclusion, microbial challenge testing is of utmost importance in different industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. It helps in evaluating the resistance of products to microbial growth, ensuring their safety, quality, and compliance with regulatory standards. By conducting this testing, companies can prevent health risks, enhance consumer trust, and maintain the integrity of their products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, conducting a microbial challenge test is essential for assessing the efficacy of antimicrobial agents and ensuring product safety. By following best practices, such as selecting appropriate test organisms, establishing realistic challenge conditions, and using validated methods for enumeration, researchers can obtain reliable and meaningful data.
It is important to carefully design the experimental protocol, including the selection of appropriate microorganisms and their inoculation level, as well as the choice of sampling points and analytical methods. Additionally, maintaining good laboratory practices, such as proper sterilization techniques and aseptic handling procedures, is crucial to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results.
Furthermore, collaboration between microbiologists, formulation scientists, and regulatory experts is beneficial in designing and interpreting microbial challenge tests. This interdisciplinary approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of the product’s microbiological safety profile and helps in making informed decisions regarding its formulation and use.
In summary, the best practices for conducting a microbial challenge test include:
- Selection of appropriate test organisms
- Establishment of realistic challenge conditions
- Validation of enumeration methods
- Careful design of experimental protocols
- Maintenance of good laboratory practices
- Collaboration between experts
Following these practices will not only ensure reliable and meaningful results but also contribute to the development of effective antimicrobial products and the protection of public health.
Q&A:
What is a microbial challenge test?
A microbial challenge test is a laboratory procedure used to determine the effectiveness of a disinfectant or antimicrobial agent against specific microorganisms. It involves exposing the microorganisms to the agent under specified conditions and measuring their survival or reduction.
What are the main purposes of a microbial challenge test?
The main purposes of a microbial challenge test are to evaluate the efficacy of disinfectants or antimicrobial agents, to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) or minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of an agent, and to compare the effectiveness of different products.
What are some best practices for conducting a microbial challenge test?
Some best practices for conducting a microbial challenge test include properly preparing and standardizing the test organisms, ensuring the test conditions mimic real-world scenarios as closely as possible, using appropriate controls and validation procedures, and accurately measuring and documenting the results.
What factors should be considered when selecting test organisms for a microbial challenge test?
When selecting test organisms for a microbial challenge test, factors such as their relevance to the intended use of the disinfectant or antimicrobial agent, their resistance to the agent, their ability to survive and multiply under the test conditions, and the availability of reference strains should be considered.
What are some potential challenges or limitations of microbial challenge tests?
Some potential challenges or limitations of microbial challenge tests include the variability of test results due to factors such as inoculum preparation and test conditions, the difficulty in accurately simulating real-world conditions, the inability to test all possible microorganisms and their interactions, and the ethical considerations of using pathogenic microorganisms.
What is a microbial challenge test?
A microbial challenge test is a laboratory test conducted to determine the effectiveness of certain antimicrobial agents or processes in reducing or eliminating microbial contamination. It involves intentionally exposing a product or material to a known population of microorganisms and evaluating the survival or reduction of these microorganisms under specified conditions.