Understanding how muscles and bones work together is essential for gaining insight into how our bodies function. With the help of the Muscles and Bones Gizmo, students can explore the relationship between these two essential components of our bodies.
Designed as an interactive learning tool, the Muscles and Bones Gizmo provides students with a virtual laboratory where they can simulate various scenarios and study the effects on muscles and bones. Through a series of experiments and observations, students can discover how muscles enable movement and how bones provide support and protection.
One of the key questions that the Muscles and Bones Gizmo addresses is how muscles interact with bones to produce movement. By manipulating the variables within the Gizmo, students can observe how different muscle contractions and bone structures affect a range of movements, from simple actions like walking to more complex tasks like lifting weights or playing sports.
The Muscles and Bones Gizmo also offers a platform for students to understand the importance of proper nutrition and exercise in maintaining healthy muscles and bones. By exploring different nutritional factors and exercise routines, students can see firsthand how these variables impact muscle strength and bone density.
Muscles and Bones Gizmo Answers
The Muscles and Bones Gizmo is a helpful tool for learning about the human body’s skeletal and muscular systems. This interactive online simulation allows users to explore how different muscles and bones work together to create movement and support the body’s structure.
One key concept that the Gizmo addresses is the relationship between muscles and bones. It demonstrates that muscles are attached to bones by tendons, and when a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone, causing movement. This understanding is essential for understanding how muscles and bones work together in activities such as walking, running, and lifting objects.
Key answers that can be explored with the Muscles and Bones Gizmo include:
- How do muscles and bones work together in different parts of the body? – By using the Gizmo, students can examine how muscles and bones work together in various parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, and back. They can manipulate the muscles’ contractions and observe how these movements affect the bones.
- What happens when a bone or muscle is injured? – The Gizmo can also be used to simulate injuries to bones and muscles. Students can examine how different injuries, such as fractures or sprains, impact the movement and function of the affected area. This can help them understand the importance of proper care and rehabilitation for injured muscles and bones.
- How does exercise and conditioning impact muscles and bones? – The Gizmo allows students to explore the effects of exercise and conditioning on muscles and bones. By manipulating the intensity and frequency of muscle contractions, students can observe how regular exercise can strengthen and enhance the functioning of muscles and bones.
Overall, the Muscles and Bones Gizmo provides an engaging and interactive platform for students to learn about the relationship between muscles and bones. By experimenting with different movements and scenarios, students can gain a deeper understanding of how these systems work together to support the human body’s structure and facilitate movement.
Understanding the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system is a complex network of muscles, bones, and connective tissues that work together to provide support, movement, and protection for the body. This intricate system allows us to perform a wide range of activities, from simple tasks like picking up objects to more complex movements like running or dancing.
At the core of the musculoskeletal system are the bones, which serve as the framework for the body. The bones not only provide structure and support, but they also act as a storage site for minerals like calcium and phosphorus. Additionally, bone marrow inside the bones produces red and white blood cells, which are crucial for immune function and oxygen transport.
Surrounding the bones are the muscles, which are responsible for generating movement. Muscles are made up of long fibers that contract and relax to produce force. They are attached to the bones via tendons, which act as connectors between muscle and bone. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone, causing movement at the joint.
- The musculoskeletal system also includes other connective tissues like ligaments, which connect bones to other bones and help stabilize joints, and cartilage, which acts as a cushion between bones.
- The musculoskeletal system is constantly adapting to the demands placed on it. Through regular exercise and physical activity, the muscles and bones can become stronger and more resilient, while a sedentary lifestyle can lead to muscle weakness and bone loss.
- Injuries to the musculoskeletal system, such as fractures or sprains, can be painful and limit mobility. Proper care and rehabilitation are essential for healing and restoring function.
Understanding the musculoskeletal system is important for maintaining overall health and well-being. By taking care of our muscles and bones through proper nutrition, exercise, and preventative measures, we can support a strong and functional musculoskeletal system that allows us to live an active and fulfilling life.
Anatomy and Function of Muscles
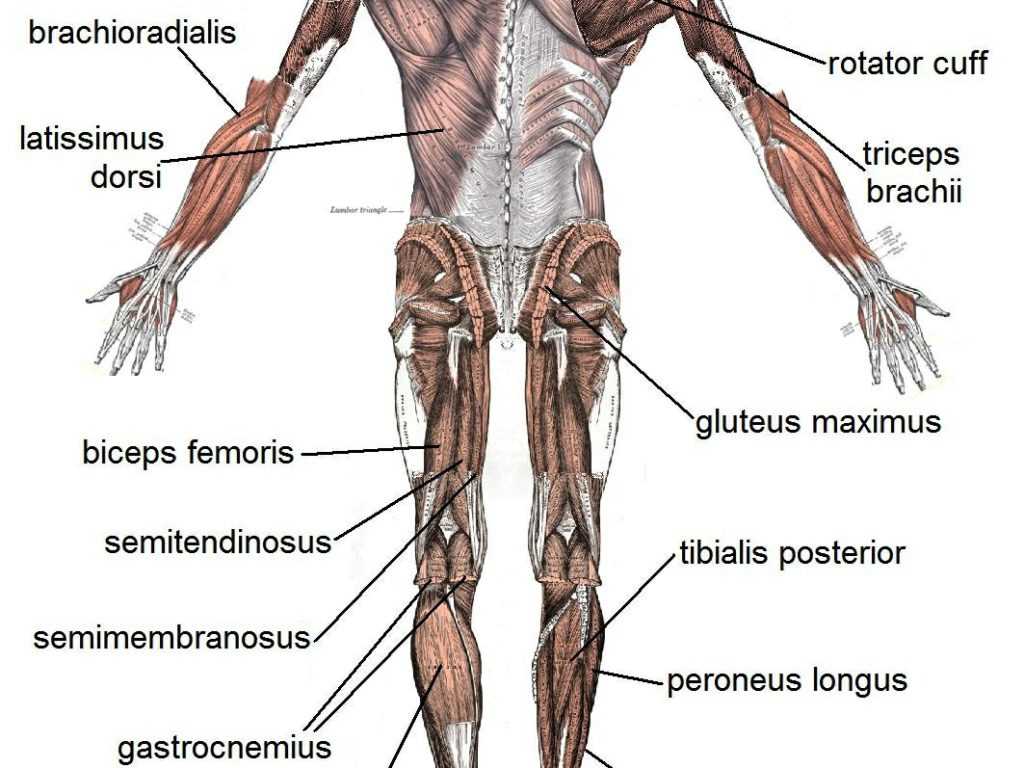
Muscles play a vital role in the movement and stability of the human body. They are responsible for generating force, controlling joint movement, and maintaining posture. Understanding their anatomy and function is essential for athletes, healthcare professionals, and individuals seeking to improve their physical fitness.
Muscle Types
There are three main types of muscles in the human body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and are responsible for voluntary movement, such as walking or lifting weights. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and control its involuntary contractions. Smooth muscles are located in the walls of organs, blood vessels, and the digestive system, and their contractions are also involuntary.
Anatomy of a Muscle
A skeletal muscle is made up of bundles of muscle fibers surrounded by connective tissue. At each end, the muscle attaches to a bone via tendons. Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils, which contain filaments called actin and myosin. During muscle contraction, these filaments slide past each other, generating force. The size and arrangement of muscle fibers contribute to a muscle’s strength and function.
Muscle Functions
Muscles allow us to perform a wide range of movements, from running and jumping to fine motor skills like writing. They work in pairs or groups to create opposing forces on either side of a joint, enabling movement and stabilization of the body. Additionally, muscles provide protection to internal organs and help regulate body temperature through heat production during exercise.
Overall, muscles are crucial for the functioning and performance of the human body. Understanding their anatomy and function can help optimize athletic performance, prevent injuries, and improve overall physical health.
Types of Bones and Their Functions
The human skeleton is made up of different types of bones, each with its own unique shape and function. These bones work together to provide support, protect the internal organs, and allow for movement and locomotion.
Long Bones
Long bones are characterized by their elongated shape and include bones such as the femur, humerus, and phalanges. These bones serve as levers and provide support and mobility. They also play a role in the production of red and white blood cells in the bone marrow.
Short Bones
Short bones are typically cuboidal in shape and are found in the wrists and ankles. These bones provide stability and weight-bearing support. They also allow for a wide range of movements and help absorb shock.
Flat Bones
Flat bones, as the name suggests, are flat and thin and include bones such as the skull, scapula, and ribs. These bones protect vital organs and provide a surface for muscle attachment. They also play a role in the production of red and white blood cells.
Irregular Bones
Irregular bones have a unique shape that does not fit into the other categories. Examples include the vertebrae and facial bones. These bones provide support, protect delicate structures, and allow for various movements, depending on their location.
Sesamoid Bones
Sesamoid bones are small, rounded bones embedded within tendons and are found near joints. The patella (kneecap) is an example of a sesamoid bone. These bones increase the efficiency of muscle movement and provide protection to the tendons.
Functions of Bones
Bones have multiple functions in the human body. They provide structural support, allowing the body to maintain its shape and posture. Bones also protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs. They act as a storehouse for minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for various bodily functions. Additionally, bones are involved in the production of red and white blood cells in the bone marrow. Finally, bones are essential for movement, as they provide attachment sites for muscles and serve as levers for locomotion.
Common Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders are conditions that affect the muscles, bones, joints, and connective tissues of the body. These disorders can cause pain, stiffness, weakness, and limited mobility. They can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life and daily activities.
One common musculoskeletal disorder is osteoarthritis, which is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. This can result in pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Another common musculoskeletal disorder is rheumatoid arthritis. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. This can lead to joint inflammation, pain, and deformity. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the hands, wrists, and feet.
Back pain is also a common musculoskeletal disorder that can be caused by various factors, such as muscle strains, herniated discs, or spinal conditions. It can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. Back pain can affect the upper, middle, or lower back, and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness or tingling in the legs.
Osteoporosis is another musculoskeletal disorder characterized by low bone density and an increased risk of fractures. It commonly affects older adults, especially women after menopause. Osteoporosis can weaken the bones to the point where they become fragile and prone to breaking, even with minor trauma. The most common sites for fractures associated with osteoporosis are the spine, wrist, and hip.
These are just a few examples of common musculoskeletal disorders. It’s important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of any musculoskeletal disorder, as early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage.
Importance of Exercise for Muscles and Bones
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and strength of our muscles and bones. Engaging in physical activity helps to promote muscle growth, improve bone density, and enhance overall physical fitness. By stimulating the muscles and bones, exercise helps to maintain their function and prevent the onset of various musculoskeletal conditions.
One of the key benefits of exercise for muscles and bones is the promotion of muscle growth and strength. When we subject our muscles to physical stress through activities such as weightlifting or resistance training, it causes small muscle fibers to tear. The body then repairs these fibers, resulting in increased muscle mass and strength. This process, known as muscle hypertrophy, helps to improve overall muscle function and power.
Exercise also plays a vital role in improving bone health and density. Weight-bearing exercises, including walking, running, or dancing, help to stimulate bone formation and strengthen bones. These activities put stress on the bones, forcing them to adapt and become stronger. Regular exercise not only helps to maintain bone density but also reduces the risk of osteoporosis and fractures in later life.
Moreover, exercise helps to improve overall physical fitness, agility, and flexibility. It enhances the coordination between muscles and bones, allowing for smooth and efficient movement. Regular physical activity also improves balance and stability, reducing the risk of falls and injuries. By keeping our muscles and bones strong and healthy, exercise enables us to lead an active and independent lifestyle as we age.
In conclusion, exercise is of utmost importance for the health and well-being of our muscles and bones. It promotes muscle growth, improves bone density, and enhances overall physical fitness. By incorporating regular exercise into our daily routine, we can ensure the long-term health and strength of our musculoskeletal system. So, let’s make exercise a priority and reap the numerous benefits it offers for our muscles and bones.
Using Gizmos to Explore Muscles and Bones
The study of muscles and bones is essential for understanding the human body and how it functions. With the help of Gizmos, interactive online simulations, students can engage in hands-on learning experiences and explore concepts related to muscles and bones in a virtual environment.
Gizmos offer an interactive and engaging way for students to learn about the structure and function of muscles and bones. These simulations allow students to manipulate variables, conduct experiments, and analyze data to gain a deeper understanding of the concepts being studied.
By using Gizmos, students can visualize the skeletal system and observe how bones function and interact with each other. They can also explore the different types of muscles and understand their roles in movement and stability. The simulations enable students to see the effects of muscle contraction on bone movement and explore the relationship between muscles and joints.
Furthermore, Gizmos provide students with the opportunity to investigate how external factors such as gravity, weight, and resistance affect muscle and bone activity. They can explore the impact of exercise and physical activity on muscle growth and strength. By manipulating variables in the simulations, students can observe the effects of different exercises on muscle fibers and bone density.
In conclusion, using Gizmos to explore muscles and bones offers students a unique and interactive learning experience. These simulations allow students to engage in hands-on exploration, visualize complex concepts, and deepen their understanding of how muscles and bones function. By providing a virtual platform for experimentation and analysis, Gizmos supplement traditional classroom learning and enhance students’ comprehension of the human body.