The neuron is a fundamental building block of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Understanding its function is crucial for understanding how the brain and nervous system work. In this POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) exercise, we will explore the different aspects of neuron function and gain a deeper understanding of this complex process.
One key aspect of neuron function is the transmission of electrical signals, known as action potentials. These electrical impulses allow neurons to communicate with each other and ultimately control our thoughts, movements, and behaviors. During an action potential, ions such as sodium and potassium move in and out of the neuron’s membrane, creating a rapid change in electrical charge. This movement of ions is carefully regulated and follows a specific pattern, allowing signals to be transmitted efficiently.
In addition to electrical signals, neurons also communicate through chemical signals called neurotransmitters. These are molecules that are released by one neuron and bind to receptors on another, allowing for the transmission of information. Different neurotransmitters have different effects on the receiving neuron, either exciting or inhibiting its activity. The balance of these neurotransmitters is crucial for maintaining normal brain function and can play a role in various neurological disorders.
By studying the function of neurons, researchers and medical professionals can gain insights into the underlying causes of neurological diseases and develop new treatments. POGIL exercises like this one are designed to encourage active learning and critical thinking, allowing students to engage with the material and develop a deeper understanding of complex topics. By working through this POGIL exercise and using the provided answer key, students can enhance their knowledge of neuron function and neuroscience as a whole.
Overview of Neuron Function POGIL Answer Key
Neuron function is a complex and vital process that allows for the transmission of signals within the nervous system. In order to understand neuron function, it is important to explore the key concepts and principles outlined in the Neuron Function POGIL answer key.
The Neuron Function POGIL answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the various components of neurons and their functions. It explains the structure and function of dendrites, axons, and synapses, which are essential for the transmission of electrical signals between neurons. The answer key also delves into the role of neurotransmitters in facilitating communication between neurons.
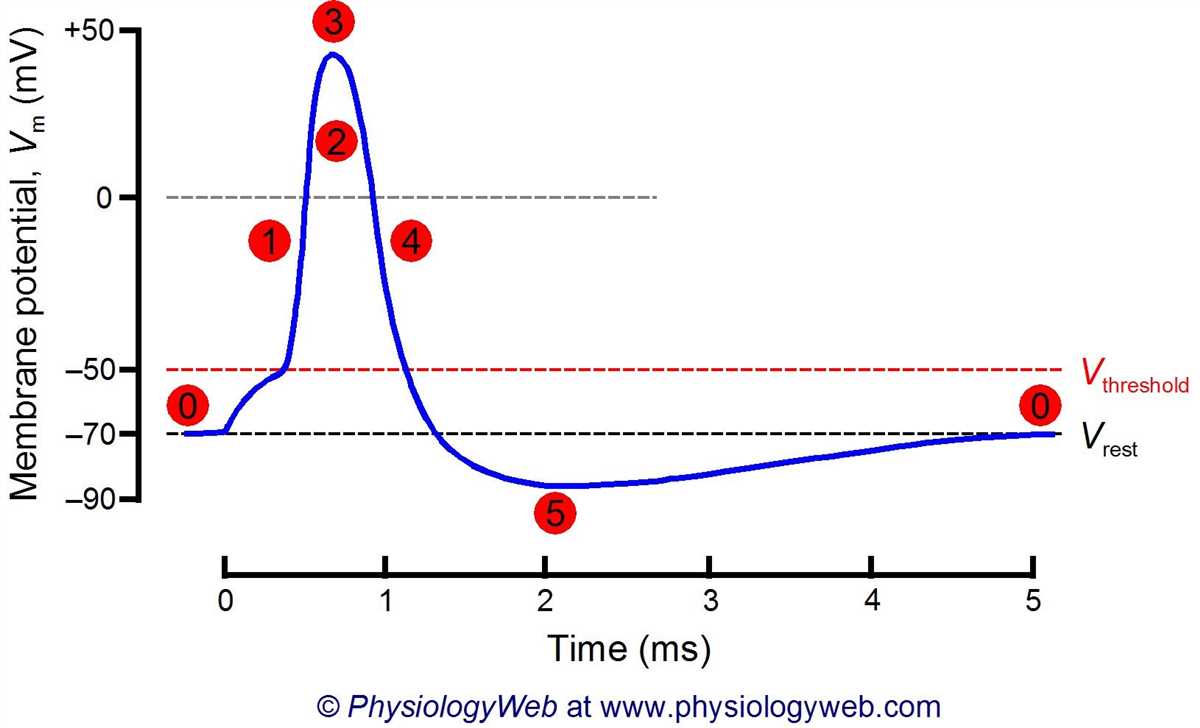
One important concept discussed in the answer key is the process of action potential. Action potential refers to the rapid change in electrical potential that occurs when a neuron is stimulated. The key outlines the different stages of action potential, including depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization, and explains how these changes in electrical potential allow for the transmission of signals across neurons.
The answer key also covers the concept of synaptic transmission, which is the process by which signals are passed from one neuron to another. It explains the role of neurotransmitters in facilitating this transmission and discusses the importance of synaptic plasticity, or the ability of synapses to change and adapt over time.
Overall, the Neuron Function POGIL answer key provides a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles of neuron function. It serves as a valuable resource for students and educators alike, helping them to grasp the intricate processes involved in neuron function and the transmission of signals within the nervous system.
Understanding Neuron Structure
The structure of a neuron is crucial for understanding its function. Neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. They have a unique structure that is essential for their role in processing and transmitting information.
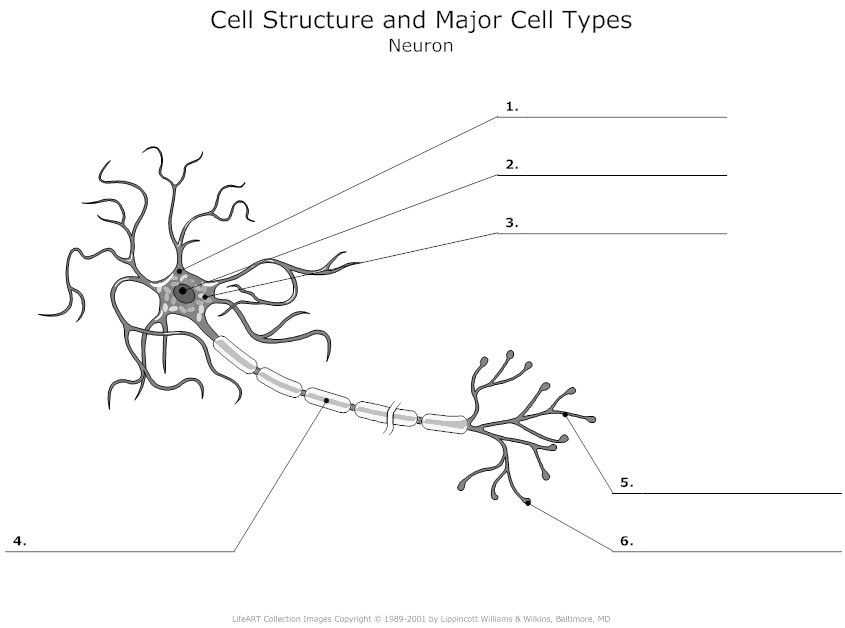
A neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axon. The cell body, also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the neuron’s metabolism and maintenance. It is the main control center of the neuron.
Dendrites are branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors. They play a vital role in the communication between neurons by collecting and integrating incoming signals. These signals are then transmitted to the cell body for further processing.
The axon is a long, single extension that carries the neuron’s electrical signal, known as the action potential, away from the cell body. The axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer and helps increase the speed of signal transmission. At the end of the axon, there are terminal branches called synaptic terminals that form connections, known as synapses, with other neurons or target cells.
The structure of a neuron allows for the efficient transmission and processing of information. The dendrites receive signals from other neurons, which are then integrated in the cell body. If the integrated signals reach a certain threshold, an action potential is generated and travels down the axon. The action potential then triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the synaptic terminals, which transmit the signal to the next neuron or target cell.
Understanding the structure of a neuron is essential for comprehending its function in the nervous system. Each component plays a specific role in the transmission and processing of information, allowing for the complex network of communication that occurs within the brain and throughout the body.
Exploring Neuron Communication
Neurons are specialized cells in the nervous system that play a crucial role in transmitting information from one part of the body to another. Neuron communication involves the transmission of electrical signals, known as action potentials, across the neuron and the release of chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, at specialized junctions called synapses.
Neurons communicate with each other through a process called synaptic transmission. When an action potential reaches the end of one neuron, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synapse. These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, causing a change in its electrical state. This change in electrical state can either excite or inhibit the receiving neuron, depending on the type of neurotransmitter and the specific receptors involved.
Excitatory neurotransmitters are those that increase the likelihood of the receiving neuron firing an action potential, while inhibitory neurotransmitters decrease the likelihood of firing. The balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals is crucial for maintaining the overall function and stability of the nervous system.
Neurons can also communicate through electrical synapses, where there is a direct flow of electrical current between neurons. These electrical synapses allow for rapid and synchronized communication between neurons, and are particularly important in coordinating activities in the brain and spinal cord.
Overall, the communication between neurons is a complex and highly regulated process that is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Understanding the intricacies of neuronal communication is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of brain function and can provide insights into the development of treatments for neurological disorders.
Roles of Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in the functioning of neurons and the transmission of signals throughout the nervous system. They are chemical messengers that allow communication between neurons and other cells, such as muscles or glands. Each neurotransmitter has a specific role and function in the nervous system.
Glutamate: Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of the brain to change and adapt in response to experience. Glutamate is involved in learning, memory, and cognition. It helps to regulate neuronal excitability and is essential for normal brain function.
GABA: GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It helps to regulate the balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals, preventing the overstimulation of neurons. GABA is involved in anxiety, sleep, and relaxation. It counteracts the effects of glutamate and helps to maintain a state of calmness.
Dopamine: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in reward and motivation. It plays a crucial role in the brain’s reward system, which is responsible for feelings of pleasure and reinforcement. Dopamine is associated with motivation, focus, and attention. It is also involved in movement, as a deficiency in dopamine can lead to motor symptoms seen in Parkinson’s disease.
Serotonin: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is involved in mood regulation and emotional well-being. It helps to regulate sleep, appetite, and digestion. Serotonin is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, as it plays a role in feelings of happiness and contentment. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to depression and other mood disorders.
Acetylcholine: Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in many functions throughout the body. It is involved in the activation of muscles, as well as cognitive processes such as attention, learning, and memory. Acetylcholine is also involved in the regulation of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions such as heart rate and digestion.
Overall, neurotransmitters are essential for normal brain function and play a crucial role in various processes, including cognition, emotion, and movement. Imbalances in neurotransmitter levels can have a significant impact on mental health and neurological disorders. Understanding the roles of different neurotransmitters can help in the development of treatments for these conditions.
Neuron Function in the Central Nervous System
Neurons are the basic functional units in the central nervous system (CNS). They are specialized cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. The CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord, and neurons play a crucial role in processing and transmitting information within these structures.
Structure of a Neuron: A typical neuron has three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the normal functioning of the cell. Dendrites are small branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them towards the cell body. The axon is a long, slender projection that carries the signals away from the cell body to other neurons or target tissues.
Neuron Function: The central function of neurons in the CNS is to transmit information in the form of electrical signals called action potentials. When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, it undergoes depolarization, which results in the generation of an action potential. The action potential then travels along the axon towards the target neuron or tissue, where it is received and decoded.
In conclusion, neuron function in the central nervous system is essential for the processing and transmission of information. Through their specialized structure and ability to generate and transmit electrical signals, neurons enable communication within the CNS and play a critical role in various cognitive and motor functions.
Neuron Function in the Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a complex network of nerves and ganglia that extends throughout the body, connecting the central nervous system (CNS) to various tissues and organs. Neurons play a crucial role in the transmission of information within the PNS, allowing for the coordination of sensory and motor functions.
One of the key functions of neurons in the PNS is to transmit sensory information from the body’s periphery to the CNS. These sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are specialized to detect different types of stimuli, such as touch, temperature, and pain. When stimulated, these neurons generate electrical signals, known as action potentials, which are then transmitted to the CNS for processing and interpretation.
The PNS also contains motor neurons, or efferent neurons, which transmit signals from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and other effector organs. These neurons enable voluntary and involuntary movements, allowing us to walk, talk, and perform various other actions. Motor neurons in the PNS receive signals from the CNS and transmit them to the target tissues, where they trigger the appropriate response.
Neurons in the PNS are supported by other types of cells, such as Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath that wraps around axons, providing insulation and enhancing the speed of signal transmission. In addition, satellite cells provide structural and functional support to neurons in the PNS, helping to maintain their health and integrity.
Overall, the function of neurons in the peripheral nervous system is crucial for coordinating sensory and motor activities throughout the body. By transmitting signals to and from the CNS, these neurons enable us to perceive and respond to our environment, ensuring our survival and well-being.
Applications of Neuron Function in Medical Research

Neuron function plays a crucial role in understanding and treating various medical conditions. This field of research has paved the way for numerous applications that have revolutionized the healthcare industry. Here are some key applications of neuron function in medical research.
1. Understanding Brain Disorders
Studying neuron function has significantly enhanced our understanding of brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. By examining the activity of neurons in affected individuals, researchers can identify abnormalities and develop targeted treatments.
2. Developing Therapies for Neurological Conditions
Neuron function research has provided valuable insights into the development of therapies for various neurological conditions. For example, deep brain stimulation, a technique that involves the use of electrical currents to modulate neuronal activity, has shown promising results in treating conditions like chronic pain and movement disorders.
3. Advancing Neural Imaging Techniques
Neuron function research has contributed to the development of advanced neural imaging techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). These imaging tools allow scientists to visualize and analyze the activity of neurons in the brain, enabling better diagnosis and treatment planning for neurological disorders.
4. Studying Cognitive Processes
Understanding neuron function has deepened our knowledge of cognitive processes such as learning, memory, and decision-making. By studying the activity of neurons during these processes, researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms and potentially develop interventions to improve cognitive function.
5. Facilitating Neuroprosthetics Development
Neuron function research has played a crucial role in the development of neuroprosthetics, which are devices that can replace or enhance the function of damaged or lost neurons. By understanding how neurons encode and transmit information, scientists can design prosthetic devices that can interface with the nervous system and restore functionality in individuals with spinal cord injuries or limb loss.
In conclusion, the study of neuron function has opened up new avenues for medical research and transformed our understanding and treatment of various medical conditions. From understanding brain disorders to developing innovative therapies and technologies, neuron function research continues to drive advancements in the field of medicine.