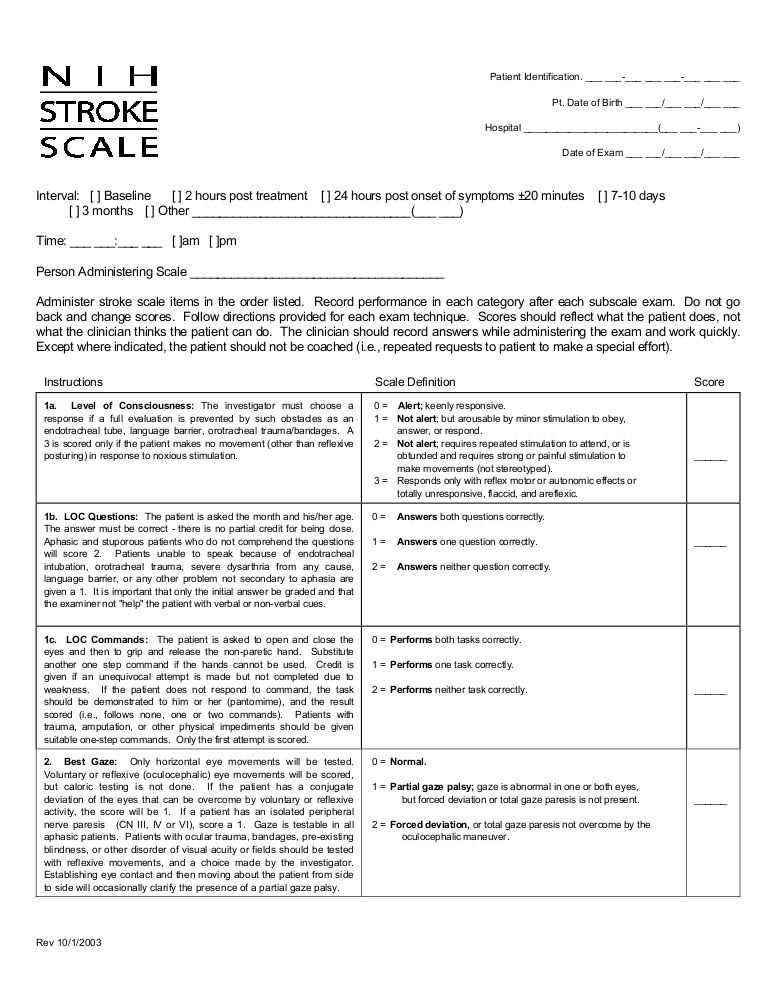
In clinical settings, evaluating the severity of neurological impairments is critical to determining appropriate care. The process involves assessing various cognitive, motor, and sensory functions to provide insights into the patient’s condition and guide treatment decisions.
Key Elements of Neurological Evaluation
During a neurological assessment, healthcare professionals examine a variety of factors that may indicate damage to the brain or nervous system. These factors include motor responses, cognitive abilities, speech patterns, and the ability to comprehend and follow instructions.
Motor Function and Coordination
Assessing the patient’s ability to perform coordinated movements provides key insights into the functioning of the motor system. Responses to commands such as lifting limbs or making specific gestures can reveal significant details about muscle control and coordination.
Speech and Comprehension
The ability to speak clearly and understand language is a vital aspect of any neurological exam. This area focuses on the patient’s ability to form words, express thoughts, and comprehend both spoken and written language.
Challenges in Accurate Scoring
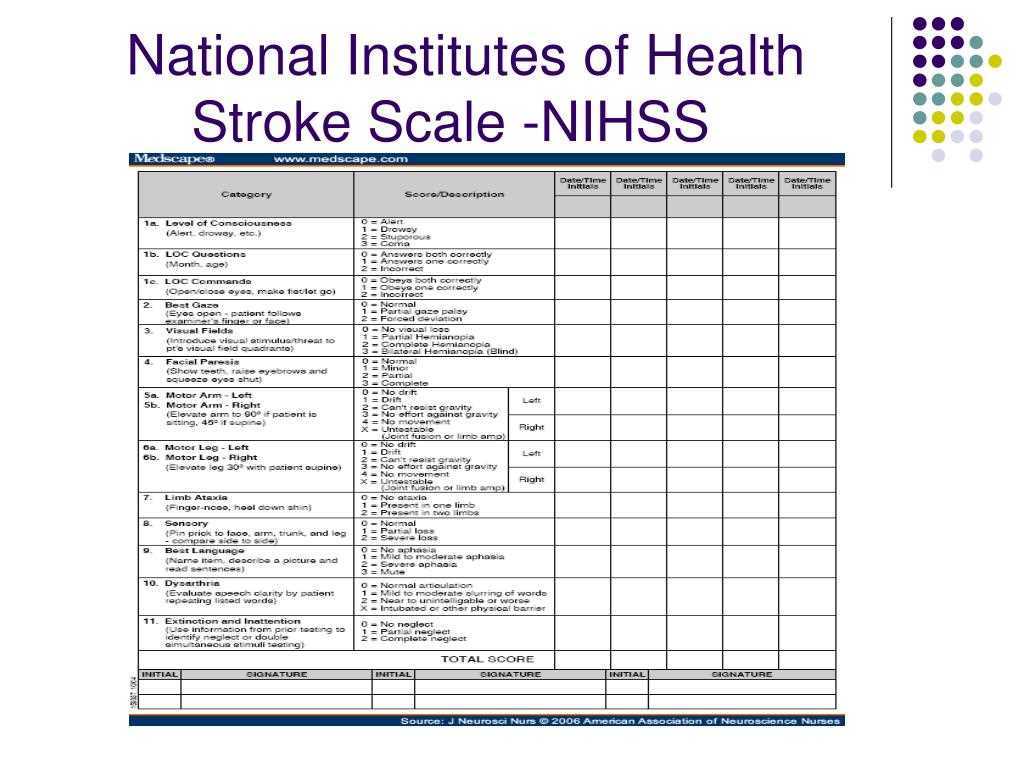
While evaluating a patient’s condition, challenges may arise due to factors like patient cooperation, cognitive limitations, and fluctuating health conditions. Inaccurate scoring can lead to incorrect treatment choices or misinterpretation of the severity of the impairment.
Influence of Patient Cooperation
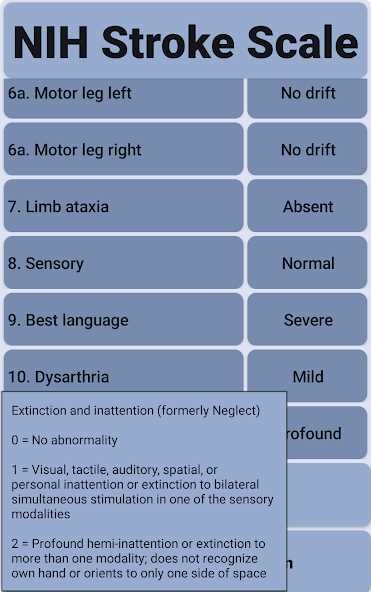
Patient cooperation is essential in obtaining reliable results. In some cases, patients may struggle to perform tasks or may not fully understand instructions, which could lead to discrepancies in the scoring process.
Fluctuating Symptoms and Conditions
Neurological conditions often present with symptoms that can vary throughout the day, depending on the severity and progression of the disorder. This can make it challenging to assess a patient’s true functional status at any given moment.
Implications for Treatment Decisions
The outcomes of a thorough neurological evaluation are crucial in guiding treatment decisions. Early and accurate identification of the nature and extent of neurological impairment allows healthcare providers to choose the most appropriate interventions, including medical therapies and rehabilitation strategies.
Determining the Need for Immediate Intervention
In cases of acute neurological decline, immediate intervention may be necessary. Prompt assessment can help determine whether the patient requires emergency treatment, surgical intervention, or intensive rehabilitation services.
Long-Term Care Planning
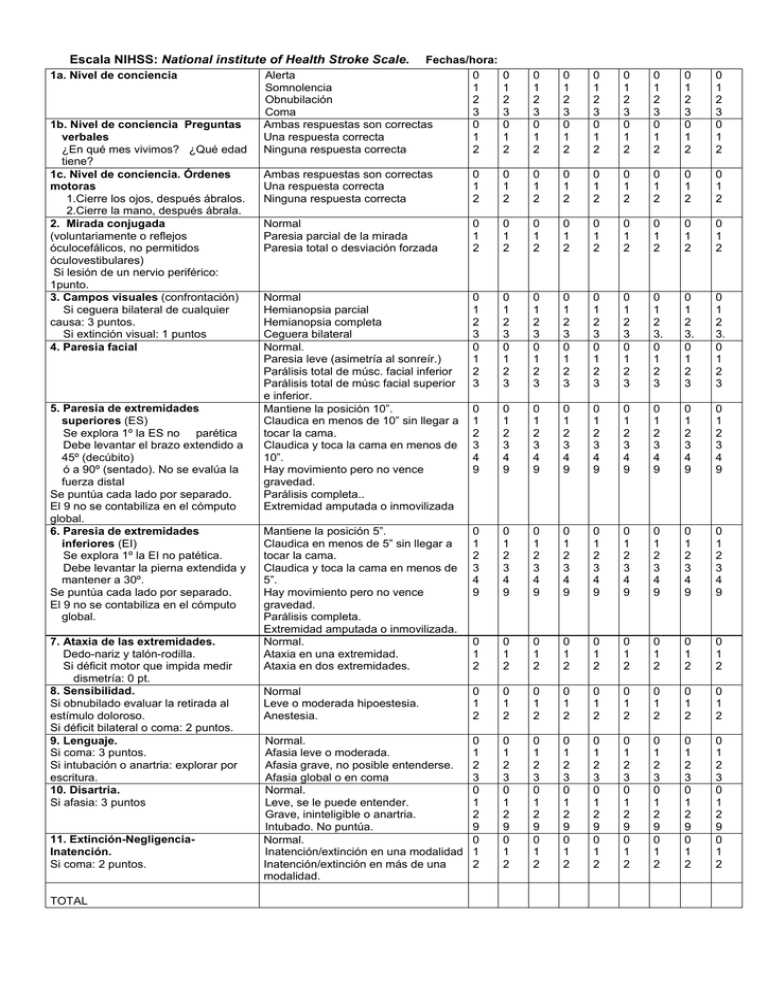
For patients with chronic or progressive conditions, understanding the long-term prognosis is vital in planning future care. A thorough evaluation allows providers to offer recommendations for ongoing monitoring and specialized care as needed.
Overview of Neurological Function Assessment
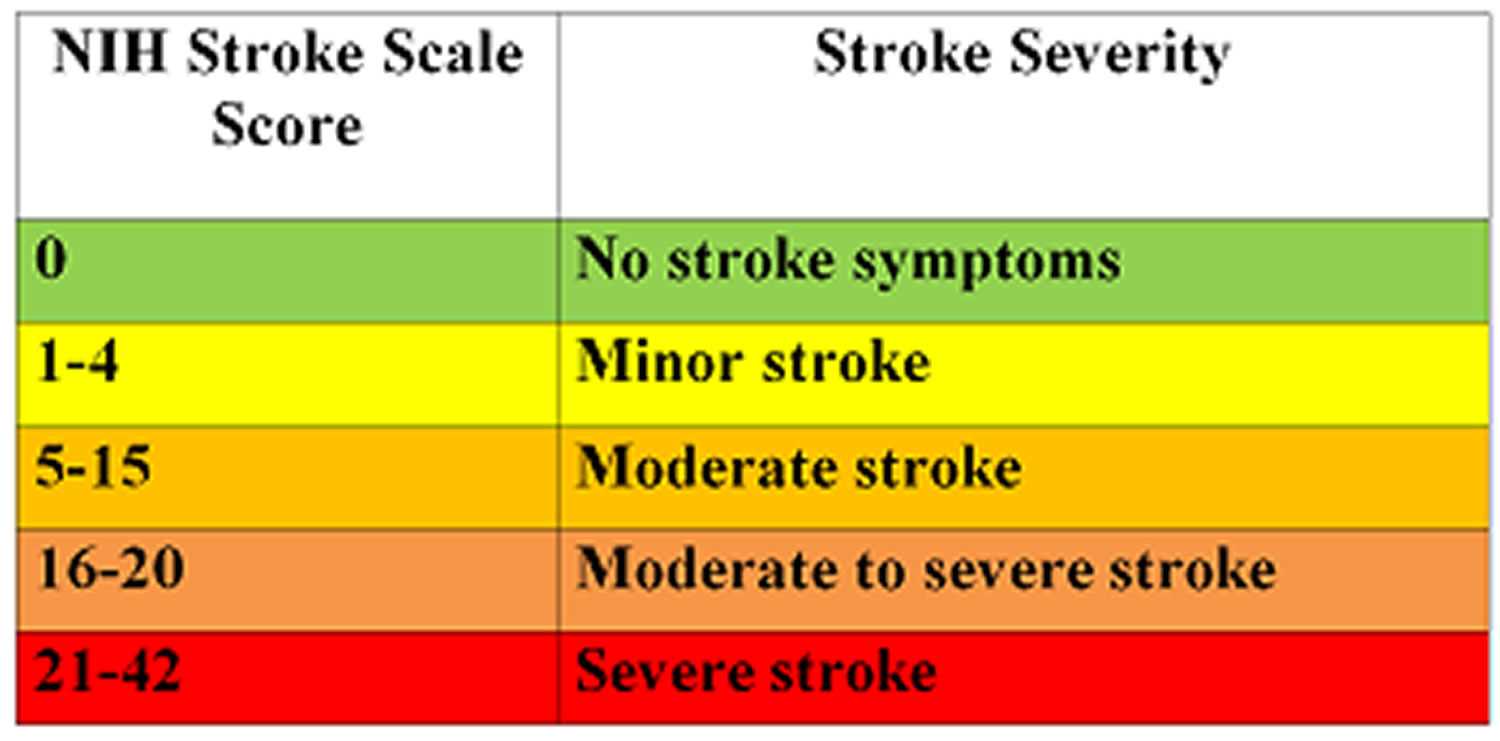
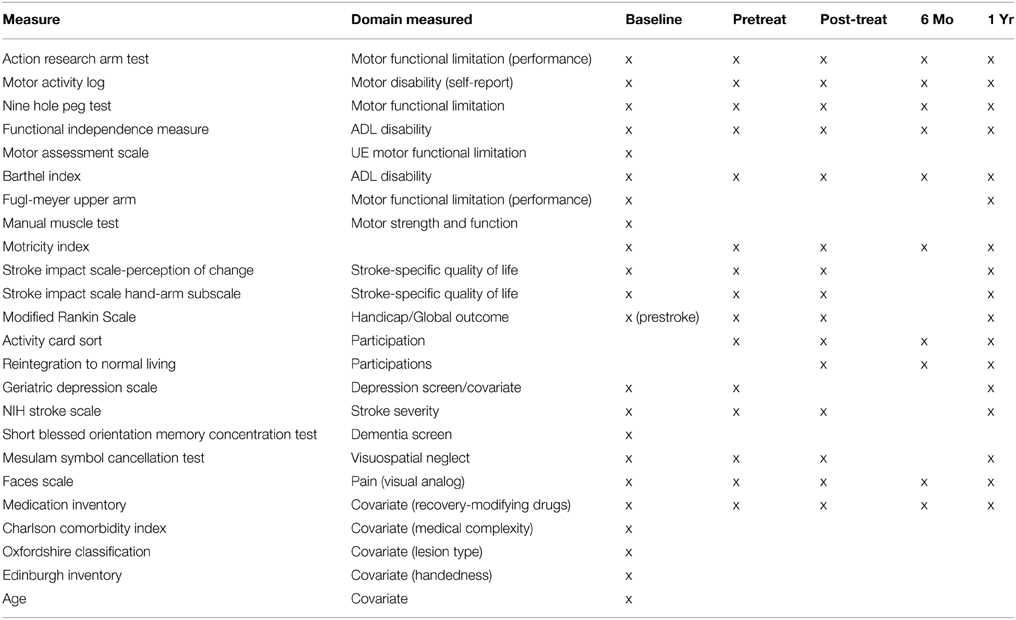
Accurately measuring the level of neurological impairment is essential for effective diagnosis and management of patients with brain injuries or neurological disorders. The evaluation process involves several components that help healthcare professionals assess the severity and progression of the patient’s condition, ensuring that appropriate interventions can be implemented in a timely manner.
One of the most important parts of this assessment is determining how well the patient can perform specific tasks, such as responding to questions, moving limbs, or recognizing familiar objects. These key elements are carefully examined to understand the extent of any damage or dysfunction in the nervous system.
Key Elements of Neurological Evaluation
The evaluation process includes testing a variety of cognitive, motor, and sensory abilities. These tests assess factors such as muscle strength, coordination, and cognitive functions like memory and comprehension. The results provide valuable insights into the patient’s current condition and guide healthcare providers in making informed decisions about treatment options.
How to Score Neurological Tests Accurately
Scoring the assessment accurately is crucial to ensure the patient receives the correct care. Scores are based on the patient’s responses to specific tasks and questions. Each task is scored on a scale, with higher scores indicating more severe impairments. It is important that clinicians follow standardized protocols to minimize errors and ensure that the scores reflect the true condition of the patient.
Challenges in Assessment Scoring
Several challenges may arise during the scoring process. These challenges include the patient’s ability to cooperate, fluctuating symptoms, and possible communication barriers. A patient’s response may not always be consistent, and various factors, such as fatigue or anxiety, can influence their performance. It is important to consider these variables when interpreting scores to avoid misdiagnosis or incorrect treatment decisions.
Impact of Neurological Scores on Treatment Decisions
The scores derived from these assessments play a critical role in determining the most appropriate treatment path. Higher severity scores may indicate the need for urgent care or more intensive rehabilitation, while lower scores might suggest that less invasive treatment is sufficient. Clinicians rely on these evaluations to tailor treatment plans, such as medication adjustments, surgery, or ongoing therapy, based on the patient’s specific needs.
Understanding Severity through Scoring
Scoring allows healthcare providers to measure the severity of the patient’s condition objectively. This helps identify the areas of the nervous system most affected by the disorder. By analyzing the score patterns, clinicians can better understand the prognosis and potential for recovery, which is crucial for planning long-term care strategies and monitoring progress over time.
Best Practices for Test Preparation
To ensure the accuracy of the assessment, healthcare providers must be well-prepared and follow best practices. This includes creating a comfortable environment for the patient, explaining the procedure clearly, and ensuring the patient is alert and capable of participating. Thorough training for those conducting the assessment is also vital to ensure consistent and reliable scoring across different situations and settings.