The Earth’s crust is not a static and unchanging structure, but a constantly shifting and evolving system. Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that explains the movement and interactions of the Earth’s lithospheric plates, which make up the rigid outer shell of our planet. This groundbreaking theory has revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s geological processes and has been instrumental in explaining the formation of mountains, the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic activity, and the distribution of continents and oceans.
Plate tectonics is based on the concept that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several large plates that are constantly moving, albeit at a very slow pace, relative to each other. These plates converge, diverge, or slide past each other along plate boundaries, which are the areas where the plates interact. The interaction at these boundaries results in various geological phenomena, such as the formation of mountain ranges at convergent boundaries, the opening of new seafloor at divergent boundaries, and the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions along transform boundaries.
The plate tectonics theory was proposed in the 1960s, and since then, it has been supported by a wealth of scientific evidence. In the past, the Earth’s continents were believed to be fixed and immovable, but the discovery of seafloor spreading and the existence of mid-ocean ridges provided strong evidence for the movement of tectonic plates. The recognition of the Ring of Fire, a major area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur, further corroborated the theory.
To understand the concept of plate tectonics and its implications, many educational resources have been developed, including the Plate Tectonics Readworks answer key in PDF format. This comprehensive guide aims to assist students and educators in exploring the fascinating world of plate tectonics, providing key information, explanations, and answers to questions related to this field of study. By delving into the pages of this guide, readers can uncover the mysteries behind the Earth’s dynamic crust and gain a deeper appreciation for the forces that shape our planet.
What are plate tectonics and why are they important?
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how the Earth’s lithosphere, which is made up of separate pieces called tectonic plates, moves and interacts with each other. These plates are constantly shifting and moving, and their interactions are responsible for many geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountains and oceanic trenches.
Plate tectonics is important because it helps scientists understand and predict these geological phenomena, and it plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface and environment. By studying the movement and interactions of tectonic plates, scientists can better understand how and why earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur, and they can develop strategies to mitigate their potential hazards and effects on human populations.
Plate boundaries are the areas where tectonic plates meet and interact with each other. There are three main types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries, where plates move apart; convergent boundaries, where plates collide; and transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other horizontally. These plate boundaries are key areas for understanding plate tectonics and its effects on the Earth’s surface.
Subduction zones are convergent plate boundaries where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another into the Earth’s mantle. These subduction zones are responsible for the formation of features such as volcanic arcs, trenches, and mountain ranges. They also play a significant role in the recycling of Earth’s crust and the distribution of minerals and resources.
Overall, plate tectonics is a fundamental concept in geology and helps us understand the dynamic nature of the Earth. It allows us to study the Earth’s past and predict future geological events, ultimately helping us make informed decisions to ensure the safety and sustainability of our planet.
Understanding the basics of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that explains how the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several large, rigid plates that move and interact with each other. These plates are constantly in motion, with some moving towards each other, some moving away from each other, and others sliding past each other. This movement of the plates is responsible for many of the Earth’s geological features, such as mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes.
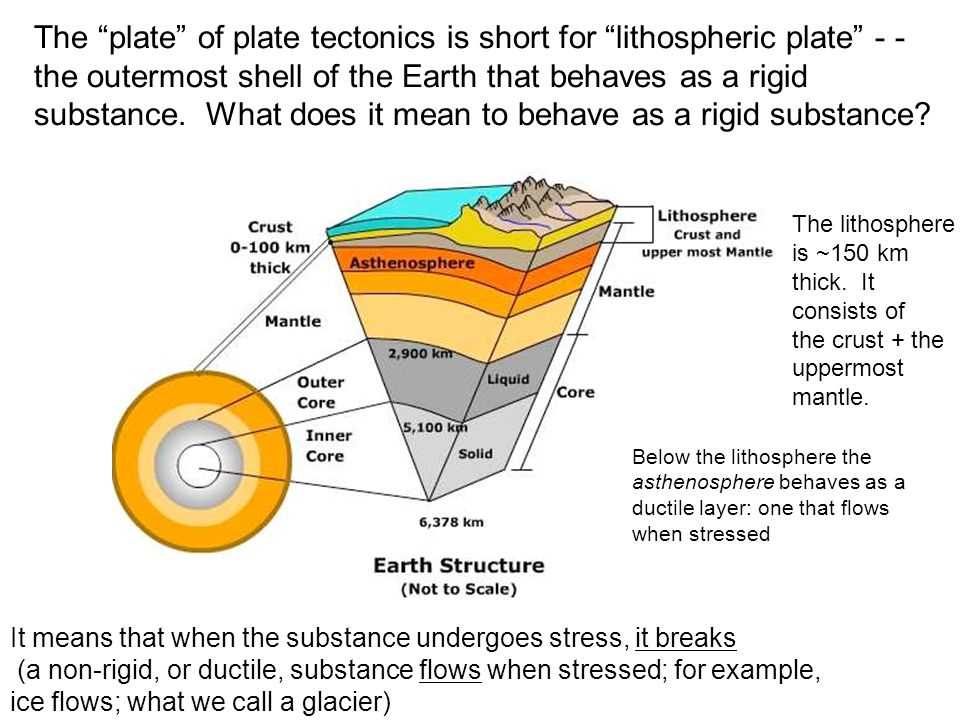
Plate tectonics is based on the idea that the Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large pieces called tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere below them. The movement of the plates is driven by convection currents in the Earth’s mantle, which is the layer of hot, semi-fluid rock that lies below the crust. When two plates collide, they can create mountains or cause one plate to be forced beneath the other in a process called subduction. When plates move away from each other, new crust is formed at the oceanic ridges and magma rises to the surface, creating volcanic activity.
Key terms:
- Lithosphere: The rigid outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
- Tectonic plates: Large pieces of the Earth’s lithosphere that move and interact with each other.
- Asthenosphere: The semi-fluid layer of the Earth’s mantle on which the tectonic plates float.
- Convection currents: Continuous movement of a fluid caused by differences in temperature and density.
- Subduction: The process by which one tectonic plate is forced beneath another.
- Volcanic activity: The eruption of magma, gases, and other materials from a volcano.
Understanding the basics of plate tectonics is crucial in order to comprehend the dynamic nature of our planet and the processes that have shaped its surface. By studying the movement and interaction of tectonic plates, scientists can predict and understand earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other geologic events. This knowledge is essential for the safety and well-being of the Earth’s inhabitants, as well as for the exploration and utilization of its resources.
The key elements of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several rigid plates that are constantly moving and interacting with each other. This theory, which emerged in the late 1960s, has revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s geological processes and has provided a framework for explaining various phenomena, such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Tectonic Plates
The first key element of plate tectonics is the concept of tectonic plates. These plates are large sections of the Earth’s lithosphere that are divided by boundaries. There are several major plates, such as the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, and Eurasian Plate, as well as numerous smaller plates. The movement of these plates is driven by the convection currents in the Earth’s mantle, which cause the plates to either collide, move apart, or slide past each other.
Plate Boundaries
Another important aspect of plate tectonics is the existence of plate boundaries. These boundaries are the areas where two plates meet and interact with each other. There are three main types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries, where plates move apart; convergent boundaries, where plates collide; and transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other. The interactions at these boundaries are responsible for many geological phenomena, such as the formation of mid-ocean ridges, the creation of volcanoes, and the occurrence of earthquakes.
Continental Drift
One of the key discoveries that led to the development of plate tectonics was the theory of continental drift. This theory, proposed by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century, suggested that the continents were once part of a single supercontinent called Pangaea, which later broke apart and drifted to their current positions. Plate tectonics builds upon this idea of continental drift and explains how the movement of the tectonic plates is responsible for the shifting of the continents over time.
Mountain Building
Plate tectonics also provides an explanation for the formation of mountain ranges around the world. When two continental plates collide at a convergent boundary, neither plate can be easily subducted into the mantle due to their low density. Instead, the two plates crumple and buckle, leading to the uplift and folding of rocks, which eventually form towering mountain ranges. Examples of such mountain ranges include the Himalayas, the Andes, and the Alps.
In conclusion, the key elements of plate tectonics include the concept of tectonic plates, the existence of plate boundaries, the theory of continental drift, and the formation of mountain ranges. Together, these elements provide a comprehensive understanding of the Earth’s dynamic geology and have revolutionized the field of earth sciences.
Exploring the theory behind plate tectonics

The theory of plate tectonics provides a framework for understanding the movement and interaction of Earth’s lithospheric plates. It explains the processes behind various geological phenomena, such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountains. By studying the theory, scientists gain insights into the dynamic nature of our planet and how it has evolved over millions of years.
Plate tectonics proposes that Earth’s crust is divided into several large plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them. These plates are constantly in motion, driven by the convective currents in the underlying mantle. As they move, they interact with each other at plate boundaries, creating a variety of geological features.
The theory classifies plate boundaries into three main types: divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries. At divergent boundaries, plates move away from each other, leading to the formation of new oceanic crust and rift valleys. Convergent boundaries involve the collision of plates, resulting in the subduction of oceanic crust beneath continental crust or the formation of mountain ranges. Transform boundaries occur when plates slide horizontally past one another, causing earthquakes along fault lines.
Plate tectonics also explains the distribution of geological features around the world. It helps us understand why earthquakes are more frequent in certain regions, such as the Pacific Ring of Fire, where several tectonic plates converge. It also accounts for the formation of mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, which were created by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
In conclusion, the theory of plate tectonics is a fundamental concept in geology that helps us understand the dynamic nature of Earth’s lithosphere. By studying this theory, scientists are able to explain the occurrence of geological phenomena and make predictions about future changes in our planet’s landscape.
The impact of plate tectonics on Earth’s surface
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that describes the movement and interaction of Earth’s lithospheric plates. These plates are large sections of the Earth’s crust that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. The theory of plate tectonics explains how these plates move, collide, and spread, leading to various geological phenomena that shape Earth’s surface.
One of the major impacts of plate tectonics on Earth’s surface is the formation of mountains. When two plates collide, the crust is compressed and pushed upward, creating mountain ranges. The Himalayas in Asia, the Andes in South America, and the Alps in Europe are all examples of mountain ranges formed by plate collisions. These mountains not only provide stunning landscapes but also impact climate patterns and serve as habitats for diverse ecosystems.
Evidence of plate tectonics
- Seafloor spreading: The discovery of mid-ocean ridges and the mapping of magnetic anomalies on the seafloor provide evidence for the movement of lithospheric plates. As new magma rises to the surface, it creates new crust, causing the existing seafloor to move away from the ridge.
- Earthquakes and volcanic activity: The majority of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur along plate boundaries. This distribution of seismic and volcanic activity supports the theory that plates are constantly moving and interacting.
- Fossil and rock records: Fossil and rock records show similarities in ancient organisms and depositional environments across continents that are now widely separated. This suggests that these landmasses were once connected and have since moved apart due to plate tectonics.
- Geomagnetic reversals: The recording of Earth’s magnetic field in rocks shows a pattern of reversals over time. These magnetic reversals are explained by the movement and spreading of lithospheric plates.
Overall, plate tectonics has significantly influenced Earth’s surface by shaping its topography, creating mountain ranges, and being responsible for various geological phenomena. It is an essential scientific framework for understanding the dynamic nature of our planet and the processes that have shaped it over millions of years.
Plate tectonics and natural disasters
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that describes the large-scale movements of Earth’s lithosphere, which is made up of several rigid plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them, and their constant motion can cause catastrophic events known as natural disasters.
Earthquakes: One of the most common natural disasters associated with plate tectonics is earthquakes. When two plates interact, it can lead to the build-up of stress along their boundaries. Eventually, this stress is released in the form of seismic waves, causing the ground to shake violently. Earthquakes can result in significant damage to infrastructure, loss of life, and economic disruption.
Volcanic eruptions: Plate tectonics also plays a critical role in the formation of volcanoes. When two plates converge, one may be forced beneath the other in a process called subduction. As the subducting plate sinks deeper into the mantle, it begins to melt, creating magma. This molten rock rises to the surface through vents and erupts as a volcano. Volcanic eruptions can cause widespread devastation, including the release of ash, lava flows, and pyroclastic debris, which can be harmful to both the environment and human populations.
Tsunamis: Another natural disaster associated with plate tectonics is tsunamis. These are large ocean waves that are usually triggered by undersea earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. When plates suddenly shift, the movement can displace large volumes of water, creating powerful waves that propagate across the ocean. Tsunamis can travel great distances and have devastating consequences when they reach coastal areas, including flooding, destruction of infrastructure, and loss of life.
Landslides and avalanches: Plate tectonics can also indirectly contribute to other natural disasters such as landslides and avalanches. The movement of tectonic plates can cause the uplift and deformation of mountain ranges. Over time, this can lead to the destabilization of slopes, resulting in landslides and avalanches. These events can be triggered by earthquakes or heavy rainfall, and they pose significant threats to human settlements and transportation networks.
Plate Tectonics and the Future of Earth’s Geography
The theory of plate tectonics has revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s dynamic processes and the formation of its landforms. It has provided insights into the movements and interactions of Earth’s lithospheric plates, explaining phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the creation of mountain ranges. But what does the future hold for Earth’s geography?
Plate tectonics is an ongoing process, constantly shaping and reshaping the Earth’s surface. Over long periods of time, continents drift, oceans open and close, and mountains rise and erode. While we cannot predict with certainty the exact changes that will occur, scientists have made some projections based on current knowledge and trends.
Continental Drift
Continental drift, the movement of Earth’s continents over geological time, will continue to shape the planet’s geography. The ongoing tectonic forces will cause continents to collide, rift apart, or slide past each other, leading to the formation of new landforms and altering the distribution of oceans and continents.
Sea Level Rise
Global warming and the resulting melting of ice caps and glaciers are causing sea levels to rise. This rise in sea level will impact coastlines around the world, leading to coastal erosion, inundation of low-lying areas, and the displacement of populations. The combination of plate tectonics and sea level rise will significantly influence the future geography of Earth.
Volcanic Activity and Earthquakes
The movement and interaction of tectonic plates will continue to generate volcanic activity and earthquakes. These events will shape the Earth’s surface, creating new mountains, islands, and oceanic trenches. They will also pose ongoing challenges for human populations living in affected areas.
Impact on Biodiversity
The changing geography of Earth due to plate tectonics will also have implications for biodiversity. As landmasses shift and climate patterns change, species will face new habitats, migration routes, and challenges for survival. Some species may thrive in the new conditions, while others may struggle to adapt or face extinction.
Conclusion
The study of plate tectonics has provided us with a framework for understanding Earth’s complex geological processes. It has given us a glimpse into the past and present, and it will continue to shape the future of our planet. As plate tectonics continue to shape Earth’s geography, it is crucial for scientists, policymakers, and society as a whole to understand and prepare for the potential impacts on our environment, infrastructure, and communities.
- Continuing continental drift will reshape landforms and alter the distribution of oceans and continents.
- Sea level rise will impact coastlines, causing erosion, inundation, and population displacement.
- Volcanic activity and earthquakes will create new landforms and pose ongoing challenges for human populations.
- The changing geography will have implications for biodiversity, affecting species’ habitats and migration patterns.
Q&A:
What are plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that explains the movement of Earth’s lithospheric plates. It states that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several large and small plates, which float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere below. These plates move relative to one another, causing earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, the creation of mountains, and the reshaping of Earth’s surface.
How do plate tectonics affect Earth’s geography?
Plate tectonics play a significant role in shaping Earth’s geography. The movement and collision of the plates have created mountain ranges like the Himalayas, the Andes, and the Rockies. It has also formed deep ocean trenches, volcanic islands, and transformed the size and shape of continents over millions of years.
What will be the future of Earth’s geography?
The future of Earth’s geography is uncertain, as it depends on the ongoing movement of tectonic plates. Over millions of years, continents will continue to drift and collide, resulting in the formation of new landforms and the reshaping of existing ones. However, the rate and direction of plate movement are not predictable, so it is difficult to determine exact future changes in Earth’s geography.
Will continents continue to drift apart in the future?
Yes, the continents will continue to drift apart in the future. This process, known as continental drift, is caused by the movement of tectonic plates. However, the rate of continental drift is very slow, with some estimates suggesting that continents move at a rate of several centimeters per year. Therefore, significant separation of continents will occur over periods of millions of years.
Can plate tectonics lead to catastrophic events?
Yes, plate tectonics can lead to catastrophic events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. When tectonic plates move and interact with each other, the accumulated stress can be released suddenly, resulting in earthquakes. Likewise, convergent plate boundaries can cause volcanic eruptions as one plate is forced beneath another. The energy released during these events can cause significant damage and loss of life.
What are plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics refers to the theory that Earth’s outer shell is divided into several large and small plates that are constantly moving. These movement of plates result in various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mountain building, and the formation of ocean basins.
How do plate tectonics affect Earth’s geography?
Plate tectonics play a major role in shaping Earth’s geography. The movement of tectonic plates creates and destroys continents, changes the shape and size of ocean basins, and forms mountain ranges. Over millions of years, plate tectonics have led to the formation of supercontinents and the breakup of land masses. The study of plate tectonics helps scientists understand the past, present, and future geological structures and processes on Earth.