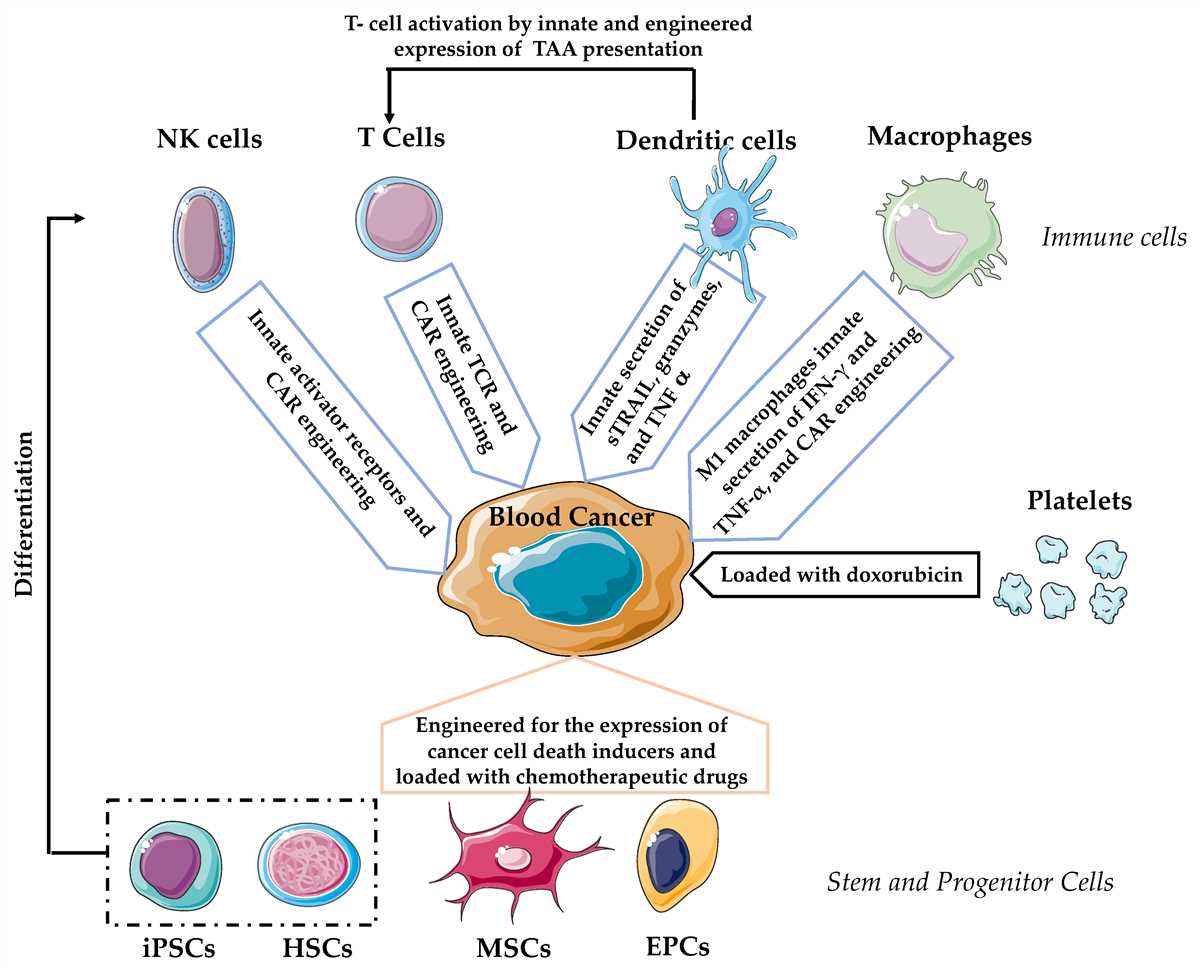
Understanding the concept of polarity and intermolecular forces is fundamental in the study of chemistry. Polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charge within a molecule, while intermolecular forces are the attractions between different molecules. The Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo is a valuable tool for exploring these concepts and providing answers to key questions.
One aspect of the Gizmo is the ability to manipulate the atoms within a molecule and observe the effects on polarity. By dragging different atoms into the molecule, students can see how the distribution of charge changes. This allows them to better understand how the arrangement of atoms within a molecule impacts the overall polarity of the molecule.
Additionally, the Gizmo provides a comprehensive exploration of intermolecular forces. Students can experiment with different molecules and observe how they interact with each other. Through simulations and observations, they can gain a deeper understanding of the various types of intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
With the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo, students are not only able to explore these concepts in a hands-on and interactive way, but they are also provided with detailed answers to guide their understanding. This tool serves as an invaluable resource for educators and students alike, enabling them to grasp the fundamental principles of polarity and intermolecular forces in a dynamic and engaging manner.
Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo Answers
In the study of chemistry, understanding polarity and intermolecular forces is crucial. The Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo is a useful tool that allows students to explore these concepts in a hands-on and interactive manner. With this Gizmo, students can investigate the effects of polarity on molecular properties, as well as the different types of intermolecular forces that exist.
The Gizmo provides answers to various questions that may arise during the study of polarity and intermolecular forces. For example, students can use the Gizmo to determine the polarity of different molecules by examining their structure and the placement of their atoms. The Gizmo also allows students to investigate how polarity influences properties such as boiling and melting points.
Furthermore, the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo answers questions related to intermolecular forces. Students can explore the three main types of intermolecular forces – London dispersion, dipole-dipole, and hydrogen bonding – and understand how they contribute to the physical properties of substances. The Gizmo also provides answers to questions about how intermolecular forces affect the behavior of molecules in various situations.
Overall, the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo is a valuable tool for students studying chemistry. With its interactive features and informative answers, it allows students to deepen their understanding of polarity and intermolecular forces and their impact on the properties and behavior of molecules.
Overview of Polarity and Intermolecular Forces

Polarity and intermolecular forces play a crucial role in the behavior and properties of molecules. Polarity refers to the distribution of electrons in a molecule and the resulting uneven distribution of charge. This is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms in the molecule. In a polar molecule, the electrons are more strongly attracted to one atom, causing that atom to have a partial negative charge and the other atom to have a partial positive charge.
Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, are the attractive forces that exist between molecules. These forces are responsible for the various physical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points, solubility, and viscosity. The strength of intermolecular forces depends on factors such as the polarity of the molecules, the size and shape of the molecules, and the presence of hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions.
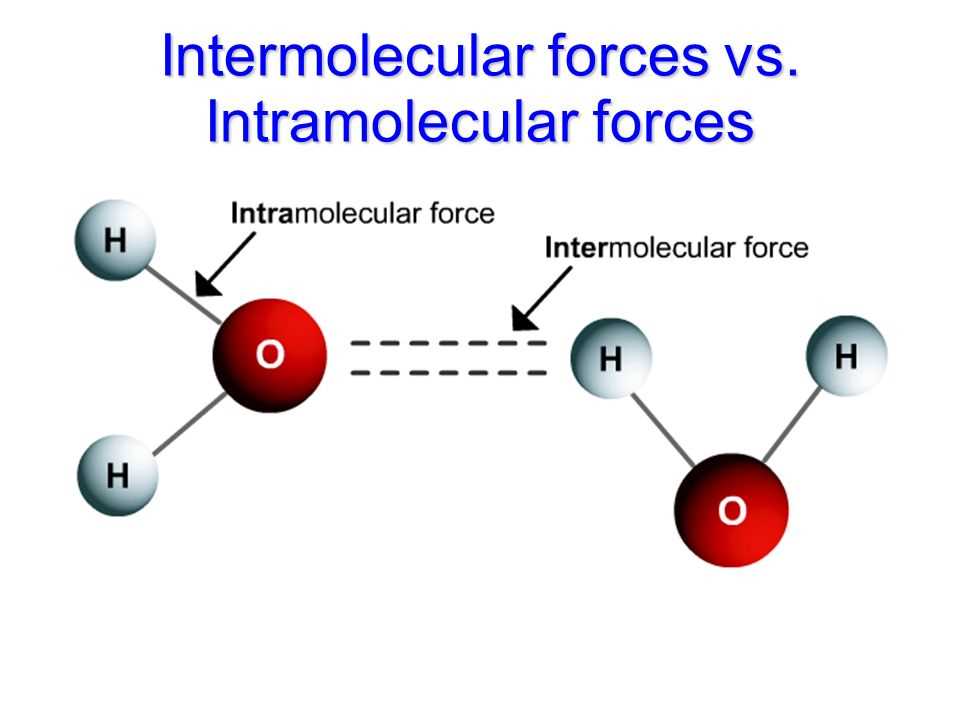
One of the most common types of intermolecular forces is van der Waals forces, which include London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. London dispersion forces occur in all molecules and are caused by temporary fluctuations in electron distribution, which result in temporary dipoles. Dipole-dipole interactions, on the other hand, occur between polar molecules and involve the attraction between the positive end of one molecule and the negative end of another.
In addition to van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding is another important type of intermolecular force. Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. The hydrogen atom experiences a high degree of partial positive charge, which allows it to form a strong attraction with nearby electronegative atoms.
Overall, understanding the concepts of polarity and intermolecular forces is essential for understanding the behavior of molecules and the properties of substances. These concepts help explain why certain substances are soluble in water, why some substances have high boiling points, and why some substances have strong odors. They also play a significant role in fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Explanation of the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo

The Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo is a simulation that allows students to explore the concept of polarity and the role of intermolecular forces in determining the properties of substances. This Gizmo provides a hands-on and interactive way for students to visualize and understand these fundamental concepts in chemistry.
The Gizmo starts by introducing the concept of polarity and how it relates to the electronegativity of atoms. Students can then experiment with different molecules and observe how the presence of polar bonds affects the overall polarity of the molecule. They can also manipulate the electronegativity values of the atoms in order to understand how this affects the polarity of the molecule.
In addition to exploring molecular polarity, students can also investigate the effects of intermolecular forces on the behavior of substances. The Gizmo allows them to compare the properties of substances with different intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. By changing the temperature and observing the behavior of the molecules, students can draw conclusions about the strength and type of intermolecular forces present in the substance.
The Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo provides a dynamic and interactive learning experience. It allows students to manipulate and observe the behavior of molecules, thereby deepening their understanding of polarity and intermolecular forces. The Gizmo also provides explanations and feedback to help students make connections between the observed phenomena and the underlying scientific concepts. Overall, this Gizmo is a valuable tool for teaching and learning about polarity and intermolecular forces in chemistry.
Step-by-Step Instructions on Using the Gizmo
The Gizmo on polarity and intermolecular forces is a valuable tool for understanding the concepts and principles behind these fundamental forces in chemistry. By following these step-by-step instructions, you will be able to navigate through the Gizmo and gain a deeper understanding of the topic.
Step 1: Start by opening the Gizmo. You will be presented with a virtual simulation of different molecules and their respective polarities. Take a moment to familiarize yourself with the layout and controls of the Gizmo.
Step 2: Select a molecule from the dropdown menu. This will allow you to focus on a specific molecule and analyze its polarity and intermolecular forces more closely. Choose a molecule that interests you or one that you would like to study in-depth.
Step 3: Observe the molecular structure of the selected molecule. Pay attention to the arrangement of atoms and the distribution of charge within the molecule. This will provide important clues about its polarity and intermolecular forces.
Step 4: Use the Gizmo’s interactive features to modify the molecule’s structure. You can rotate the molecule, zoom in and out, and even change the bond angles. Experiment with these controls to see how they affect the molecule’s polarity and intermolecular forces. Take note of any changes you observe.
Step 5: Utilize the information provided in the Gizmo to analyze the molecule’s polarity and intermolecular forces. Look for indicators such as dipole moments, intermolecular forces diagram, and bond polarities. These will help you understand how the molecule interacts with other molecules and the overall nature of its intermolecular forces.
Step 6: Repeat steps 2-5 for different molecules of interest. Explore a variety of molecules to gain a comprehensive understanding of polarity and intermolecular forces. Compare and contrast the different molecular structures, polarities, and intermolecular forces to identify patterns and trends.
Step 7: Take advantage of the Gizmo’s interactive quizzes and assessments to test your knowledge and reinforce your understanding of polarity and intermolecular forces. These quizzes will provide immediate feedback and help you identify any areas of weakness or confusion.
By following these step-by-step instructions and actively engaging with the Gizmo, you will be able to enhance your understanding of polarity and intermolecular forces. The interactive nature of the Gizmo will allow you to explore and experiment with different molecules, leading to a deeper comprehension of these important concepts in chemistry.
Common Questions and Troubleshooting
In using the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo, users may have some common questions and encounter certain troubleshooting issues. Here are some frequently asked questions and solutions to common problems:
1. How do I determine the polarity of a molecule?
In order to determine the polarity of a molecule, you can first analyze its shape and symmetry. If the molecule has a symmetrical shape, with all the elements surrounding the central atom evenly distributed, it is likely nonpolar. However, if the shape is asymmetrical or if there are lone pairs present on the central atom, the molecule is likely polar. You can also use information about the electronegativity of the atoms in the molecule to determine polarity.
2. Why is the molecule I am constructing not changing polarity when I add or remove atoms?
If you are constructing a molecule and it is not changing polarity when you add or remove atoms, there may be a few reasons for this. First, check that you are correctly representing the structure of the molecule and that you have included all the necessary atoms and bonds. If you have accurately represented the molecule, it is possible that the addition or removal of atoms is not significantly affecting the overall polarity of the molecule. In some cases, the polarity may be determined more by the arrangement of the atoms and the electronegativity differences, rather than the specific number of atoms present.
3. The Gizmo is not loading properly or is not functioning correctly. What should I do?
If the Gizmo is not loading properly or is not functioning correctly, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try. First, make sure that you have a stable internet connection and that you have the necessary software and plugins installed to run the Gizmo. Clearing your browser cache and cookies can also help resolve any loading or functionality issues. If the problem persists, you can try accessing the Gizmo on a different browser or device to see if that resolves the issue. If none of these steps work, you may need to contact technical support for further assistance.
4. Can I use the Gizmo on a mobile device?
Yes, the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo can be accessed and used on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. However, please note that the user interface and functionality may be slightly different compared to using the Gizmo on a desktop or laptop computer. It is always recommended to use the Gizmo on a device with a larger screen for optimal viewing and interaction.
Important Tips and Tricks for Understanding Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
Understanding polarity and intermolecular forces is crucial in many areas of chemistry. Here are some important tips and tricks that can help you grasp these concepts more effectively:
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Understanding the concept of electronegativity is essential for determining the polarity of a molecule. The greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms forming a bond, the more polar the bond is.
- Dipole Moment: A dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule. Molecules with a non-zero dipole moment are polar, while molecules with a zero dipole moment are non-polar. Understanding how to calculate and interpret dipole moments can help determine the polarity of a molecule.
- Intermolecular Forces: Intermolecular forces are attractive forces between molecules. There are three main types of intermolecular forces: hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces. Understanding the strength and nature of these forces is important in predicting properties such as boiling point, solubility, and viscosity.
- Solubility: Understanding the intermolecular forces between solute and solvent molecules is crucial in determining solubility. Like dissolves like: polar solutes typically dissolve in polar solvents, while non-polar solutes dissolve in non-polar solvents. Knowing the types of intermolecular forces involved can help predict solubility.
- Shape and Polarity: The shape of a molecule can greatly affect its polarity. Even if a molecule has polar bonds, its overall polarity depends on the shape and symmetry of the molecule. Learning about the various molecular geometries and how they affect polarity can be a helpful tool.
By understanding these important concepts and applying the tips and tricks mentioned above, you will be better equipped to tackle problems and questions related to polarity and intermolecular forces. Remember to practice and reinforce your understanding through hands-on activities and simulations, such as using the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo, to further enhance your learning.
Q&A:
What is polarity?
Polarity refers to the separation of electric charge within a molecule, causing one end of the molecule to have a slightly positive charge and the other end to have a slightly negative charge. Polarity is determined by differences in electronegativity between atoms in a molecule.
How is the polarity of a molecule determined?
The polarity of a molecule is determined by the electronegativity difference between its constituent atoms. If the electronegativity difference is significant, the molecule is polar. If the electronegativity difference is small or zero, the molecule is nonpolar.
What are intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction between molecules. They determine the physical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points, and play a crucial role in chemical reactions and interactions.
What are the main types of intermolecular forces?
The main types of intermolecular forces are hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force, followed by dipole-dipole interactions and then London dispersion forces.
How do intermolecular forces affect physical properties?
Intermolecular forces affect physical properties by determining the strength of attraction between molecules. They affect boiling and melting points, as stronger intermolecular forces require more energy to overcome. They also affect solubility and viscosity of substances.
What is polarity?
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electron density in a molecule, resulting in a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end.