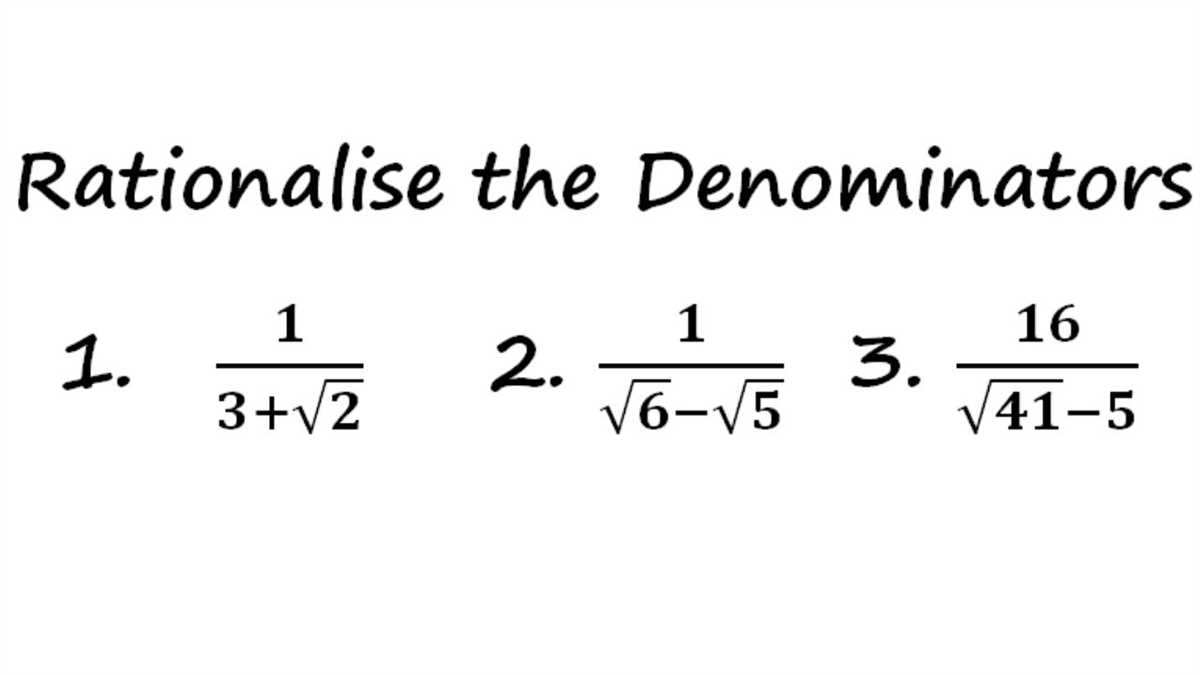
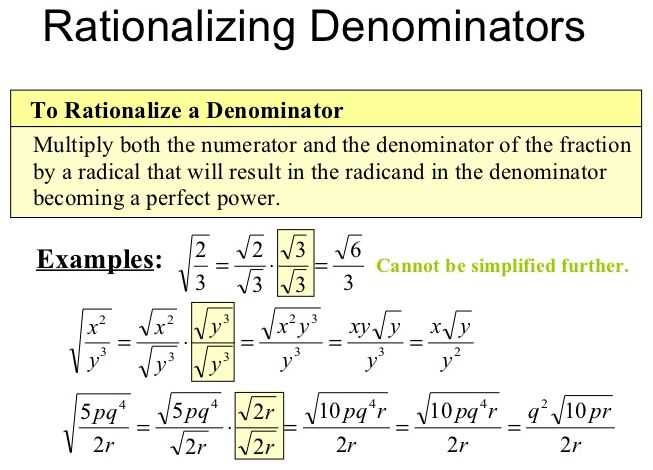
When it comes to simplifying radical expressions, one common technique is to rationalize the denominator. This process involves getting rid of any square roots or other radicals in the denominator, resulting in a simplified expression. While this may seem complicated at first, it becomes much easier with practice and understanding of the underlying principles.
One way to rationalize the denominator is by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by the conjugate. The conjugate is formed by changing the sign of the radical term in the denominator. By doing this, we eliminate the radical in the denominator and create a new expression that is equivalent to the original.
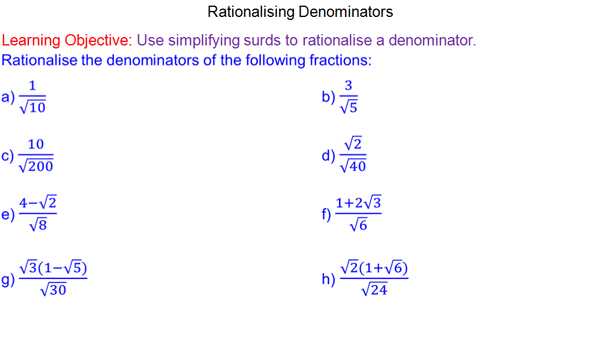
In order to demonstrate the process of rationalizing the denominator, we have prepared a worksheet with various examples and their solutions. This worksheet contains a range of problems, covering different levels of difficulty to help you develop and improve your skills in rationalizing the denominator.
Each question in the worksheet presents a radical expression with a denominator that needs to be rationalized. Alongside each question, you will find step-by-step instructions and an answer key. These answers will guide you through the process and provide you with the correct solution, allowing you to check your own work and identify any mistakes made.
Rationalizing the Denominator Worksheet Answers
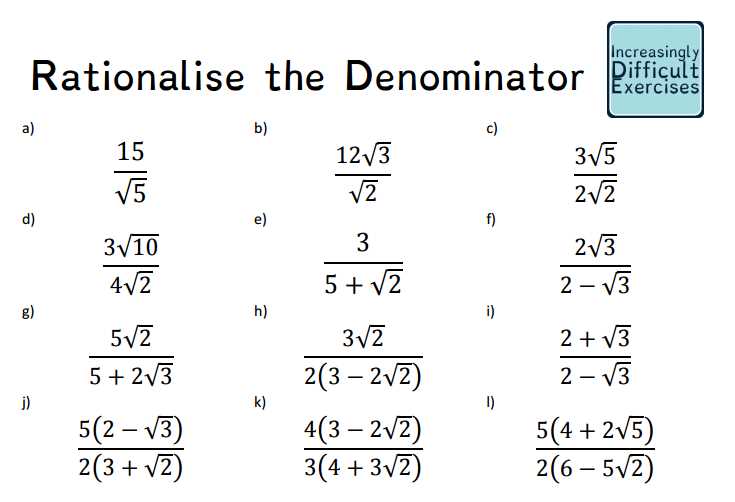
When it comes to rationalizing the denominator, it is important to know the correct steps and procedures to follow. A worksheet can be a useful tool in practicing and reinforcing these skills. By providing answers to the worksheet, students can check their work and make sure they are on the right track. The answers serve as a guide and can help students identify any mistakes they may have made.
The rationalizing the denominator worksheet typically includes different types of problems involving radicals or square roots in the denominator. The answers to these problems can vary depending on the specific question. It is important for students to understand that the goal of rationalizing the denominator is to eliminate the radicals or square roots from the denominator and make it a rational number.
One popular method for rationalizing the denominator is multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator. This involves changing the sign of the radical or square root in the conjugate. By doing this, the radicals in the denominator will cancel out, resulting in a rational number. The worksheet answers can show students the correct steps to take when applying this method.
Furthermore, the worksheet may also include word problems or application questions that require rationalizing the denominator. These types of questions can help students see the real-life relevance of rationalizing the denominator. The answers to these problems can provide students with a better understanding of how to solve similar problems in the future.
In conclusion, having the answers to a rationalizing the denominator worksheet can be beneficial for students. It can serve as a helpful tool in checking their work, identifying mistakes, and reinforcing their understanding of the topic. By practicing with the answers, students can gain confidence in their abilities and improve their problem-solving skills.
What is Rationalizing the Denominator?
Rationalizing the denominator is a process in mathematics used to eliminate radicals or complex expressions from the denominator of a fraction. The goal is to simplify the fraction and make it easier to work with. This technique is commonly used in algebra and calculus to solve equations or simplify expressions.
In many cases, the presence of a radical in the denominator can make calculations or solving equations more difficult. By rationalizing the denominator, we can eliminate the radical and make the expression more manageable. This is achieved by multiplying the numerator and denominator of the fraction by a suitable expression that will eliminate the radical in the denominator.
The process of rationalizing the denominator depends on the type of radical or complex expression present. For a square root in the denominator, we can multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator to eliminate the radical. For higher order radicals or complex expressions, additional techniques may be required.
Rationalizing the denominator is an important skill in mathematics and is often used in various applications such as solving equations, simplifying expressions, or evaluating limits. It allows us to work with fractions in a more straightforward manner and enables us to solve problems more effectively.
Simplifying Radical Expressions
In mathematics, a radical expression is an expression that contains a square root or other roots. Simplifying radical expressions involves finding a simpler form of an expression by taking out any perfect square factors under the radical sign and multiplying them to create a simplified expression.
To simplify a radical expression, we need to follow a set of rules. First, we need to identify any perfect square factors inside the radical. We can then take these factors out of the radical and write them as separate terms outside the radical. Next, we simplify any remaining factors under the radical by finding their prime factorization. Finally, we combine the terms inside and outside the radical to create the simplified expression.
For example, consider the expression √12. We can simplify this by recognizing that 12 can be broken down into the factors 4 and 3. Since 4 is a perfect square, we can take it out of the radical and write it as √4. The remaining factor 3 stays under the radical. The expression becomes 2√3, which is the simplified form of √12.
To simplify radical expressions with variables, we follow the same steps. We identify any perfect square factors and take them out of the radical. We then simplify any remaining factors under the radical by finding their prime factorization. Finally, we combine the terms inside and outside the radical to create the simplified expression.
Overall, simplifying radical expressions is an important skill in mathematics as it helps us to find the most simplified form of expressions involving roots. It allows us to work with these expressions more easily and solve problems accurately.
Rationalizing Denominators with Square Roots
When working with square roots in fractions, it is sometimes necessary to rationalize the denominator. This means that we need to eliminate the square root from the denominator and make it a rational number, or a number that can be expressed as a fraction.
One common situation is when the denominator contains a single square root term. To rationalize the denominator in this case, we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator of the fraction by the conjugate of the square root term. The conjugate is simply the term with the opposite sign in the middle. For example, if the denominator is √x, the conjugate would be -√x.
By multiplying the fraction by the conjugate, we can use the difference of squares formula to eliminate the square root. The resulting denominator will be a rational number. However, it is important to remember to also apply the same operation to the numerator to maintain the equality of the fraction.
It is worth noting that when rationalizing the denominator, the actual value of the fraction does not change. It only changes the way the fraction is represented. Rationalizing the denominator often makes it easier to work with the fraction in further calculations or simplifications.
In conclusion, rationalizing the denominator with square roots is a necessary step in certain situations to eliminate the square root and express the fraction as a rational number. By multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the square root term, we can eliminate the square root and obtain a rational denominator. Remember to also apply the operation to the numerator to maintain the equality of the fraction.
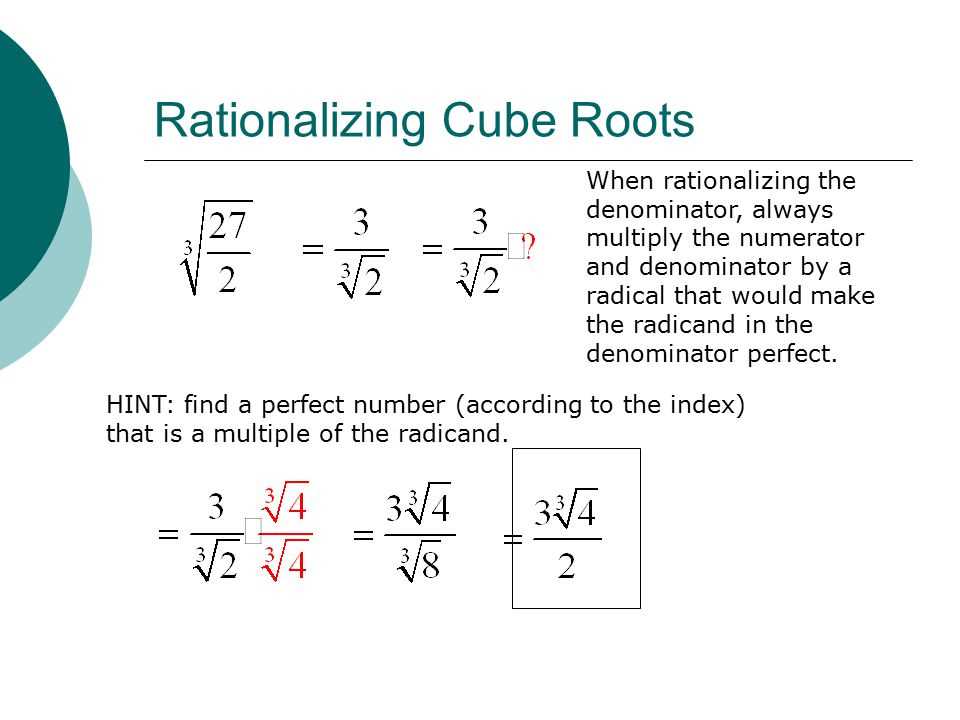
Rationalizing Denominators with Cube Roots
When simplifying or rationalizing a fraction with a cube root in the denominator, we need to eliminate the cube root from the denominator by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by a suitable expression. This process is known as rationalizing the denominator.
To rationalize a denominator with a cube root, we need to create a perfect cube in the denominator. This can be done by multiplying the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the cube root expression. The conjugate of a cube root expression is obtained by changing the sign of the second term.
For example, if we have the fraction 1 / (∛2), to rationalize the denominator, we multiply the numerator and the denominator by (∛2)^2, which is (∛2)^2 / (∛2)^2 = 2. So the rationalized form of the fraction is 1 / 2.
Another example is if we have the fraction 5 / (∛3 + 2), we need to multiply the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate (∛3 – 2). This gives us the rationalized form of the fraction as 5(∛3 – 2) / ((∛3 + 2)(∛3 – 2)) = 5(∛3 – 2) / (∛3^2 – 2^2) = 5(∛3 – 2) / (∛9 – 4) = 5(∛3 – 2) / 1 = 5(∛3 – 2).
Rationalizing denominators with cube roots may seem complex at first, but with practice, it becomes easier to understand and apply. It is an important skill in algebra and helps simplify mathematical expressions and equations.
Practice Problems and Solutions
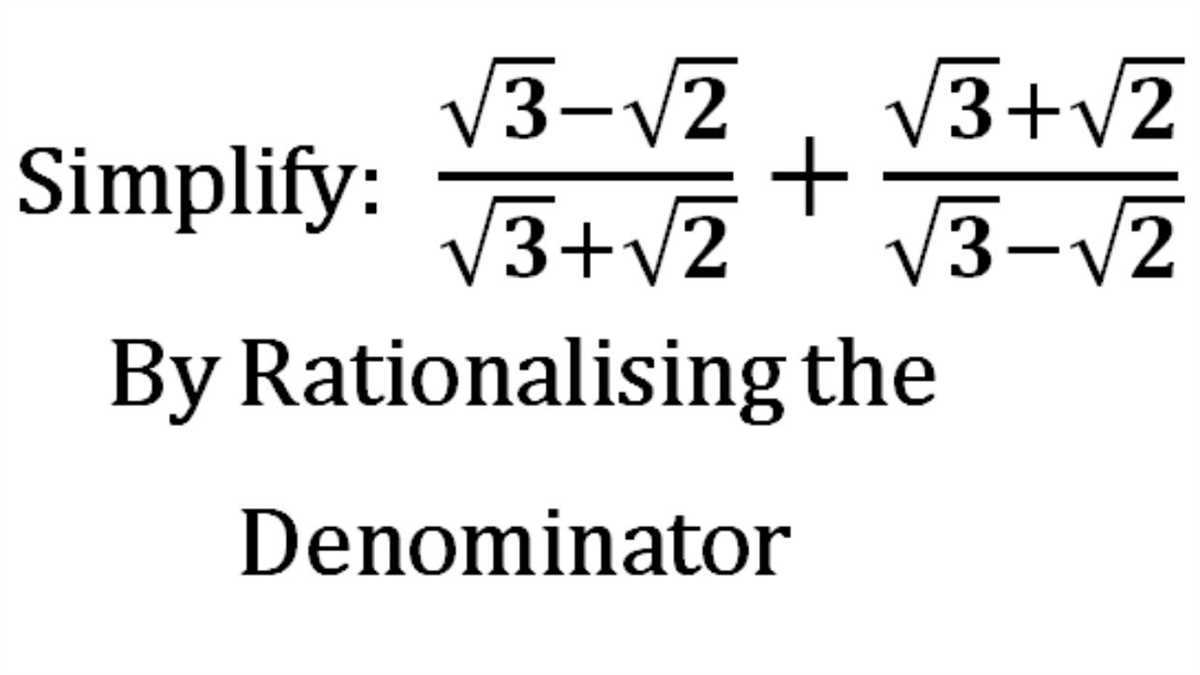
Below are some practice problems on rationalizing the denominator, along with their solutions:
Problem 1:
Rationalize the denominator of the expression $frac{4}{sqrt{2}}$.
Solution:
To rationalize the denominator, we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by $sqrt{2}$:
$frac{4}{sqrt{2}} times frac{sqrt{2}}{sqrt{2}} = frac{4sqrt{2}}{2} = frac{2sqrt{2}}{1} = 2sqrt{2}$
Problem 2:
Rationalize the denominator of the expression $frac{3}{sqrt{5}+sqrt{3}}$.
Solution:
To rationalize the denominator, we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator: $sqrt{5}-sqrt{3}$.
$frac{3}{sqrt{5}+sqrt{3}} times frac{sqrt{5}-sqrt{3}}{sqrt{5}-sqrt{3}} = frac{3(sqrt{5}-sqrt{3})}{(sqrt{5})^2 – (sqrt{3})^2} = frac{3(sqrt{5}-sqrt{3})}{5-3} = frac{3(sqrt{5}-sqrt{3})}{2} = frac{3sqrt{5}-3sqrt{3}}{2}$
Problem 3:
Rationalize the denominator of the expression $frac{1}{sqrt[3]{2}}$.
Solution:
To rationalize the denominator, we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the cube root of 2 squared: $sqrt[3]{2^2} = sqrt[3]{4}$.
$frac{1}{sqrt[3]{2}} times frac{sqrt[3]{4}}{sqrt[3]{4}} = frac{sqrt[3]{4}}{2}$
Summary:
Rationalizing the denominator is the process of eliminating radicals in the denominator of an expression. It is done by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by an appropriate expression to get rid of the radicals. In this article, we discussed the concept of rationalizing the denominator and provided examples of practice problems with solutions. By practicing these problems, you can improve your understanding and skills in rationalizing the denominator.
Q&A:
What are practice problems?
Practice problems are exercises given to students to help them apply and reinforce the concepts they have learned.
Why are practice problems important?
Practice problems are important because they allow students to actively engage with the material and develop a deeper understanding of the subject. They also help identify areas where the student may need additional help or clarification.
How do practice problems help in learning?
Practice problems help in learning by allowing students to actively apply what they have learned in a more practical context. This helps reinforce their understanding and retention of the material.
How can practice problems be solved?
Practice problems can be solved by carefully reading and understanding the problem statement, identifying and applying the relevant concepts, and working through the solution step by step. It is important to double-check the answer to ensure accuracy.
Where can I find practice problems and solutions?
Practice problems and solutions can be found in textbooks, online learning platforms, educational websites, and study guides. Teachers and instructors may also provide practice problems as part of their course materials.
What are practice problems and solutions?
Practice problems and solutions are educational exercises designed to help individuals learn and improve their problem-solving skills in various fields. These problems often require analytical thinking, critical reasoning, and creative problem-solving abilities. The solutions provide step-by-step explanations and strategies to help learners understand and solve the problems effectively.