If you’re looking for answers to a worksheet on rhombi and squares, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will provide you with the solutions to various questions related to these geometric shapes. Rhombi and squares are both types of quadrilaterals, but they have distinct properties and characteristics that set them apart.
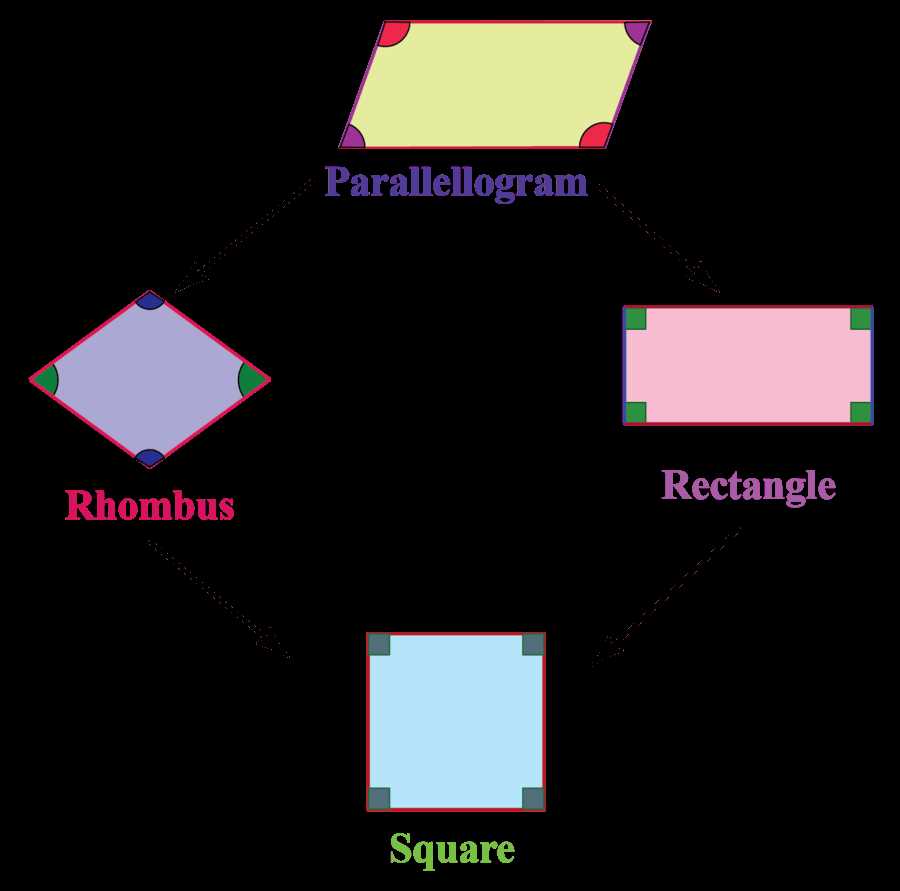
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with four equal sides. Each angle of a rhombus measures 90 degrees, which means it is also a type of rectangle. On the other hand, a square is a special type of rhombus where all angles are right angles and all sides are equal in length. This makes squares a type of quadrilateral and rectangle as well.
When completing a worksheet on rhombi and squares, you may come across questions involving their properties, formulas for calculating area and perimeter, or identifying specific rhombi and squares based on given information. Our answers will guide you through the different exercises and help you better understand these geometric concepts.
Rhombi and Squares Worksheet Answers
When working on a rhombi and squares worksheet, it is important to understand the properties and characteristics of these shapes. Rhombi and squares are types of quadrilaterals, which are polygons with four sides. They have unique properties that distinguish them from other quadrilaterals.
- A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. Its opposite angles are congruent, and its diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
- A square is a special type of rhombus, as it has all the properties of a rhombus but with the additional characteristic that all angles are right angles. This means that all four sides of a square are equal in length, and its diagonals are congruent.
When solving a rhombi and squares worksheet, it is important to have a good understanding of these properties. The worksheet may include questions about finding the measures of angles, sides, or diagonals of rhombi and squares. It may also involve identifying the type of quadrilateral based on given properties or characteristics.
When answering the worksheet questions, it is helpful to remember specific formulas and theorems related to rhombi and squares. For example, if given the length of one side of a square, you can easily find the length of its diagonal by using the Pythagorean theorem. Additionally, if given the measures of certain angles in a rhombus, you can find the measures of other angles using the properties of rhombi and their congruent opposite angles.
Overall, when working on a rhombi and squares worksheet, it is important to have a solid understanding of the properties and characteristics of these shapes. By applying the appropriate formulas and theorems, you can confidently solve the questions and find the correct answers.
Understanding Rhombi and Squares
Rhombi and squares are two types of quadrilaterals that have distinct characteristics. Understanding their properties and relationships is vital in geometry.
Rhombi:
- A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides of equal length.
- Opposite angles in a rhombus are congruent.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
- Both pairs of opposite sides in a rhombus are parallel.
Example: If a rhombus has side lengths of 5 cm, then all four sides of the rhombus will measure 5 cm each. The opposite angles of the rhombus will also be congruent.
Squares:
- A square is a special type of rhombus where all four angles are right angles.
- All sides of a square are equal in length.
- The diagonals of a square bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length.
- Both pairs of opposite sides in a square are parallel.
Example: If a square has side lengths of 7 cm, then all four sides of the square will measure 7 cm each. Additionally, all four angles of the square will be right angles. The diagonals of the square will also be equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
In summary, rhombi and squares are quadrilaterals with unique properties. While rhombi have four equal sides and opposite angles, squares go further to have all four right angles. Understanding these properties can help in solving geometry problems involving rhombi and squares.
Key Properties of Rhombi and Squares
In geometry, rhombi and squares are two types of quadrilaterals that have special properties and characteristics. Understanding these key properties is crucial for solving problems and working with these shapes.
Rhombus:
- A rhombus is a quadrilateral with four sides of equal length.
- All four angles of a rhombus are equal.
- The opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Square:
- A square is a special type of rectangle with all four sides of equal length.
- All four angles of a square are right angles (90 degrees).
- The opposite sides of a square are parallel.
- The diagonals of a square bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length.
- The diagonals of a square are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
These key properties of rhombi and squares can be used to solve various problems related to their angles, sides, diagonals, and symmetry. It is important to understand these properties in order to classify shapes correctly and apply them in different geometric contexts.
Identifying Rhombi and Squares

A rhombus is a special type of quadrilateral with several unique properties. One key characteristic of a rhombus is that it has four congruent sides. This means that all four sides of a rhombus have the same length. Another important property of a rhombus is that its opposite angles are congruent. In other words, if we label the vertex angles of a rhombus as A, B, C, and D, then angle A is congruent to angle C, and angle B is congruent to angle D. These angle properties make a rhombus a parallelogram as well.
A square, on the other hand, is a specific type of rhombus that has even more special properties. Like a rhombus, a square has all four sides congruent, but in addition, it also has all four angles congruent. This means that every interior angle of a square measures 90 degrees. Because of these angle properties, a square is not only a rhombus, but also a rectangle and a parallelogram. In fact, a square is a quadrilateral with the most symmetrical properties, with all sides, angles, and diagonals being congruent.
To identify whether a given quadrilateral is a rhombus or a square, we can use the side and angle properties described above. If all four sides of the quadrilateral are equal in length, it is a rhombus. If not only the sides, but also all four angles of the quadrilateral measure 90 degrees, then it is a square. It is important to carefully measure the sides and angles of the quadrilateral using a ruler and a protractor to accurately determine its classification.
Key Properties of a Rhombus:
- All four sides are congruent
- Opposite angles are congruent
- Diagonals bisect each other at right angles
Key Properties of a Square:
- All four sides are congruent
- All four angles are congruent and measure 90 degrees
- Diagonals bisect each other at right angles
Calculating Perimeter of Rhombi and Squares
When working with geometric shapes such as rhombi and squares, it is important to understand how to calculate their perimeters. The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its sides. For both rhombi and squares, the perimeter can be calculated by adding up the lengths of all four sides.
In the case of a square, all four sides are equal in length, so calculating the perimeter is as simple as multiplying the length of one side by 4. For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units, its perimeter would be 5 * 4 = 20 units. This means that the total distance around the square is 20 units.
A rhombus, on the other hand, has opposite sides that are equal in length, but they are not necessarily the same length as the other pair of opposite sides. To calculate the perimeter of a rhombus, you can either add up the lengths of all four sides or multiply the length of one side by 4, just like in the case of a square. For example, if a rhombus has a side length of 7 units, its perimeter would be 7 * 4 = 28 units.
To summarize, when calculating the perimeter of rhombi and squares, it is important to consider the lengths of all four sides. For squares, the perimeter can be found by multiplying the length of one side by 4, while for rhombi, you can either add up all four side lengths or multiply the length of one side by 4. By understanding these calculations, you will be able to find the perimeter of these shapes accurately in any given scenario.
Calculating Area of Rhombi and Squares
In geometry, the area of a figure refers to the amount of space inside that figure. When it comes to rhombi and squares, calculating the area is relatively straightforward. Both rhombi and squares are types of quadrilaterals with special properties that make their area calculations simple and efficient.
Rhombi: A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides of equal length. To find the area of a rhombus, you can use the formula A = base x height, where the base and height are perpendicular diagonals of the rhombus. The base can be any of the diagonals, and the height is the length of the other diagonal. Once you have the values for the base and height, simply multiply them together to find the area.
Squares: A square is a special type of rhombus where all angles are right angles. The area of a square can be calculated using the formula A = side length x side length, or A = side^2. Since all four sides of a square are equal in length, there is no need for separate base and height measurements. Simply take the length of one side and square it to find the area.
For example, let’s say we have a rhombus with a base of 6 units and a height of 8 units. Using the formula A = base x height, the area of this rhombus would be 6 units x 8 units = 48 square units.
Now, let’s consider a square with a side length of 5 units. Using the formula A = side^2, the area of this square would be 5 units x 5 units = 25 square units.
In summary, calculating the area of rhombi and squares is relatively simple. For a rhombus, use the formula A = base x height, and for a square, use the formula A = side^2. By determining the appropriate measurements and applying the formulas correctly, you can easily find the area of these geometric figures.
Applying Rhombi and Squares in Real-Life Situations
Rhombi and squares are geometric shapes that can be found in various real-life situations. Understanding the properties and characteristics of these shapes can help us make sense of the world around us and solve everyday problems.
In Construction:
Rhombi and squares are commonly used in construction for their stability and symmetry. They are often utilized in the design and layout of buildings, bridges, and other structures. The regularity and uniformity of these shapes make them ideal for ensuring structural integrity and balance.
In Design:
The aesthetic appeal of rhombi and squares makes them popular in various design fields. They are frequently incorporated into patterns, logos, and artwork to create visual interest and balance. The geometric precision of these shapes can enhance the overall composition and convey a sense of order and harmony.
In Mathematics:
Rhombi and squares are fundamental shapes in the field of mathematics. They serve as building blocks for more complex geometric concepts and formulas. Understanding the properties and formulas associated with these shapes is essential in solving mathematical problems and equations.
In Everyday Life:
Rhombi and squares can also be found in everyday objects and situations. For example, floor tiles, window panes, and certain types of containers often have square or rhombus shapes. Recognizing and understanding these shapes can help us organize space more efficiently and make informed decisions in our daily lives.
In Conclusion:
Rhombi and squares have practical applications in various fields and can be found in numerous real-life situations. Their stability, symmetry, and aesthetic appeal make them versatile shapes that are widely used in construction, design, mathematics, and everyday life. Understanding the properties and characteristics of these shapes enables us to analyze and solve problems more effectively, and enhances our overall understanding of the world around us.